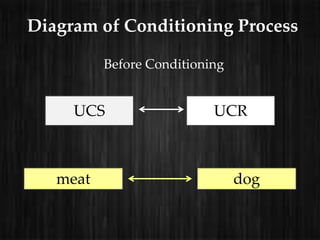
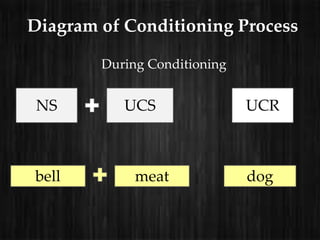
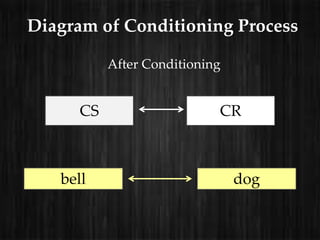
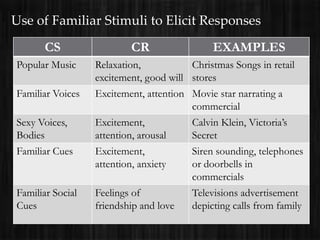
The document outlines consumer learning as an evolving process influenced by knowledge and experience, highlighting classical and operant conditioning as key learning theories. Classical conditioning, as developed by Ivan Pavlov, involves pairing stimuli to elicit conditioned responses, applied in marketing to evoke emotional reactions. Operant conditioning, proposed by B.F. Skinner, reinforces behaviors through positive and negative reinforcements, detailing various schedules of reinforcement based on responses and time intervals.