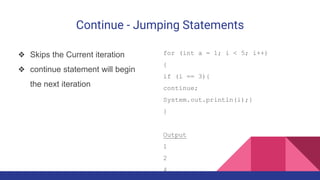
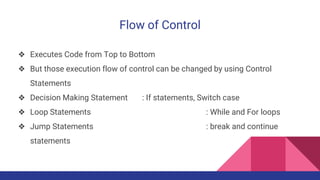
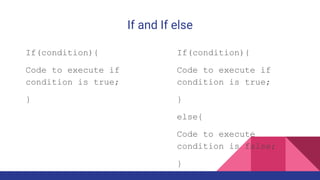
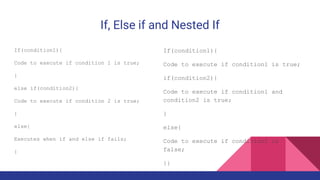
The document explains Java control statements that alter the flow of execution, including decision-making statements (if, else if, switch), loop statements (while, do while, for, for each), and jump statements (break, continue). It provides syntax examples for each control structure and describes their functionality and use cases. Overall, the content aims to help users understand how to manage and control program flow in Java.




![For Each Loop
❖ Used to iterate and get the
elements from an array.
❖ No increment is needed
int a[] = {18,25,28,29,30};
for (int eachvalueina : a) {
//Code to execute
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javasession4-210824110639/85/Java-Control-Statements-9-320.jpg)