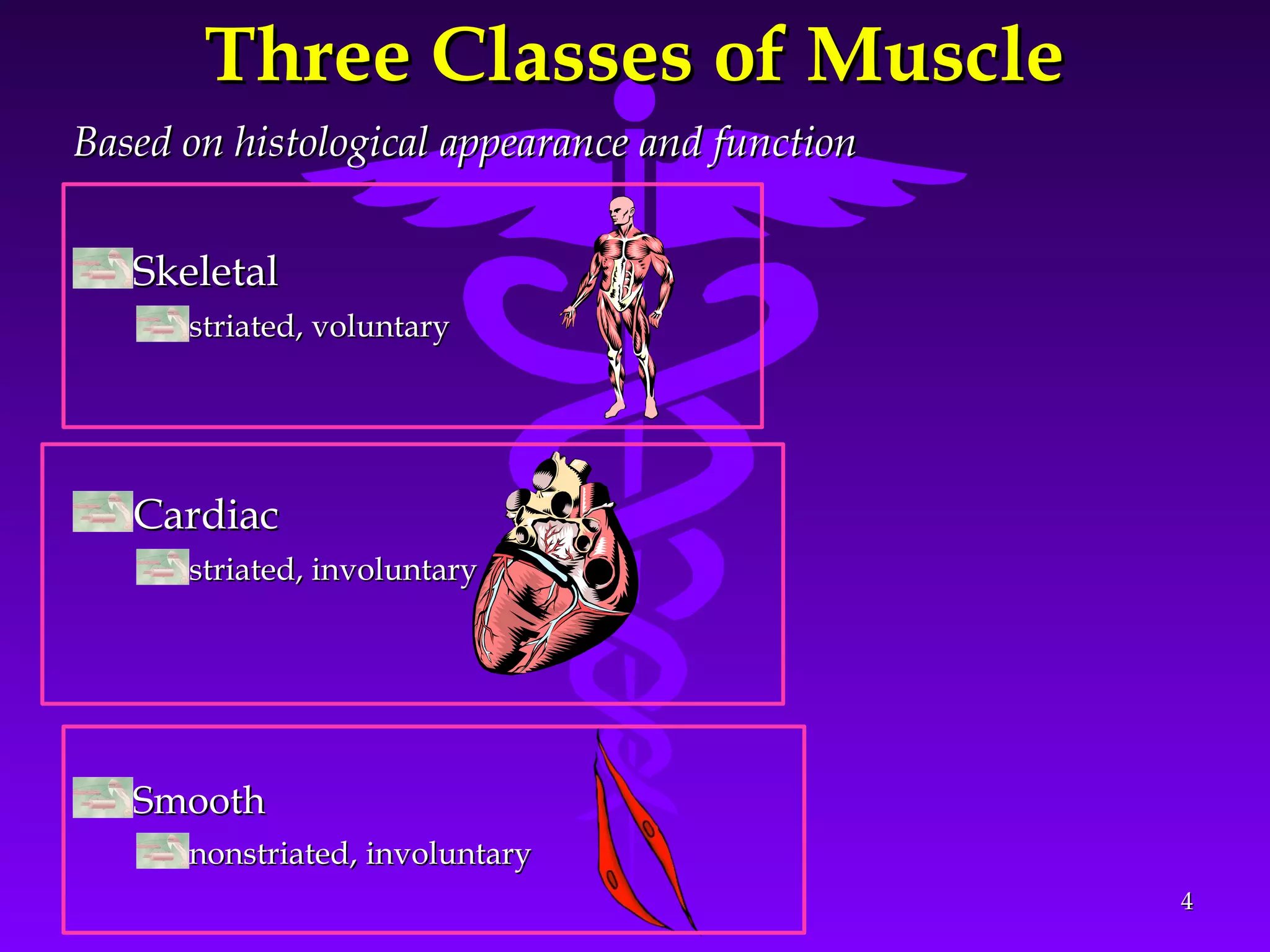
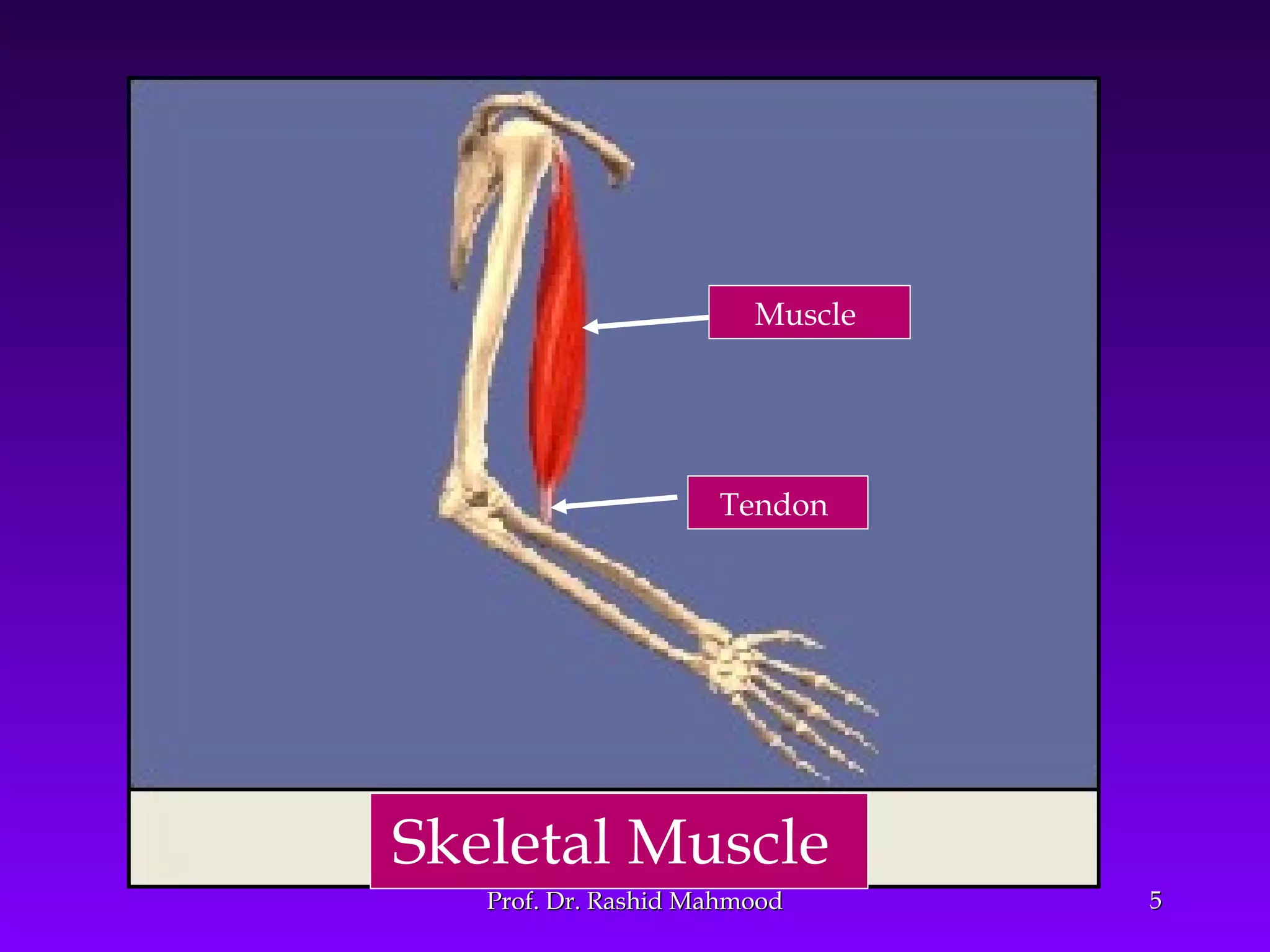
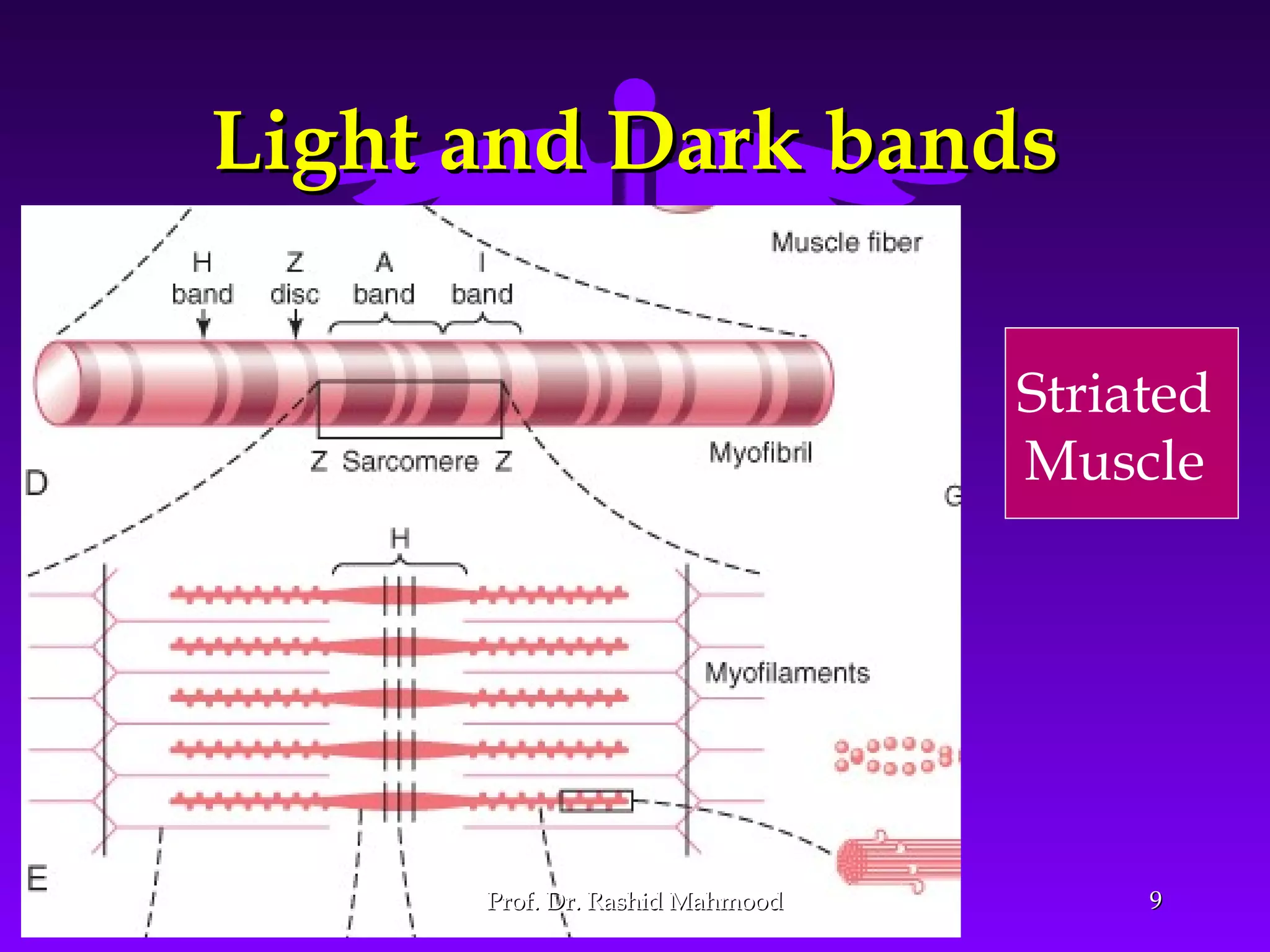
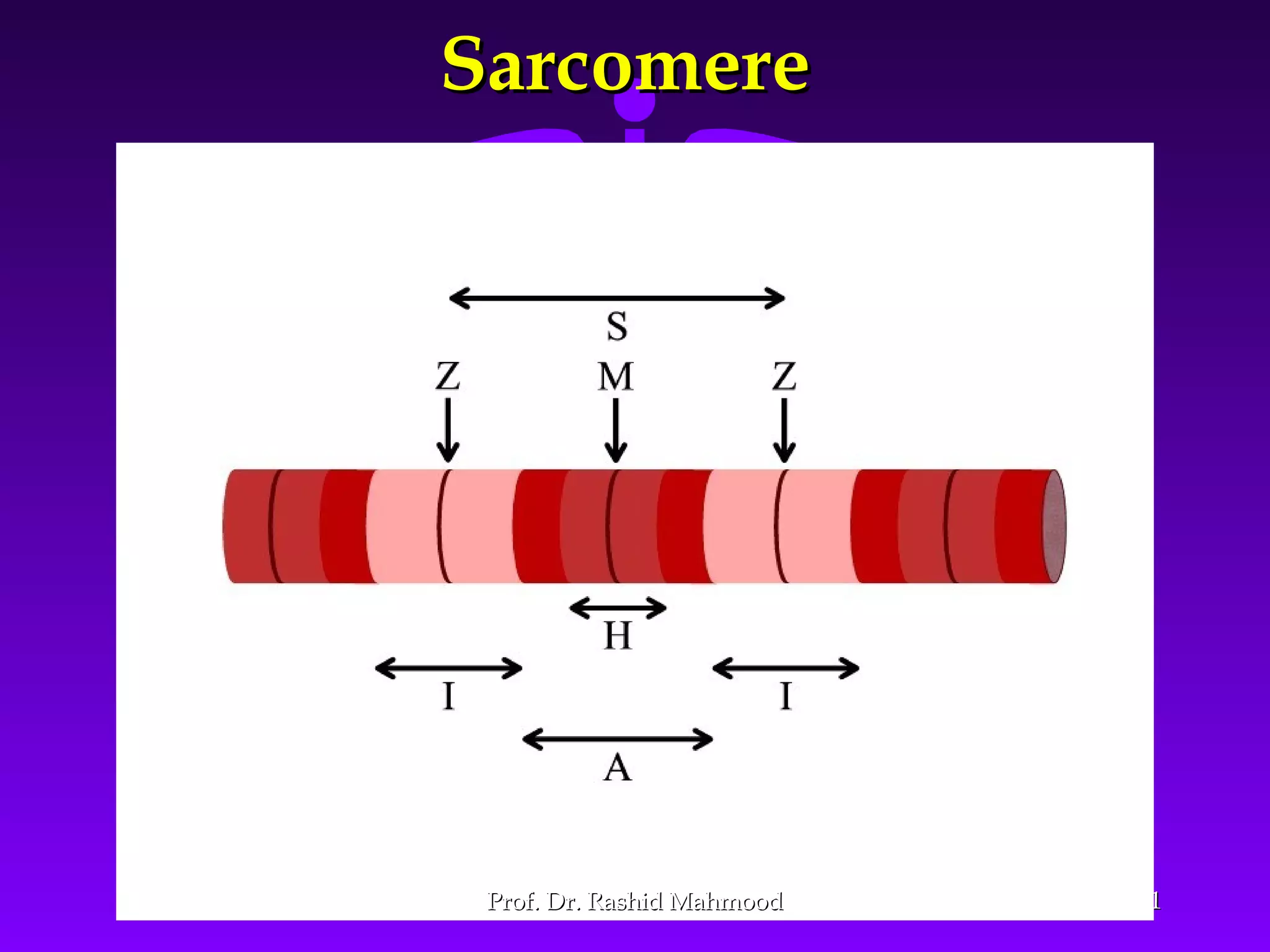
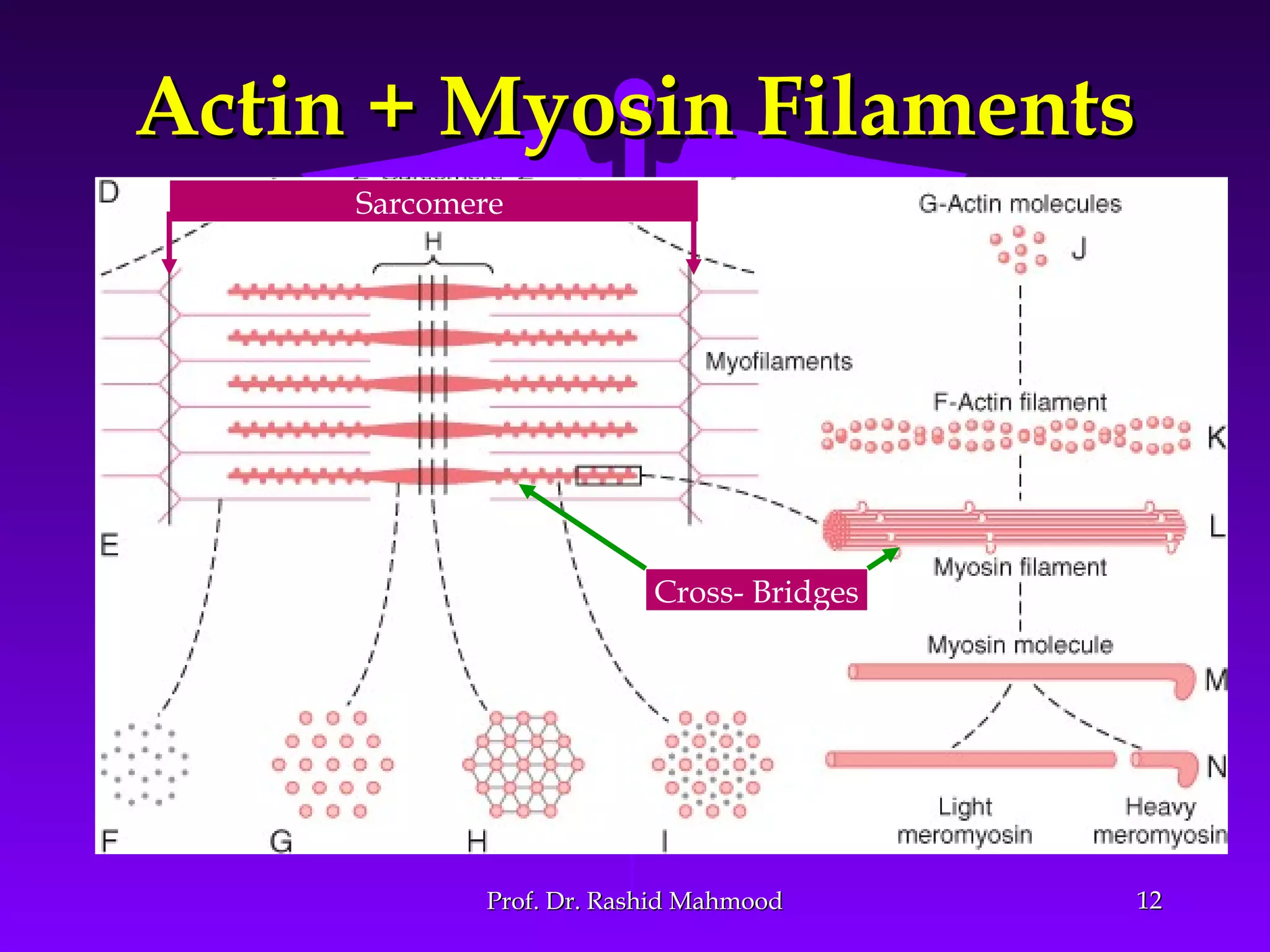
