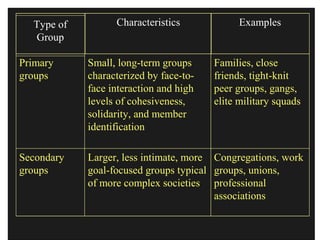
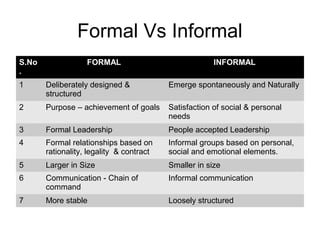
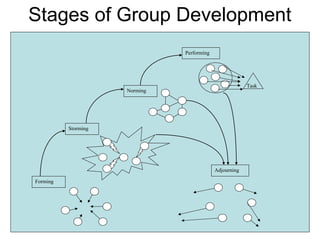
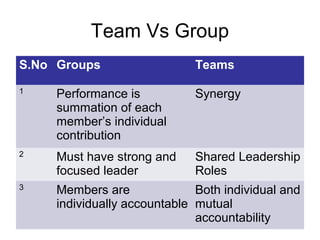
This document discusses group dynamics and different types of groups. It defines a group as two or more individuals connected by social relationships. Groups are classified into primary groups like families and secondary groups like work groups. Formal groups are deliberately designed to achieve goals, while informal groups emerge spontaneously to satisfy social needs. The stages of group development are forming, storming, norming, and adjourning. Group dynamics examines how groups are formed and structured, as well as how they influence members and other groups. Teams differ from groups in that they create synergy from members and use shared leadership rather than a single focused leader.