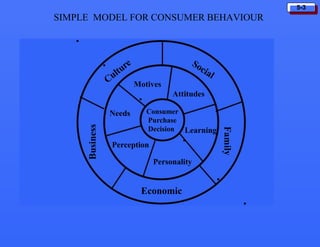
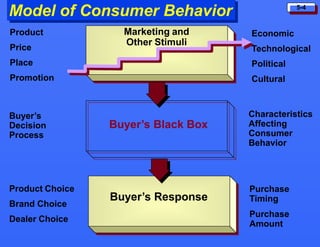
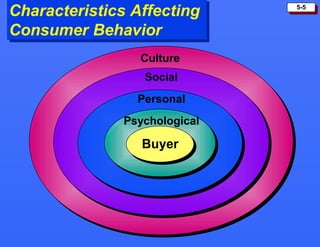
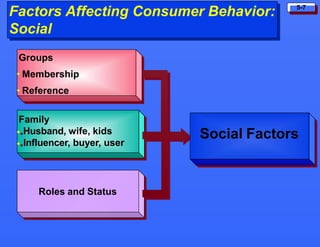
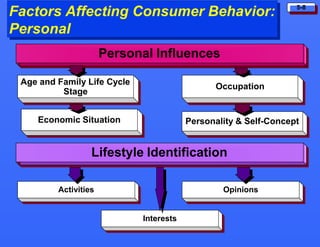
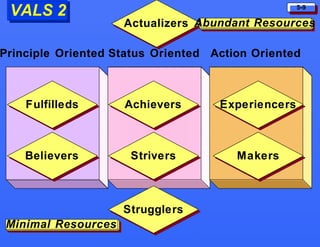
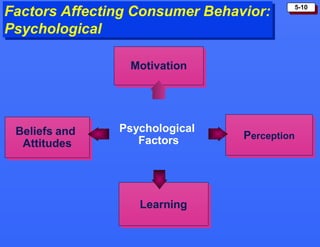
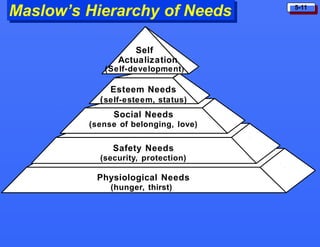
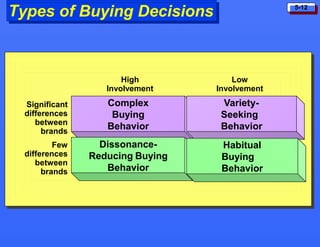
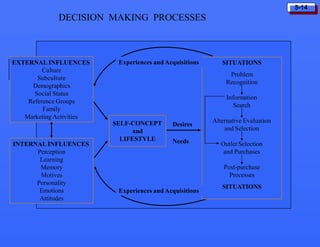
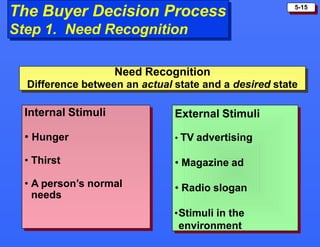
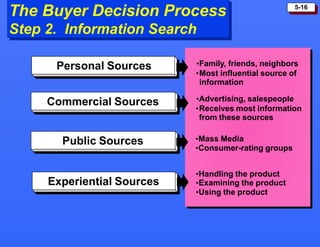
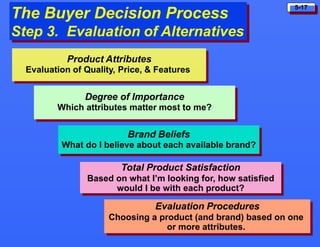
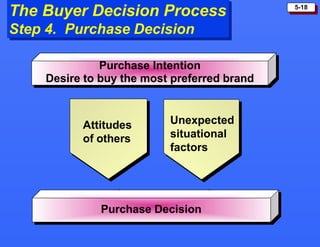
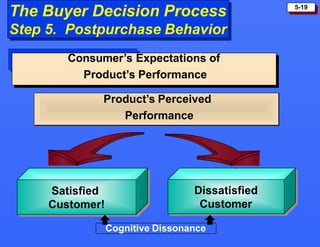
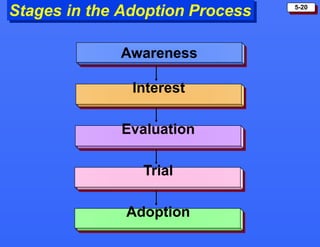
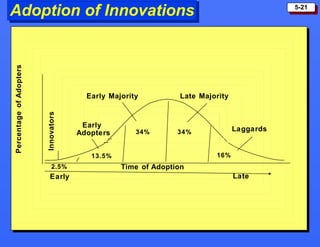
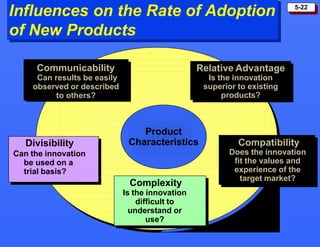
This document discusses consumer buying behavior and the factors that influence it. It provides a model of consumer behavior that shows how marketing stimuli interact with a consumer's characteristics to influence their decision process. The consumer decision process is outlined in 5 stages: need recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives, purchase decision, and post-purchase behavior. Cultural, social, personal and psychological characteristics all impact a consumer's buying behaviors. Models like Maslow's hierarchy of needs and VALS help explain consumer motivations. The rate of adoption of new products depends on their perceived advantages, compatibility, complexity, divisibility, and communicability.