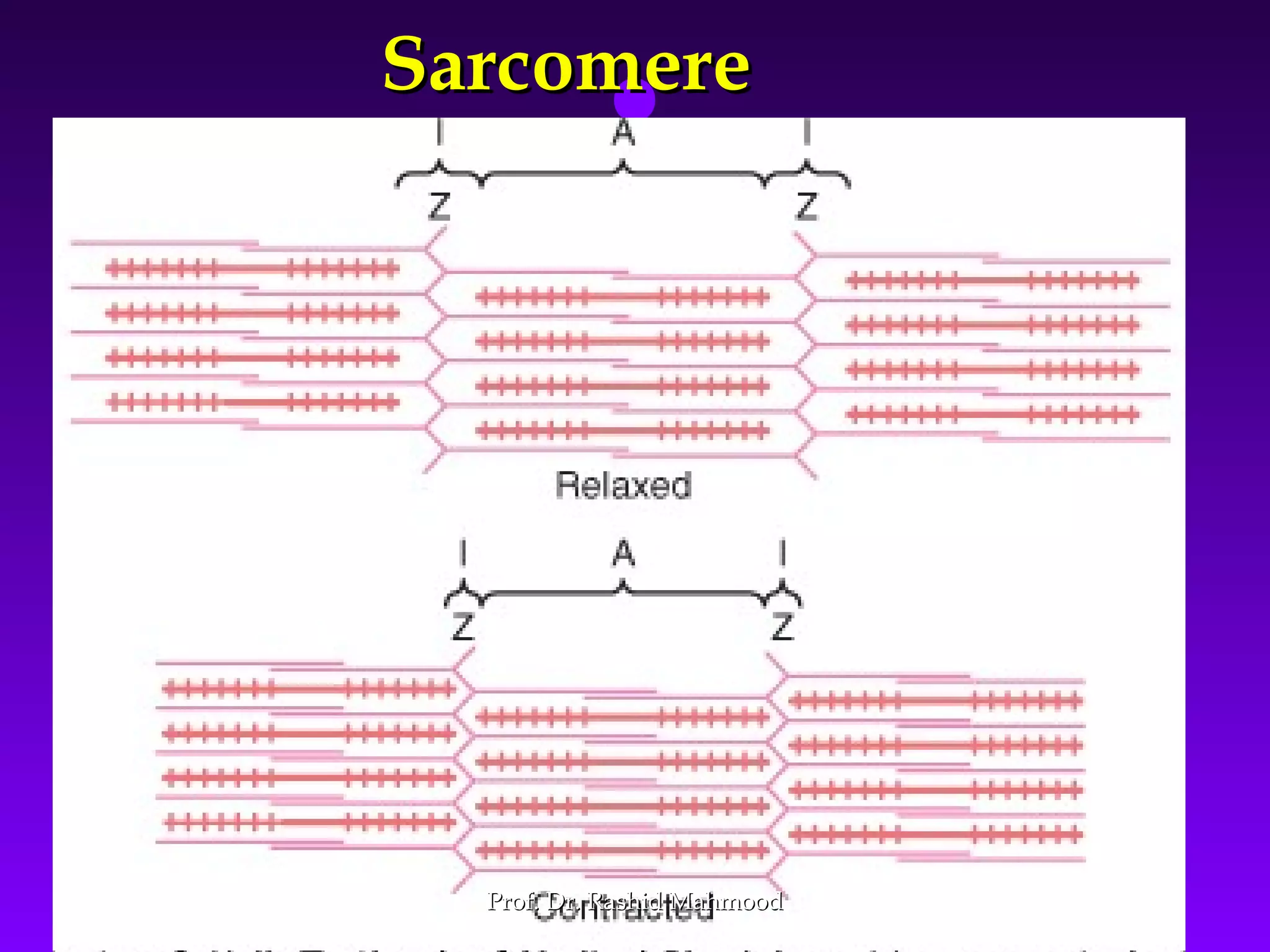
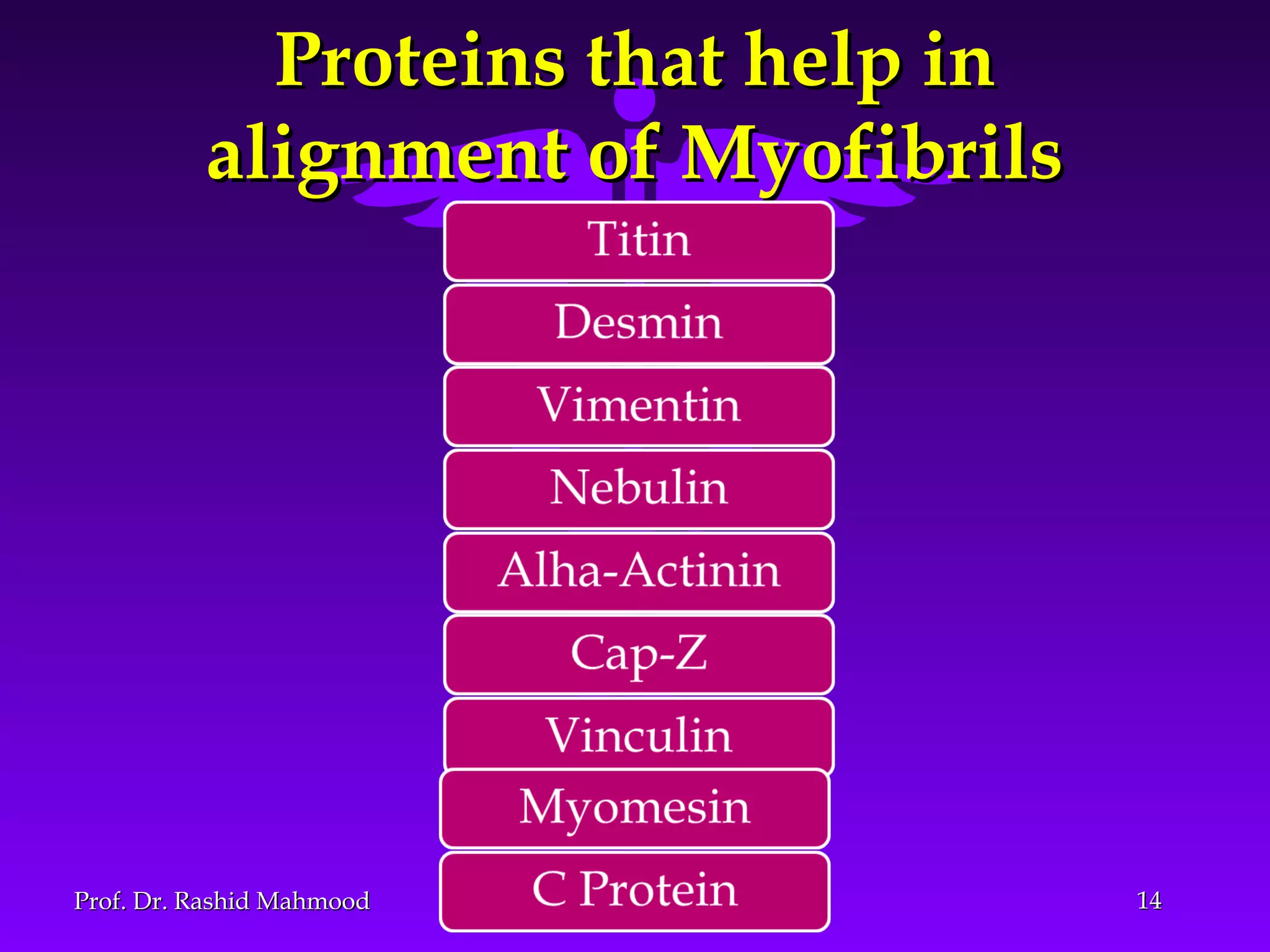
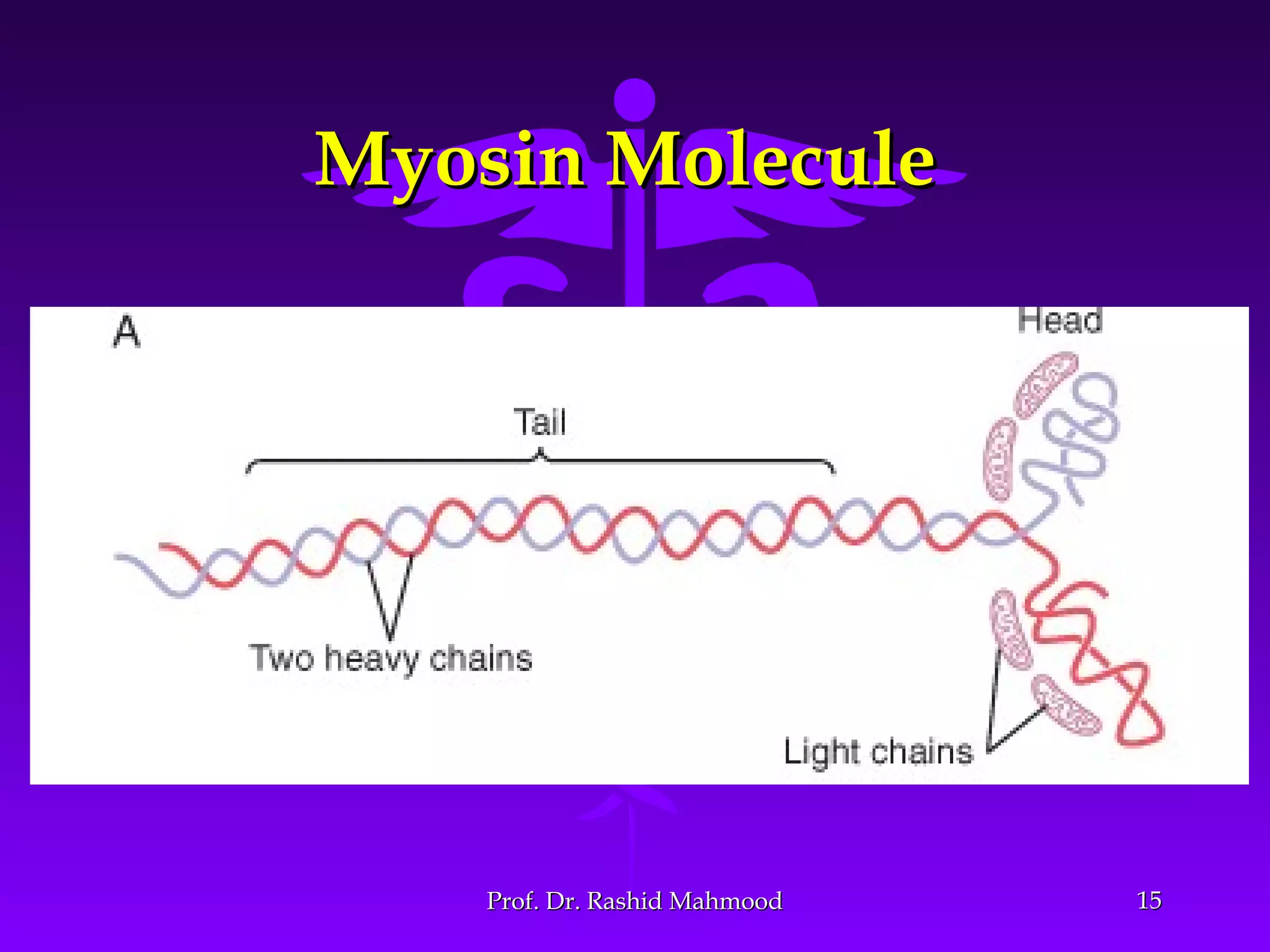
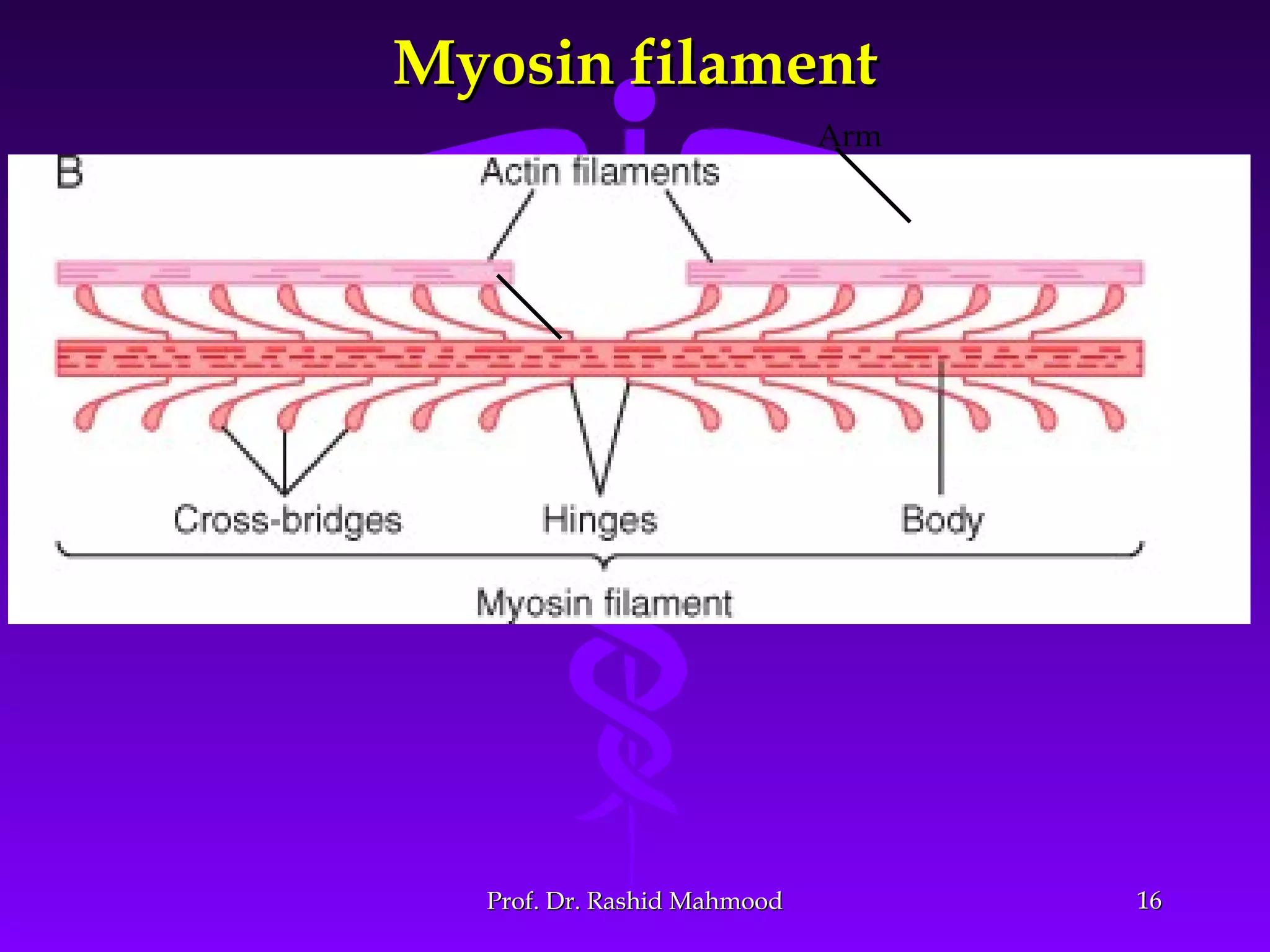
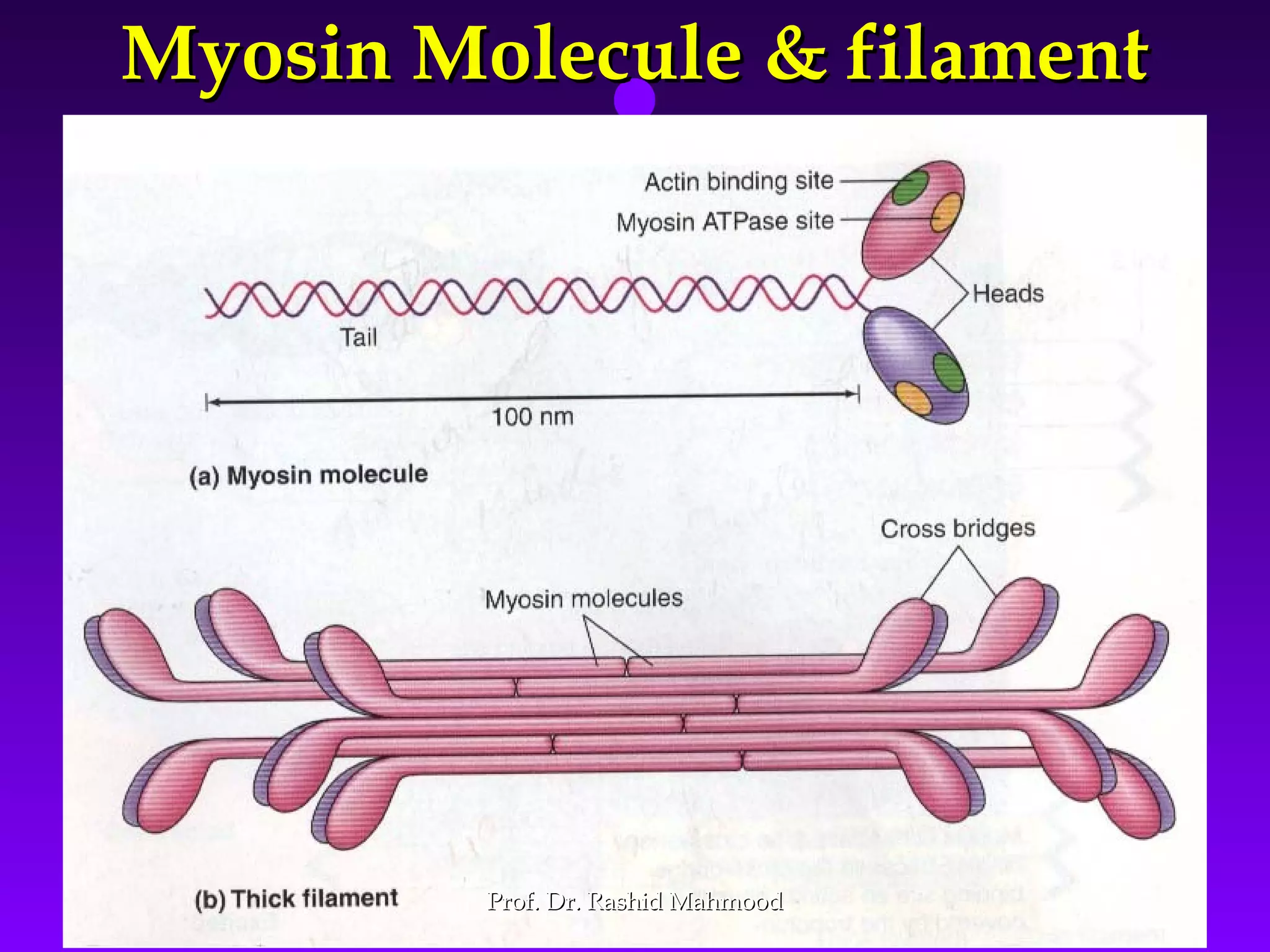
