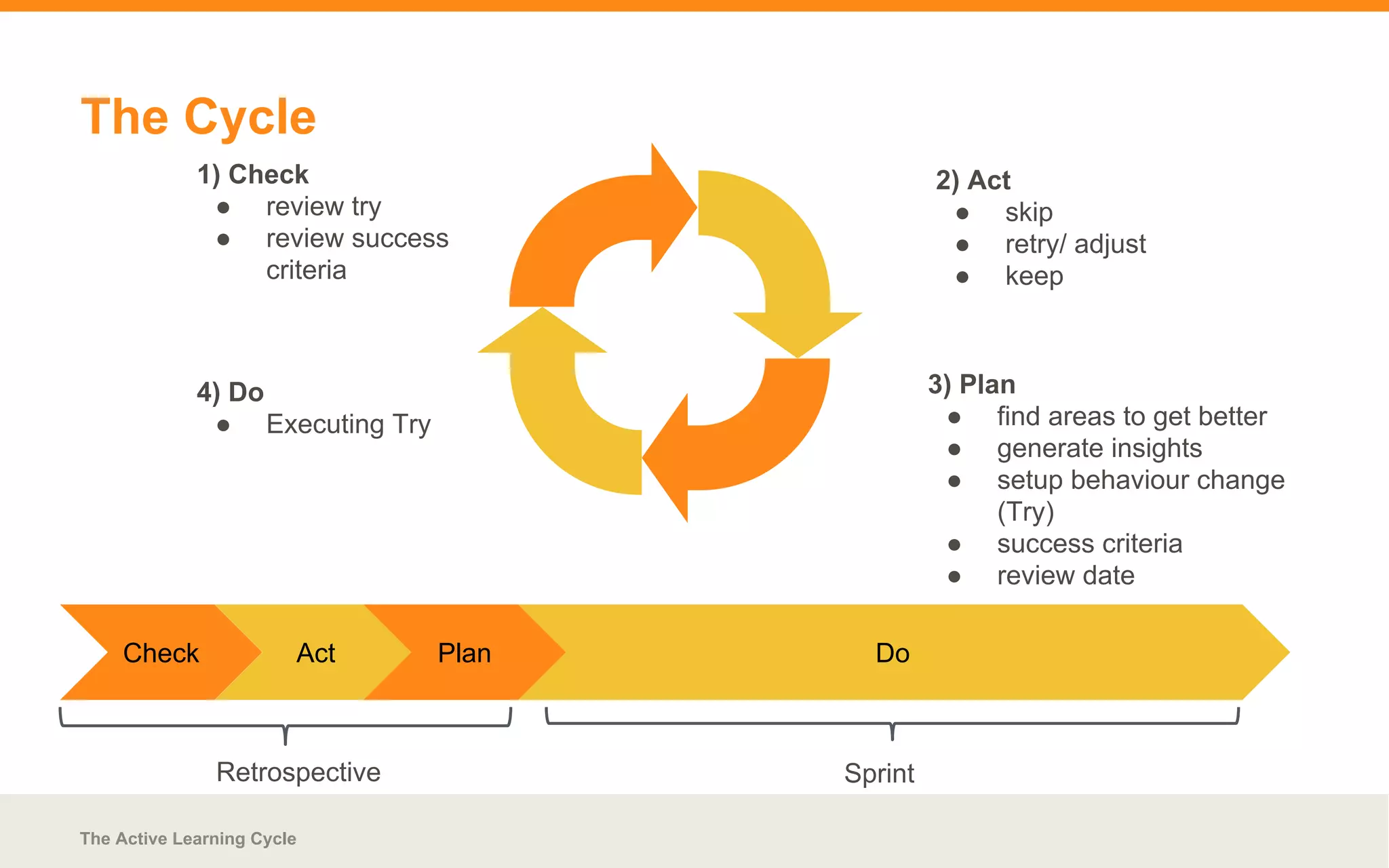
This document discusses continuous improvement and the active learning cycle. It provides background on concepts like kaizen and defines continuous improvement. The active learning cycle is presented as a method for continuous improvement consisting of a cycle with four steps: check, plan, do, and act. This allows a team to regularly inspect their work, plan improvements, implement changes, and review the results in a repeating feedback loop aimed at incremental and ongoing enhancement. Advantages and potential failure patterns of this approach are outlined.