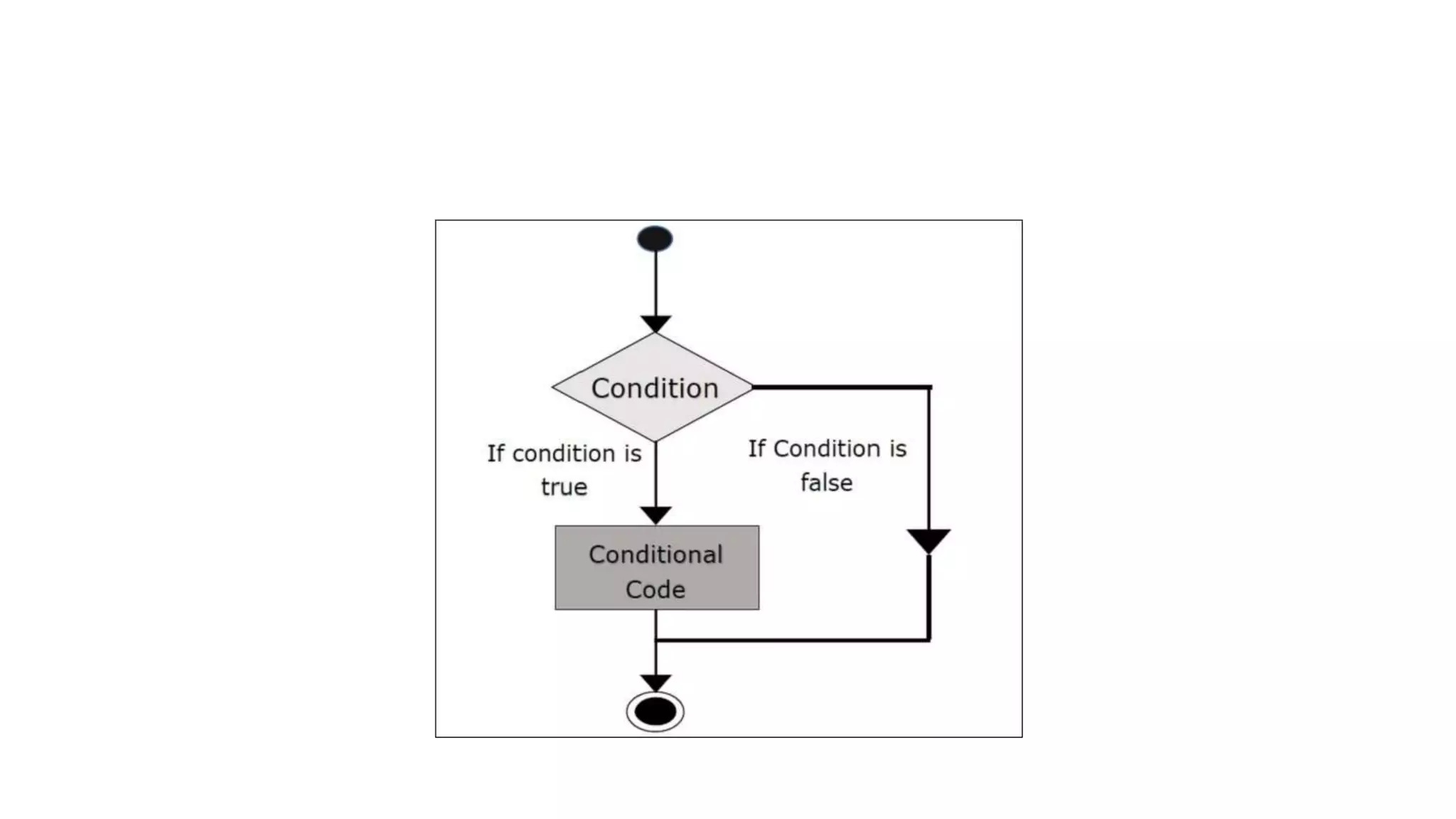
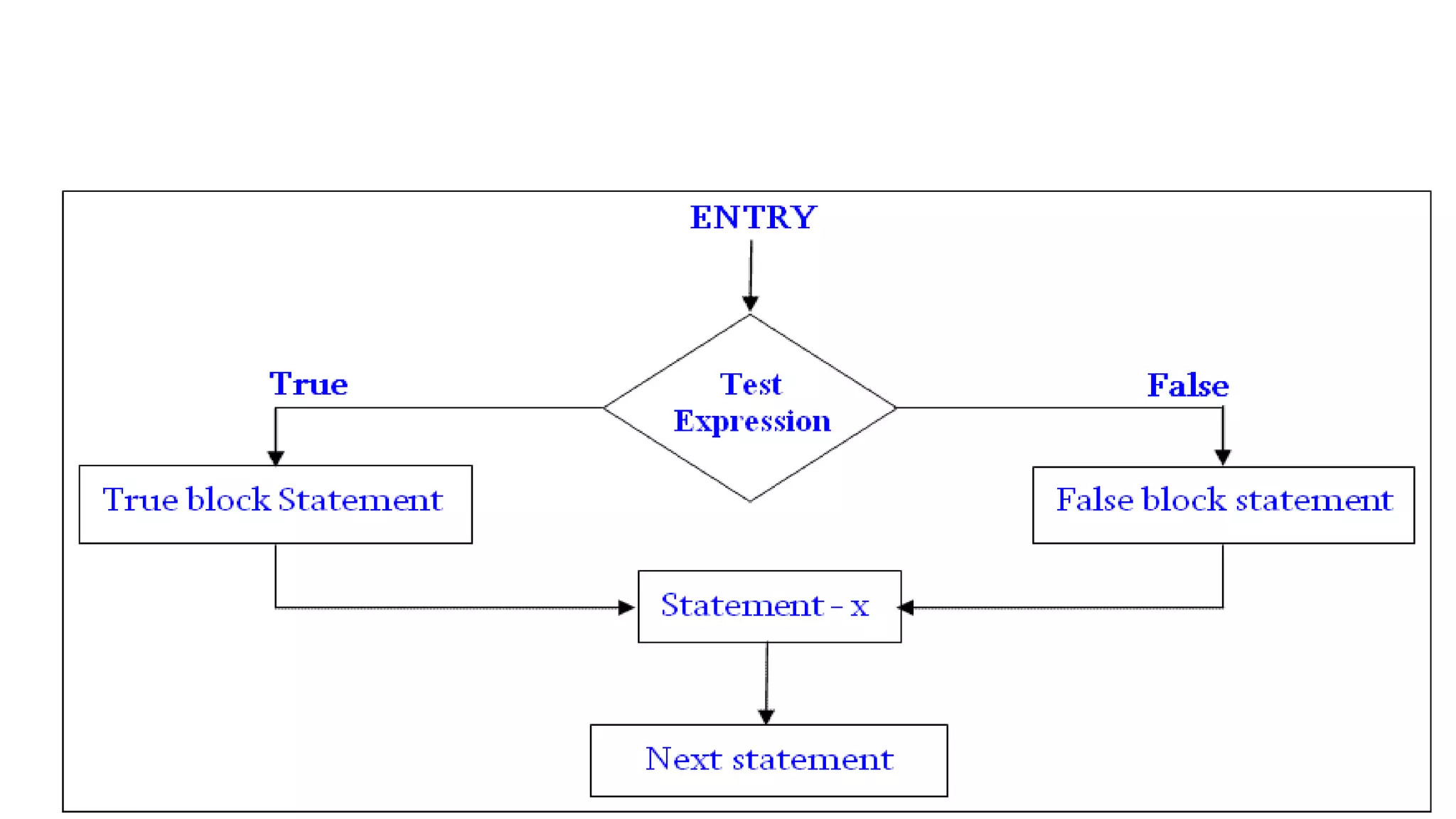
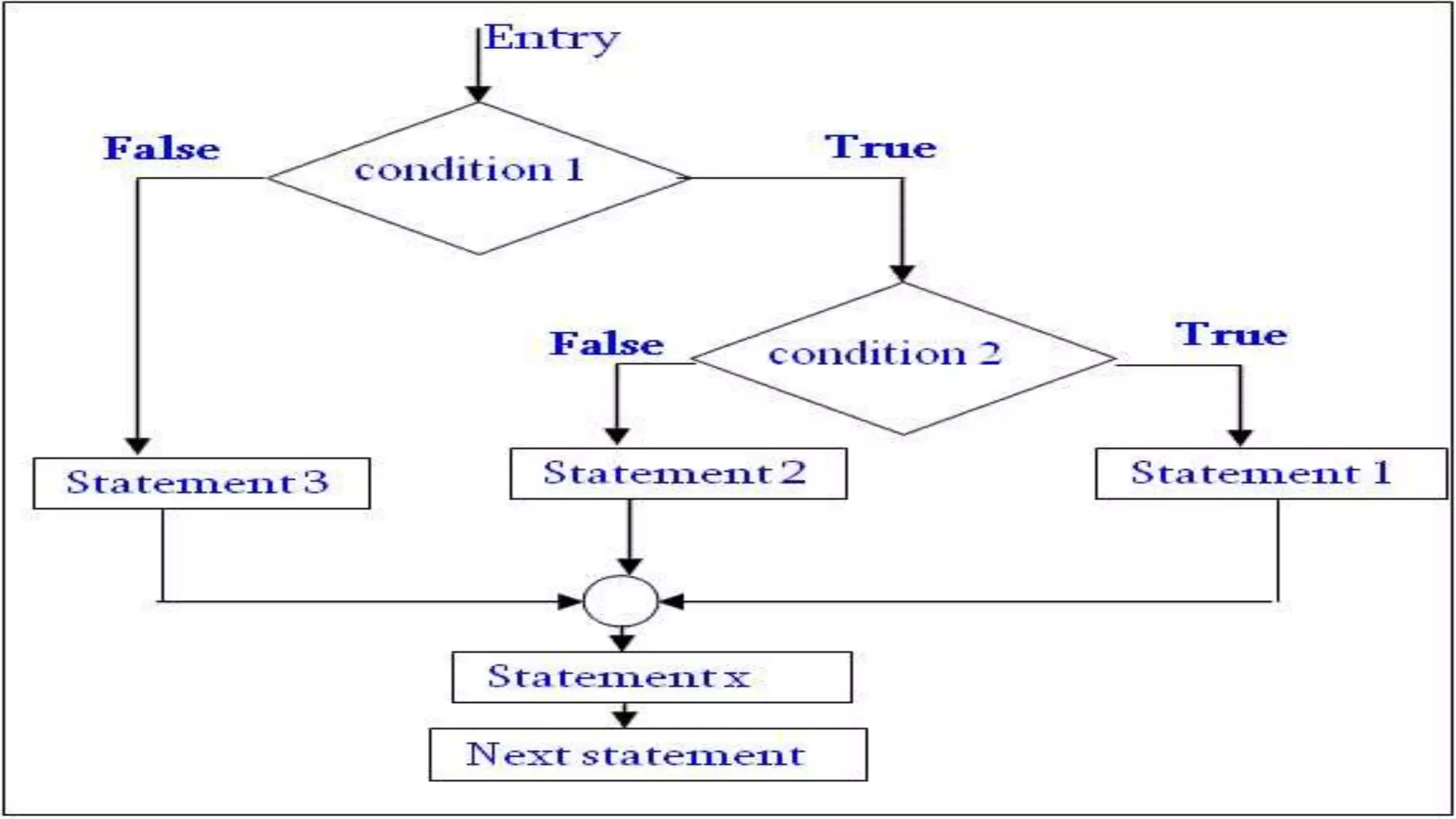
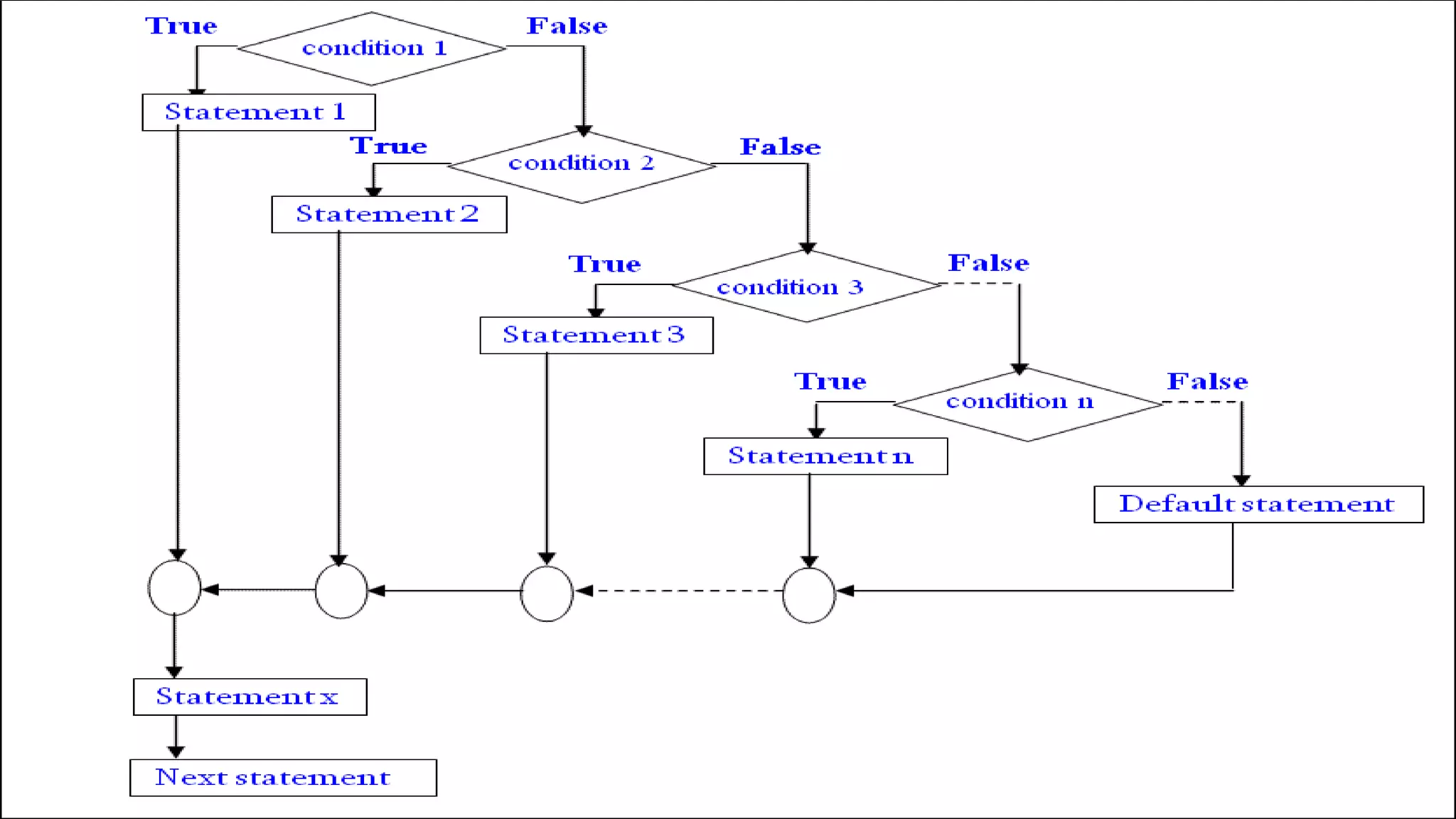
