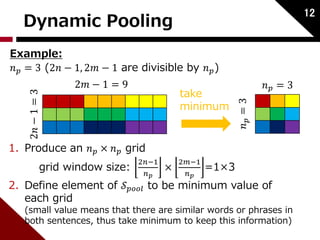
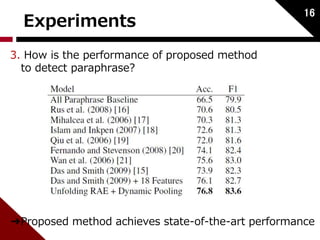
This paper proposes a method using recursive autoencoders and dynamic pooling to detect paraphrases. It represents words as vectors using distributed representations trained with a neural language model. It uses recursive autoencoders to obtain word and phrase embeddings, and constructs a similarity matrix between sentences. It then applies dynamic pooling to map this matrix to a fixed size input for a classifier. The method achieves state-of-the-art performance on paraphrase detection tasks.


![Word Representation
In general, words are represented as vectors.
1. One-hot representation
This assigns ID to each word individually.
2
[ 0,0,…,1,0,…,0]
Problem:
• Very sparse
• High dimension
• Unable to measure the similarity
between words
1:apple
2:book
⋮
200:zoo
⋮
Vocabulary](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamicpoolingandunfoldingrecursiveautoencodersforparaphrasedetection-140924050558-phpapp01/85/Dynamic-pooling-and-unfolding-recursive-autoencoders-for-paraphrase-detection-3-320.jpg)
![Word Representation
2. Distributed Representation
:word embedding
This method aims to learn this representation
Merit:
• Low dimension
• Similar words take similar vector
3
zoo [ 1.5, 1.8, 0.3, 4 ]
This represents the semantic, syntactic information](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamicpoolingandunfoldingrecursiveautoencodersforparaphrasedetection-140924050558-phpapp01/85/Dynamic-pooling-and-unfolding-recursive-autoencoders-for-paraphrase-detection-4-320.jpg)
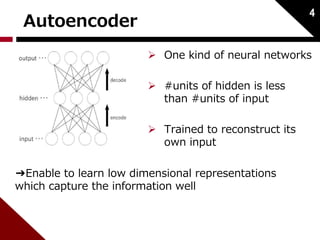
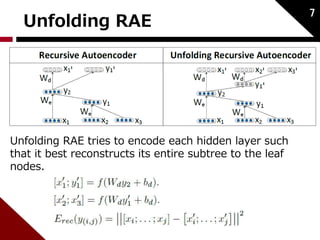
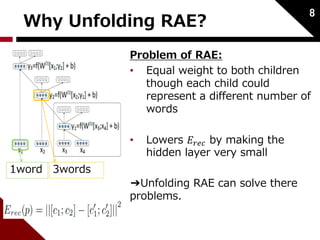
![Autoencoder
푊푑:weight of decode
푊푒 :weight of encode
Considered as binary tree;
Input:2 childs [푐1; 푐2] ∈ ℝ2푛 Hidden:푝 ∈ ℝ푛
5
푥 ∈ ℝ푛:word embedding
(initialized by neural language model)
푐1 푐2
푝
푐1 ′
푐2 ′
childs to parent:
reconstruction:
reconstruction error:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamicpoolingandunfoldingrecursiveautoencodersforparaphrasedetection-140924050558-phpapp01/85/Dynamic-pooling-and-unfolding-recursive-autoencoders-for-paraphrase-detection-6-320.jpg)


![Similarity Matrix
After training, we compute the similarities (Euclidean
distances) between all word and phrase vectors of the
two sentences.
These distances fill a similarity matrix 풮.
10
S[3,4] represents the similarity between node 4 of
sentence1(mice) and node 3 of sentence2 (mice).
➔zero distance](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamicpoolingandunfoldingrecursiveautoencodersforparaphrasedetection-140924050558-phpapp01/85/Dynamic-pooling-and-unfolding-recursive-autoencoders-for-paraphrase-detection-11-320.jpg)