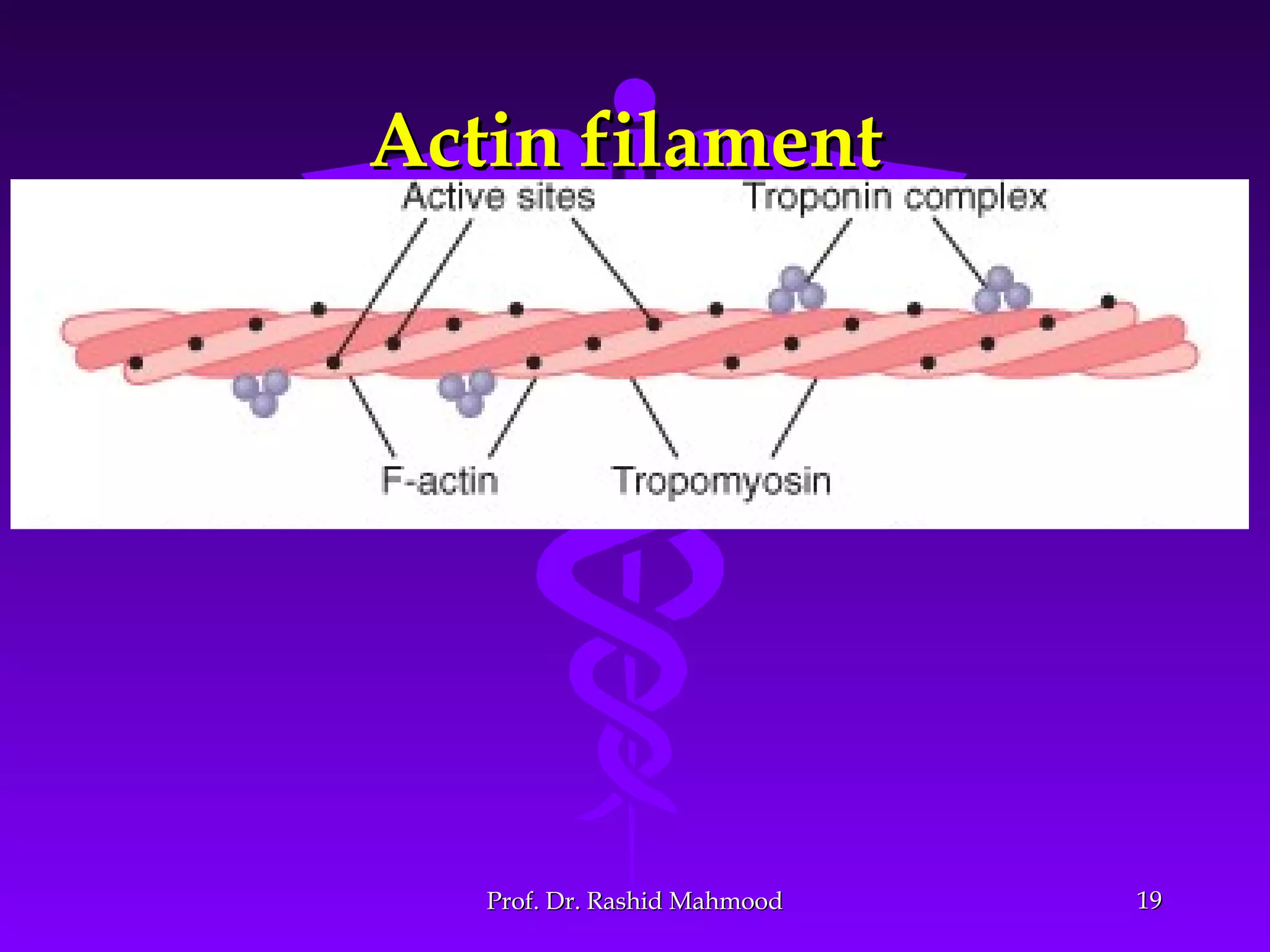
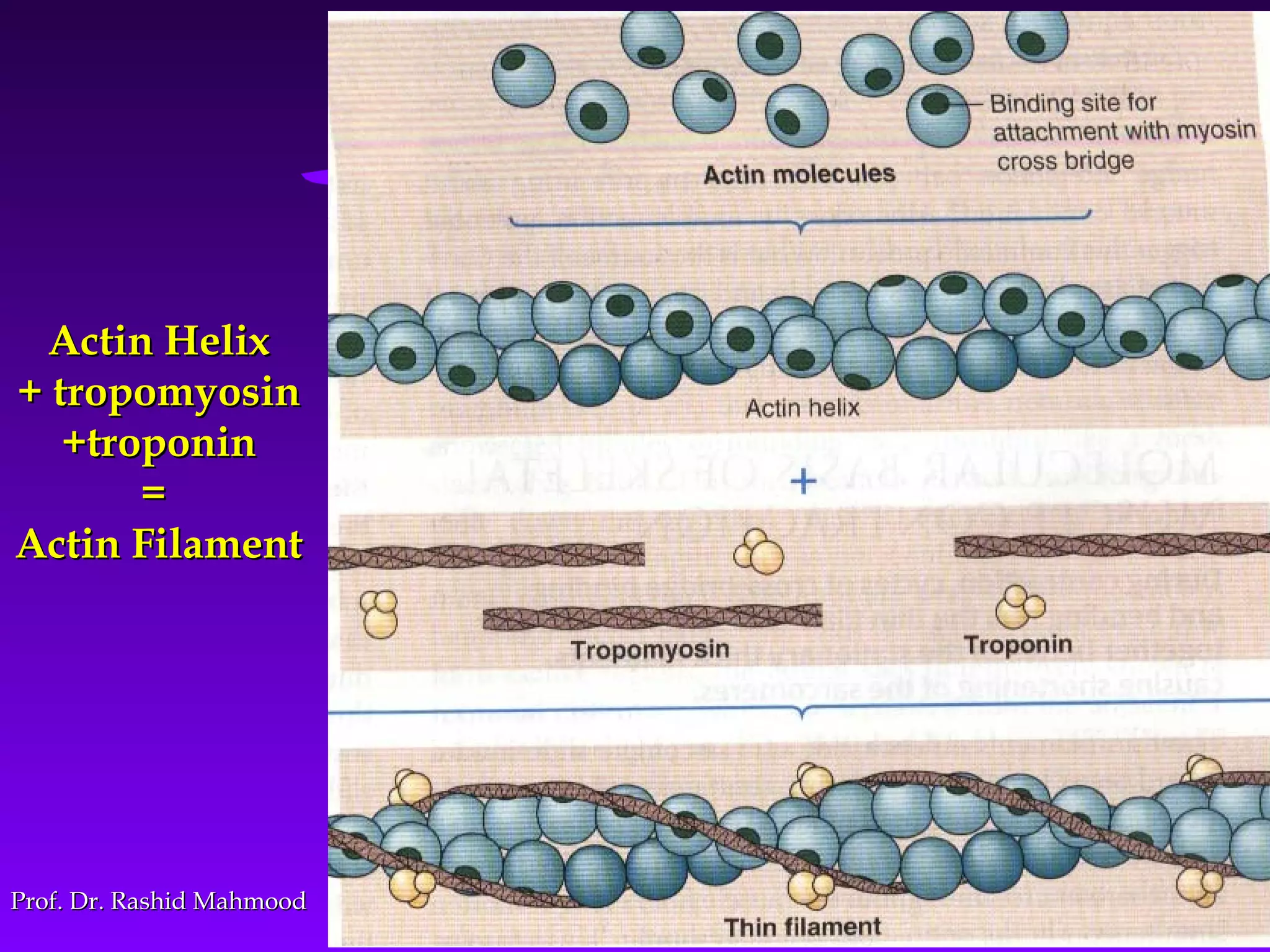
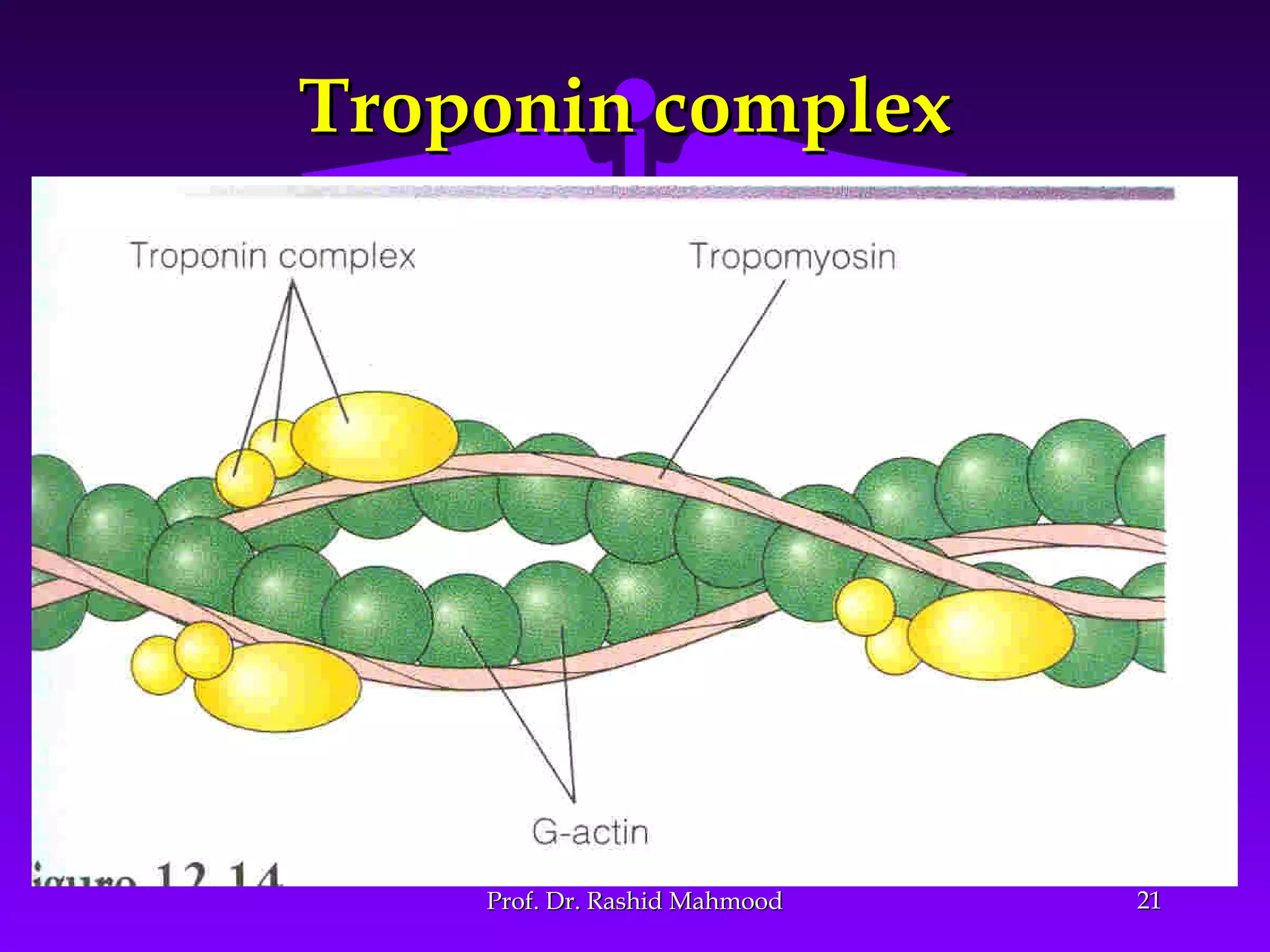
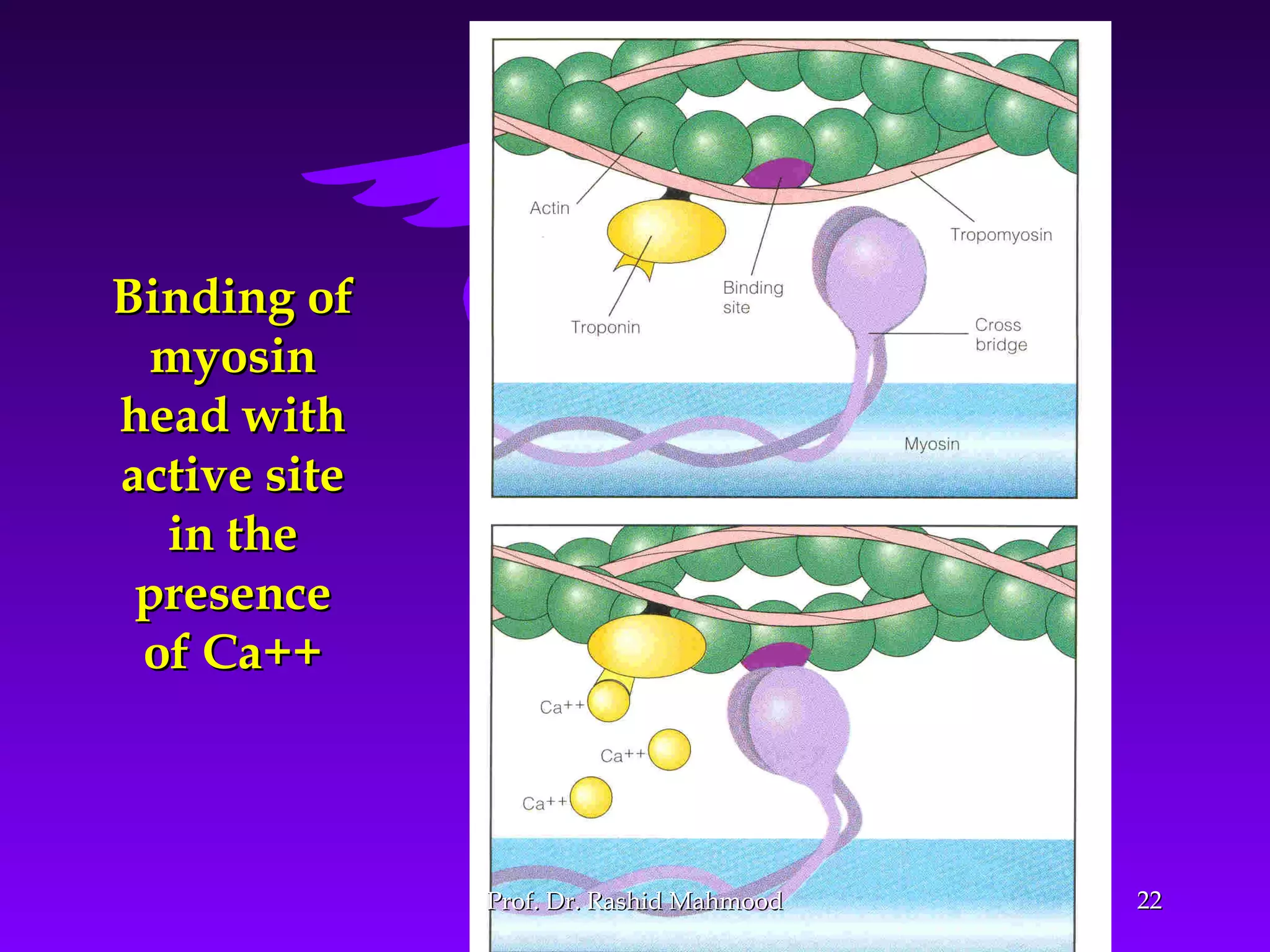
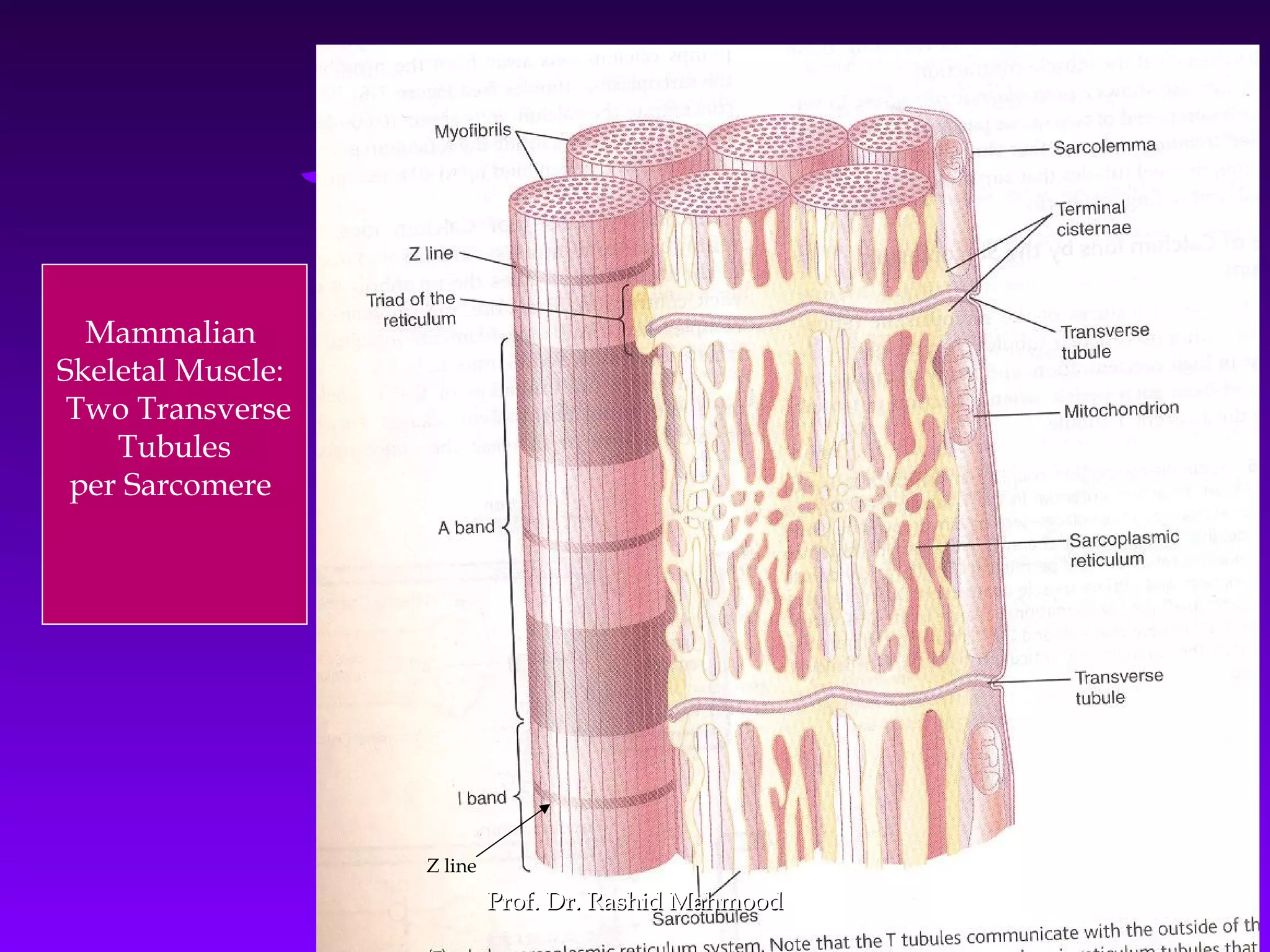