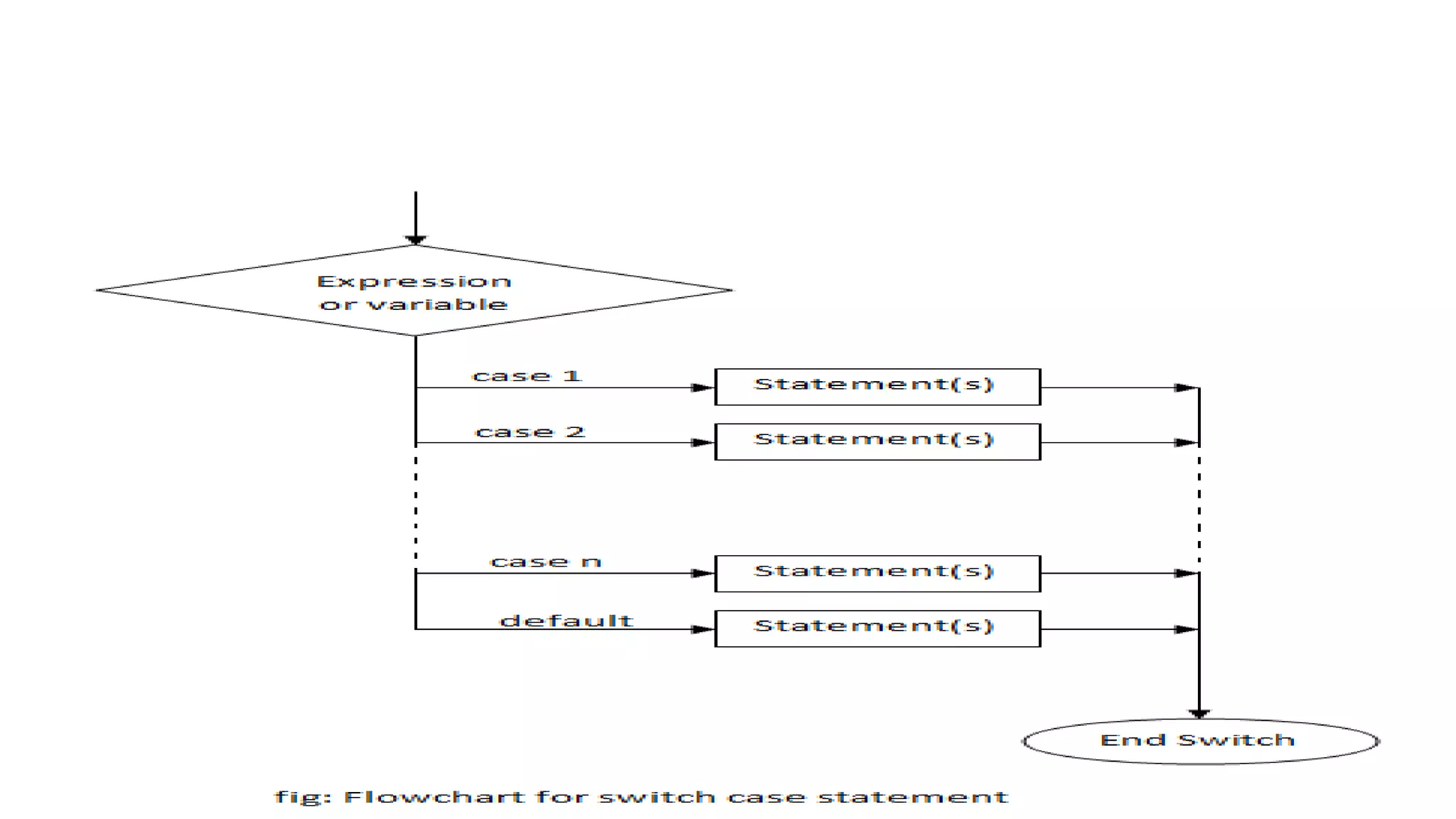
The document discusses different types of conditional statements in C including if, if-else, nested if-else, if-else ladder, switch, and goto statements. It provides the syntax and explains the logic and flow of each statement. The if statement executes code if a condition is true. The if-else statement executes one block if true and another if false. Nested if-else tests multiple conditions in sequence. The if-else ladder tests conditions from top to bottom. Switch compares a value to multiple cases and executes the matching block. Goto unconditionally transfers control to a labeled statement.