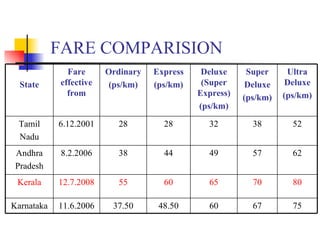
The document discusses the recent fare hike by KSRTC, the state-run bus service in Kerala. It provides background on KSRTC and reviews the current scenario. The hike was necessary due to rising operational costs from increased fuel prices. However, KSRTC faces problems like an aging fleet, high staff ratios, and competition from private operators. Suggestions are made to nationalize more routes, improve management techniques, and maintain support from the government and public.