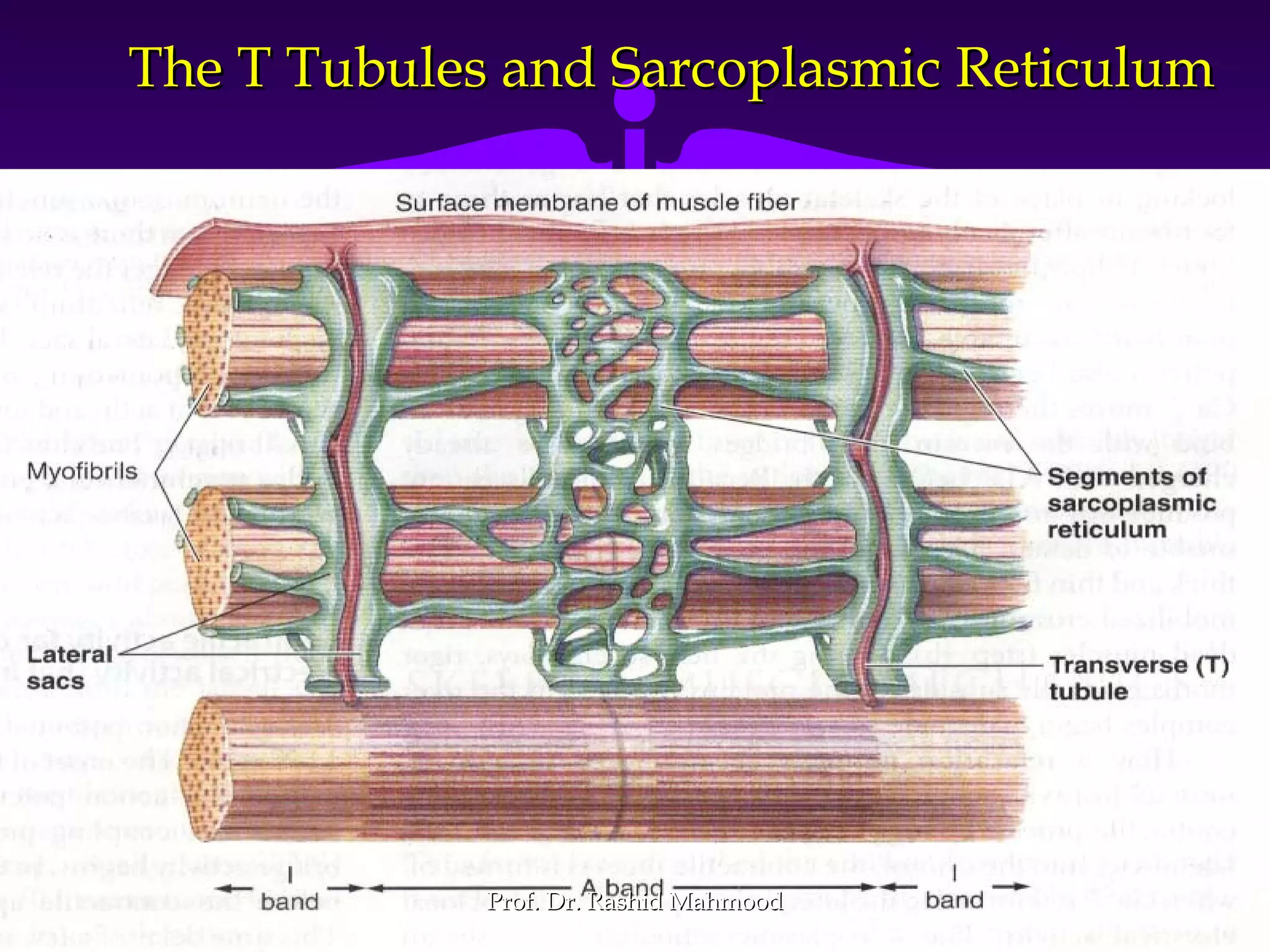
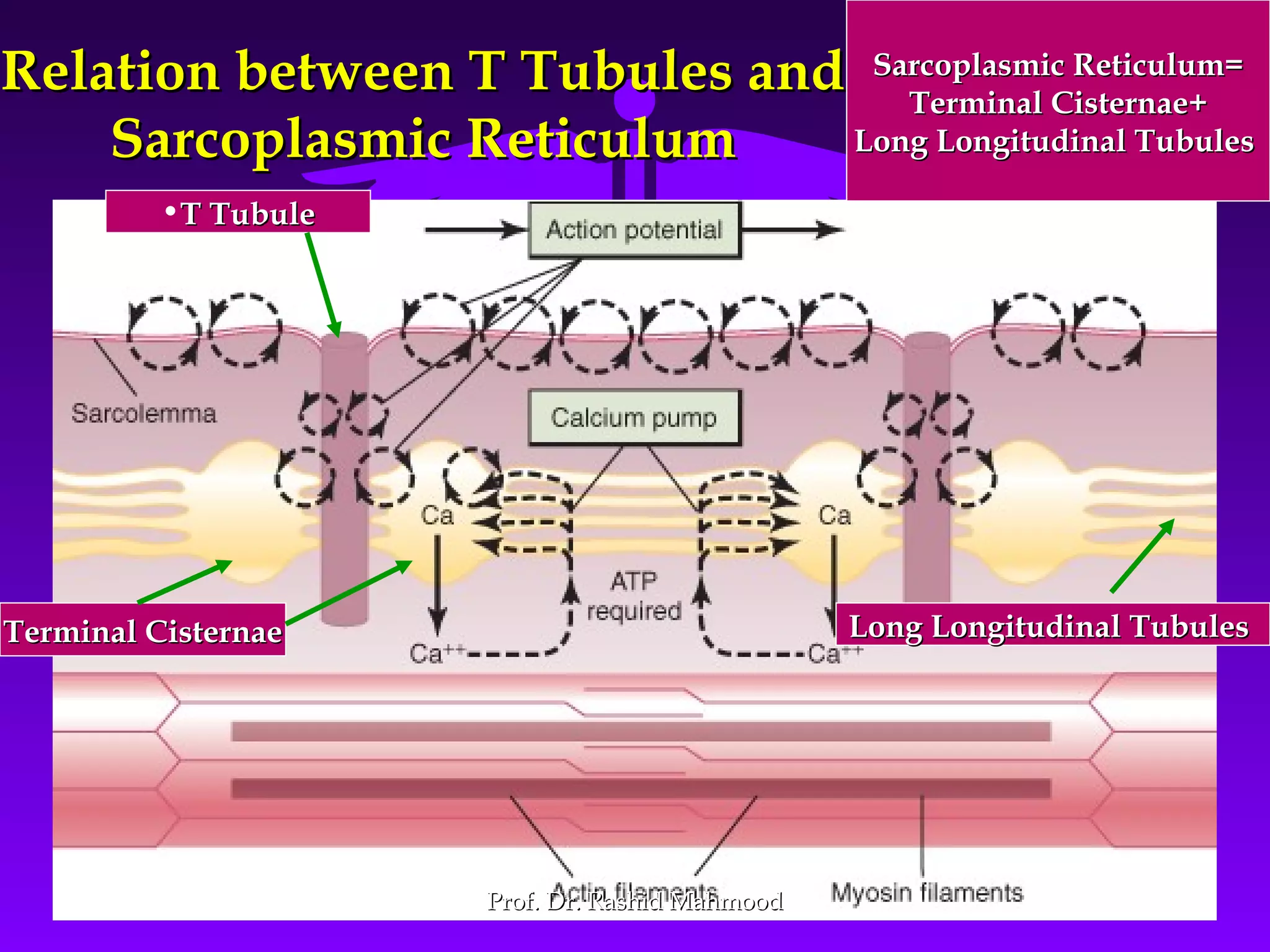
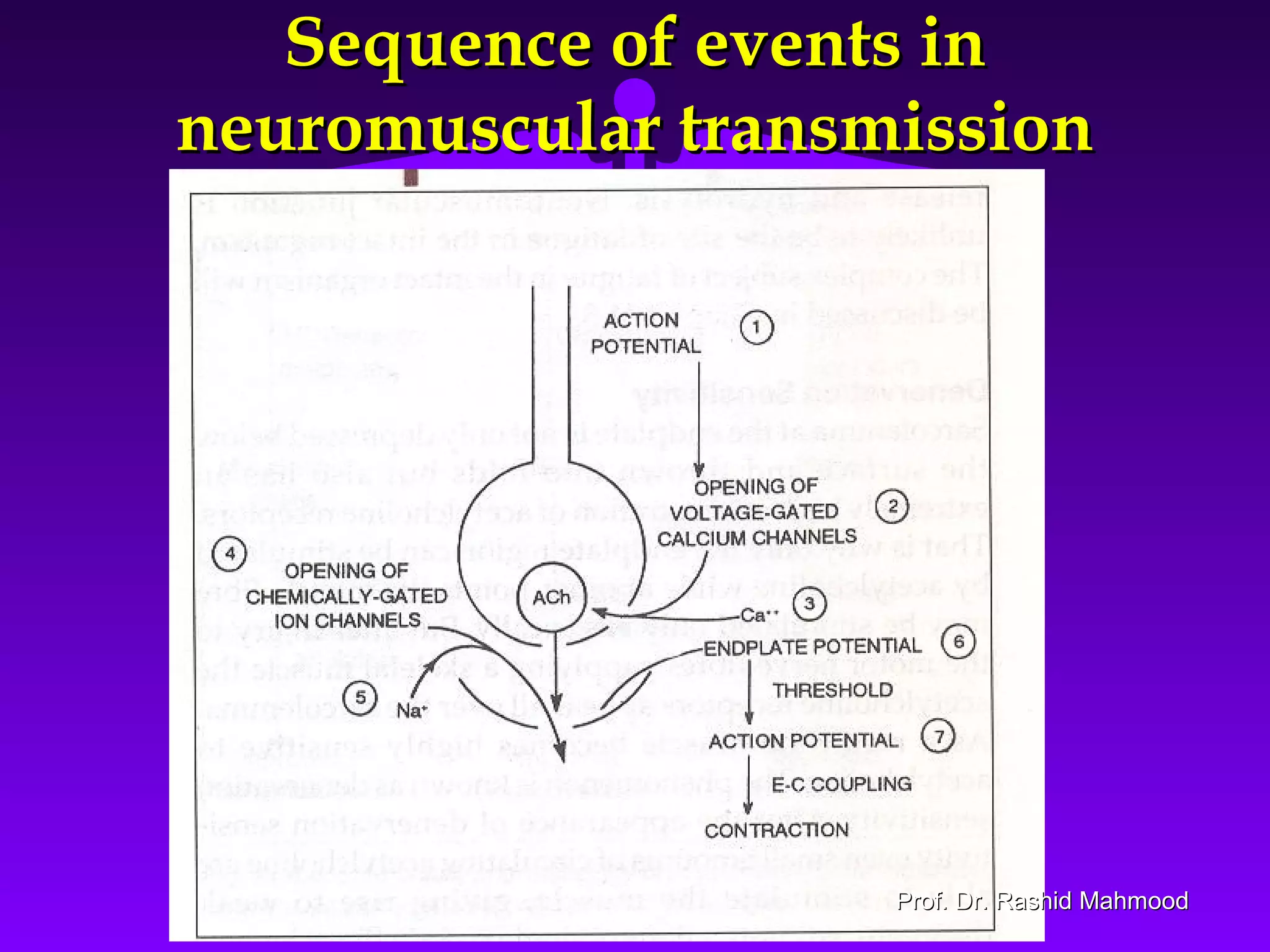
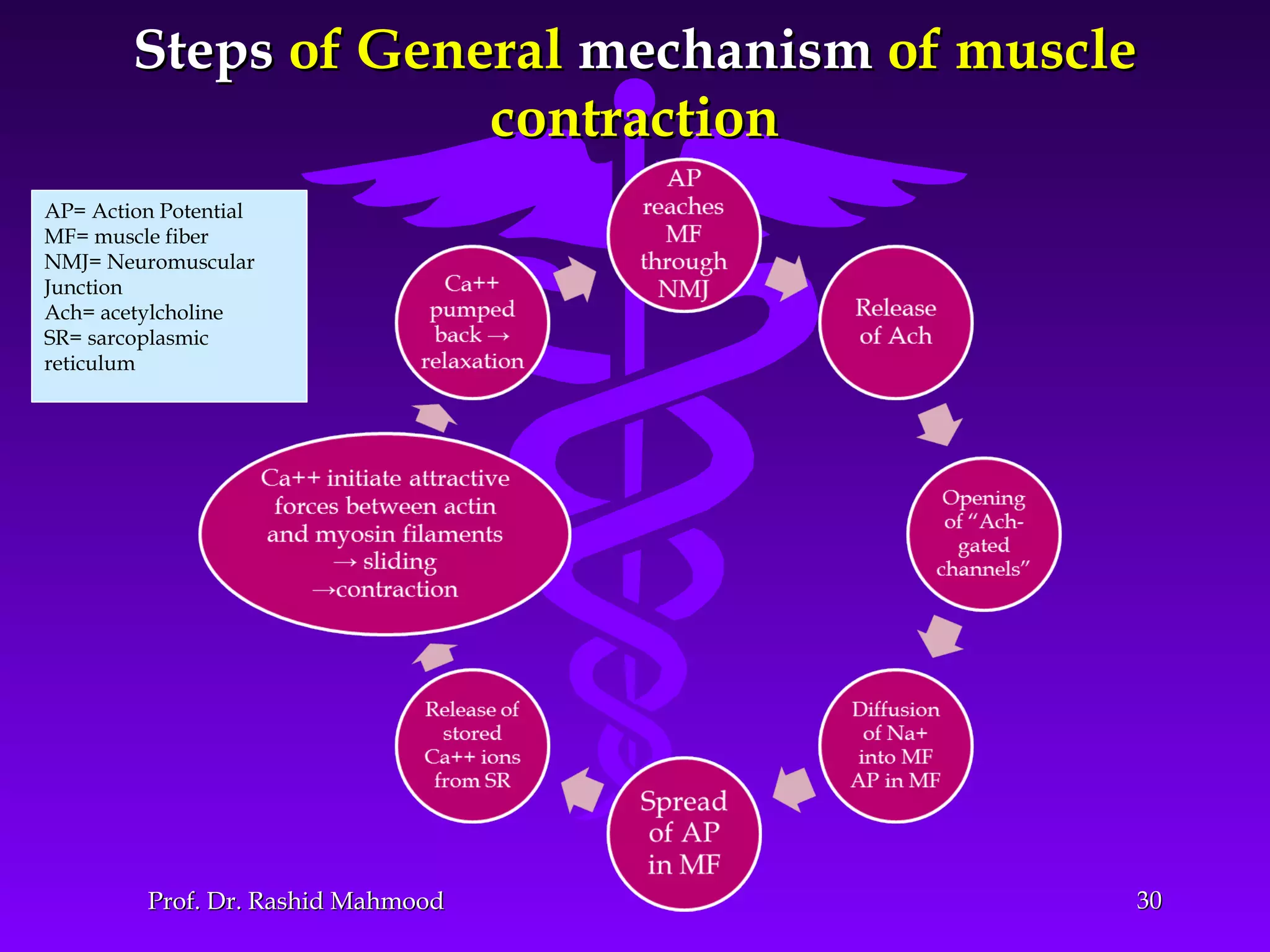
