This document discusses reference groups and the family as consumer reference groups. It covers the following key points:
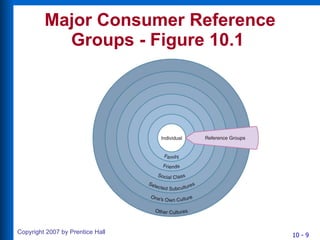
1) Reference groups are people or groups that individuals compare themselves to in forming attitudes and behaviors. Major consumer reference groups include friendship groups, shopping groups, work groups, and virtual communities.
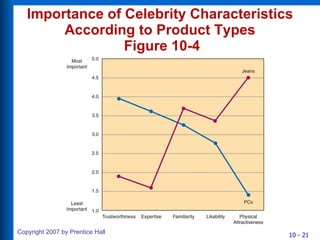
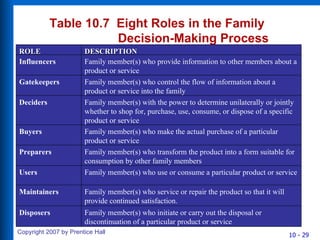
2) Celebrity endorsements, experts, and common people are often used in reference group appeals in advertising. Family roles in decision making include influencers, gatekeepers, deciders, buyers, and others.
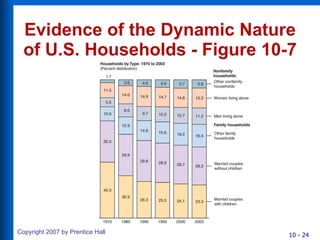
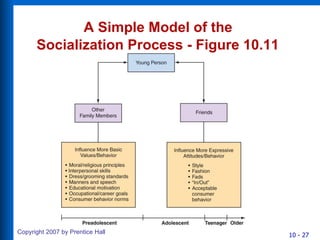
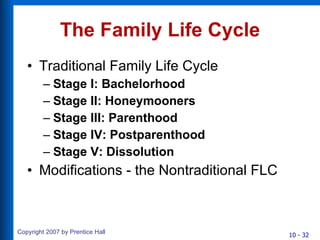
3) The traditional American family is changing with more non-family households, working mothers, and childless women. Consumer socialization is how children learn consumer skills and roles. Marketers can influence this process