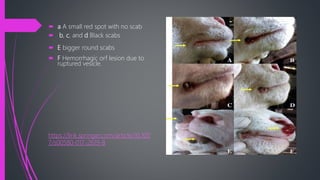
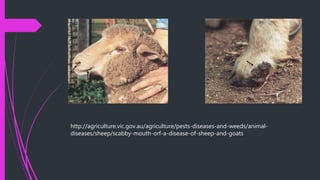
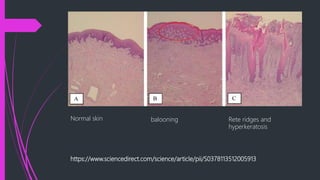
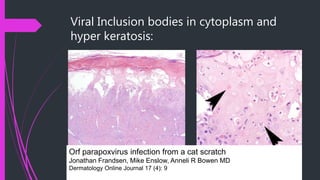
Contagious ecthyma, also known as orf, is a viral disease that affects small ruminants like sheep and goats. It causes lesions around the mouth and lips. The virus belongs to the parapoxvirus genus in the poxvirus family. Young animals are most susceptible. Transmission occurs through direct contact. Clinical signs include papules, pustules, and scabs around the mouth. The disease is usually self-limiting and lesions resolve in 3-4 weeks. Differential diagnosis includes other viral skin diseases and bacterial infections.