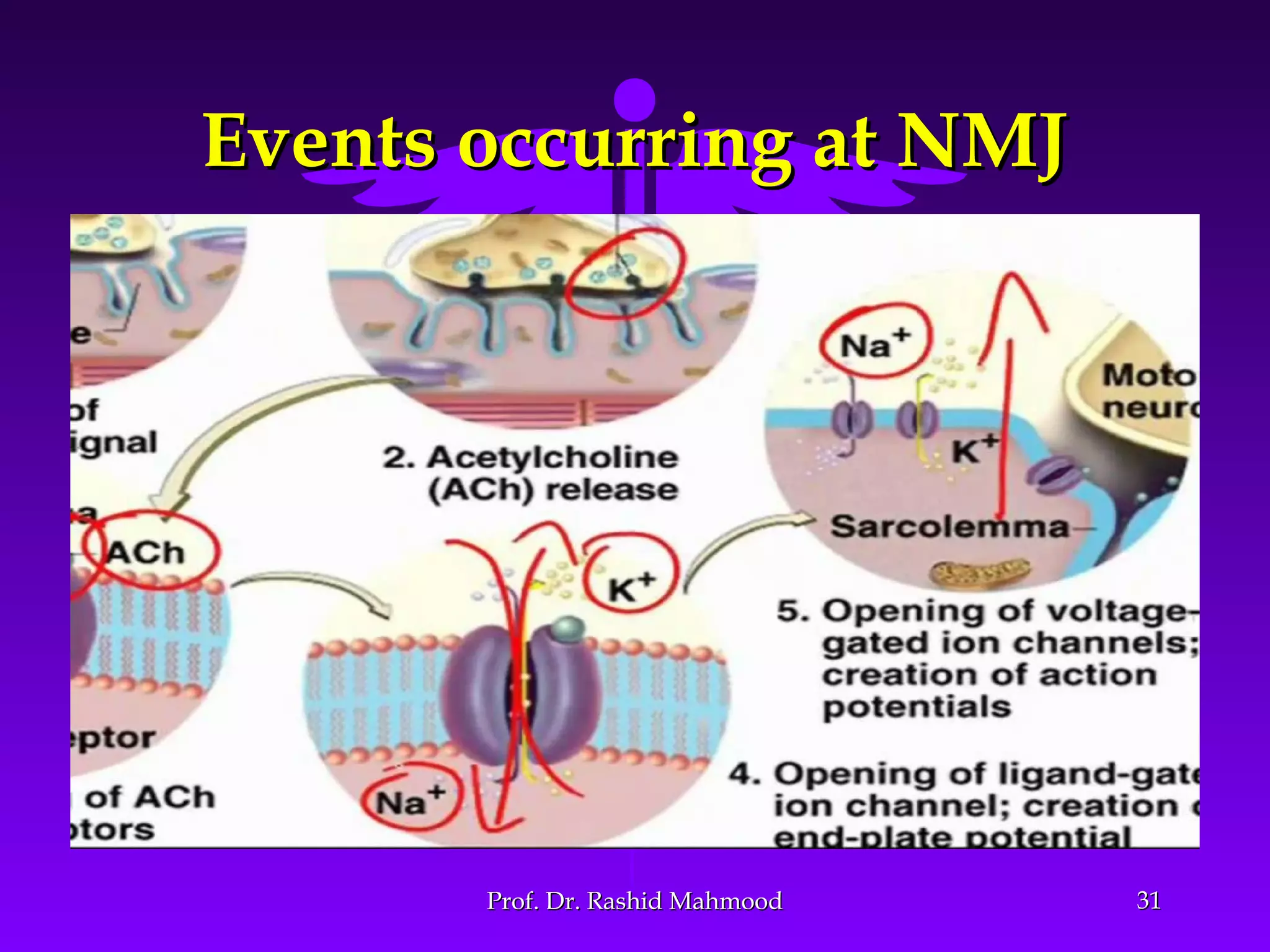
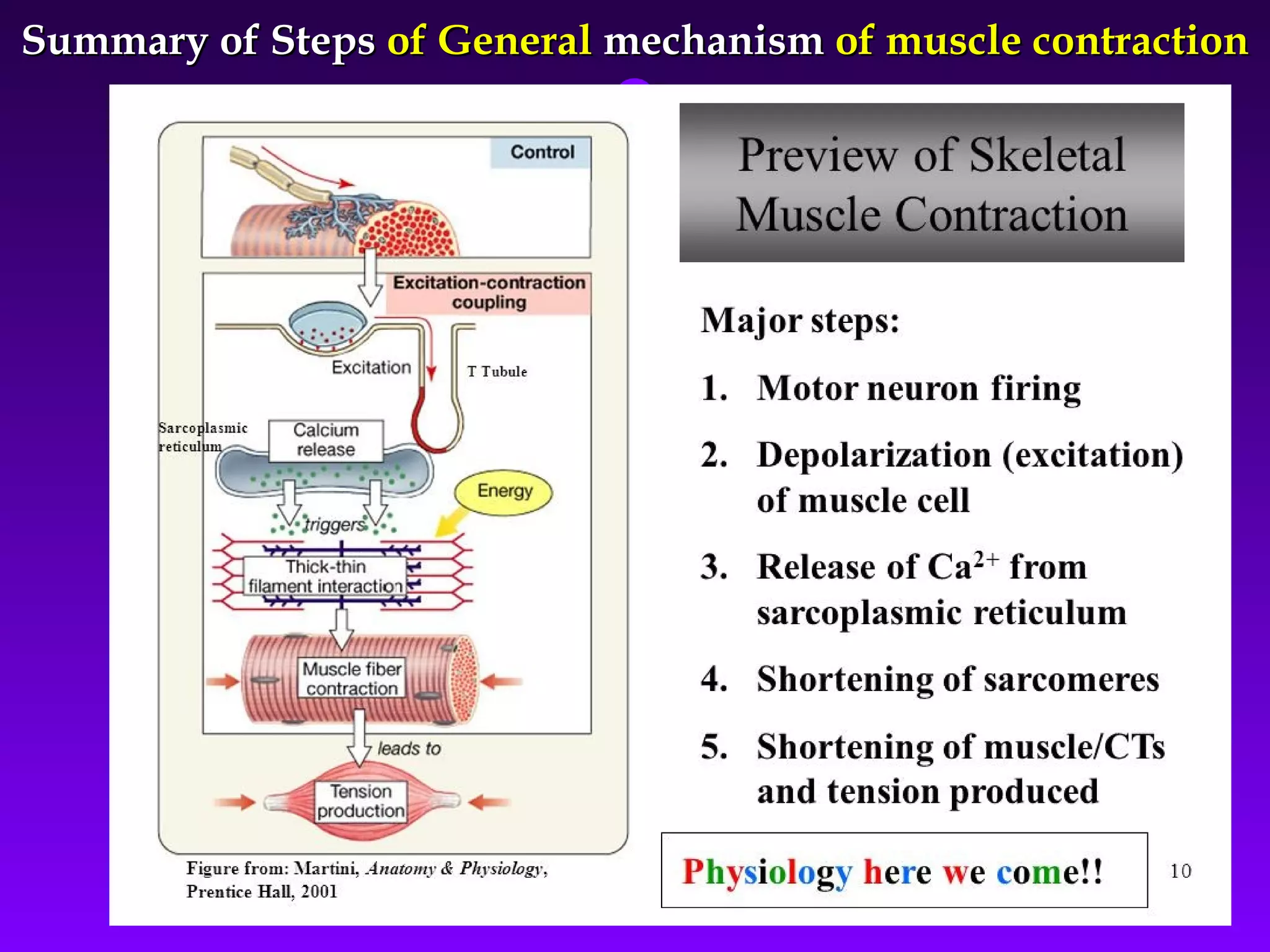
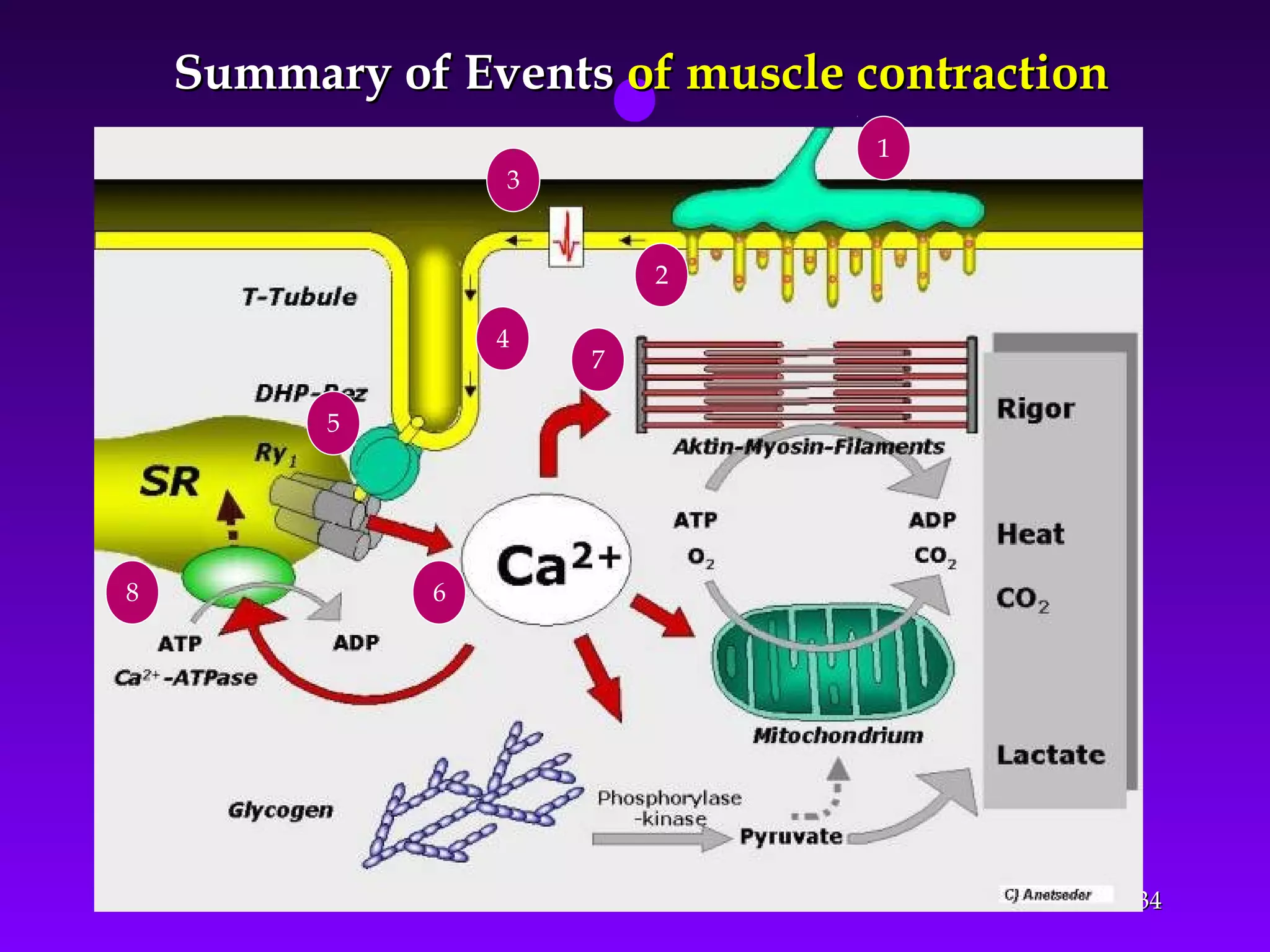
The document summarizes the mechanism of skeletal muscle contraction. It discusses three classes of muscles - skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscles. The functional unit of skeletal muscle is the muscle fiber, composed of myofibrils containing actin and myosin filaments. Contraction occurs through a series of events starting with acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction, spreading of the action potential through the muscle, calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, and the sliding of actin and myosin filaments through the cross-bridge cycle. The current theory that explains this sliding is the walk-along or ratchet theory.