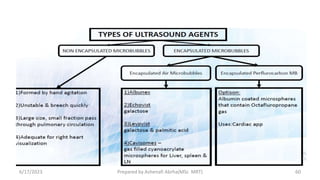
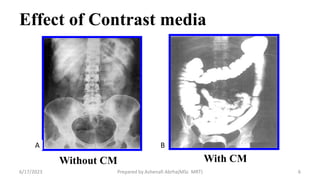
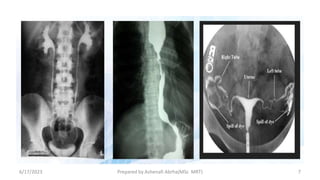
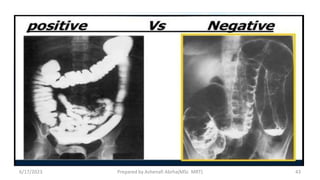
This document discusses contrast media used to enhance visualization of structures in radiographic examinations. It begins by outlining the objectives and introducing contrast agents. It then differentiates between positive and negative contrast media, with positive agents appearing bright and negative agents appearing dark. The two main positive agents discussed are barium sulfate and iodinated compounds. Barium sulfate is insoluble and used to coat gastrointestinal structures, while iodinated compounds can be water-soluble or oil-based depending on the exam. The document outlines the properties, uses, and considerations of both contrast agent types.











































![Types by body compartment
Gadolinium(III) contrast agents can be categorized into:
Extracellular fluid agents
• gadoterate (Dotarem, Clariscan)
• gadodiamide (Omniscan)
• gadobenate (MultiHance)
• gadopentetate (Magnevist)
• gadoteridol (ProHance)
• gadoversetamide (OptiMARK)
• gadobutrol (Gadovist [EU] / Gadavist [US])
• gadopentetic acid dimeglumine (Magnetol)
6/17/2023 Prepared by Ashenafi Abrha(MSc MRT) 51](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/contrastmedia1-230617100110-48065d37/85/contrast-media-1-pptx-51-320.jpg)



![Cont`d…
• Hepatobiliary (liver) agents
Gadoxetic acid (Primovist [EU] / Eovist [US]) is used as a
hepatobiliary agent as 50% is taken up and excreted by the
liver and 50% by the kidneys.
6/17/2023 Prepared by Ashenafi Abrha(MSc MRT) 55](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/contrastmedia1-230617100110-48065d37/85/contrast-media-1-pptx-55-320.jpg)