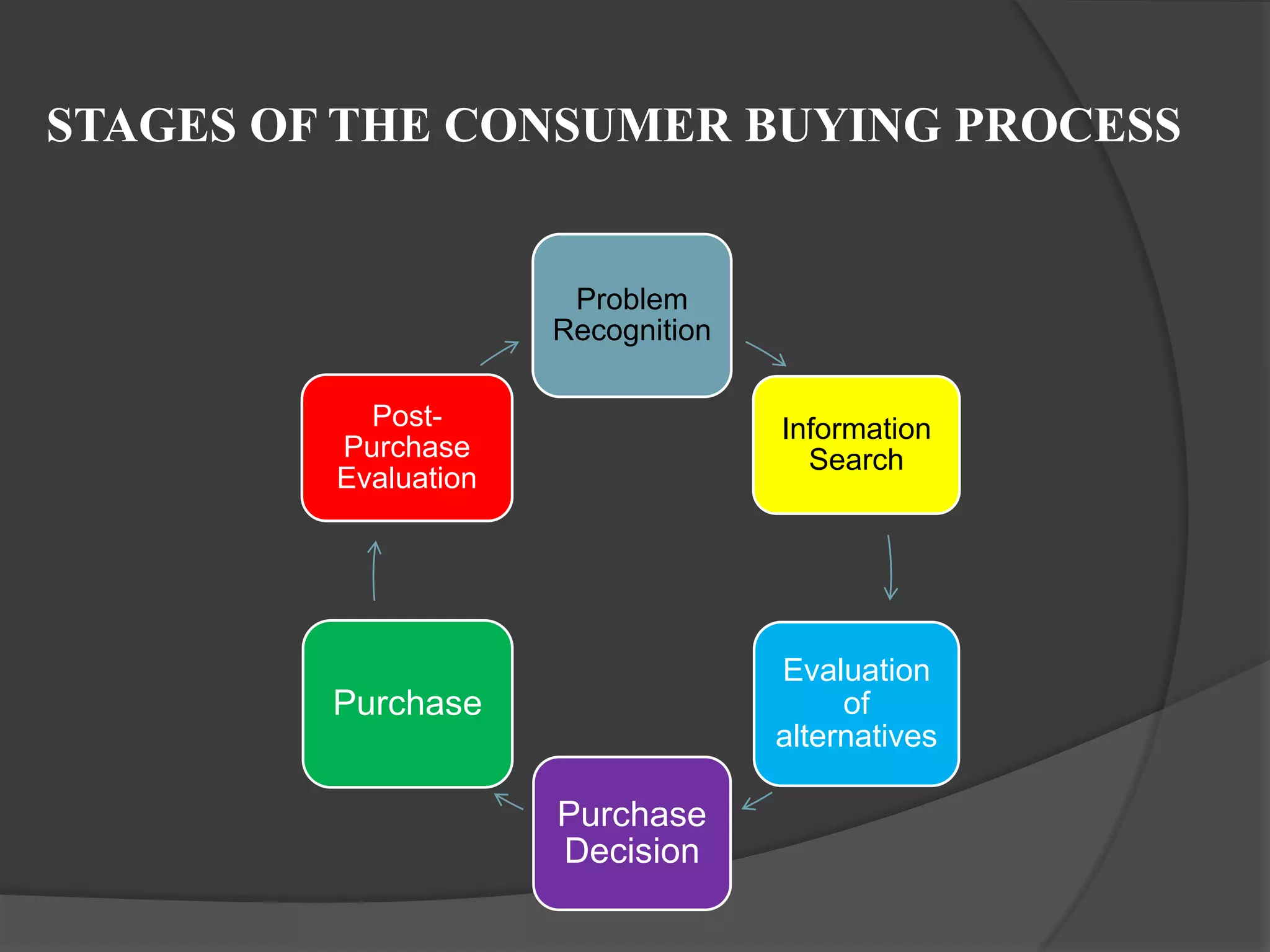
The document summarizes the stages of the consumer buying process. It discusses the key stages as:
1) Problem recognition, where a consumer identifies an unmet need. An example is a student needing a laptop for college assignments.
2) Information search, where the consumer searches for information about products that could meet their need. This includes internal memory and external sources like friends.
3) Evaluation of alternatives, where the consumer evaluates different products based on criteria like price, quality and features. The student evaluates laptop brands.
4) Purchase decision, where the consumer decides on a product, brand, store. The student chooses an HP laptop.
5) Post-purchase evaluation, where the consumer is satisfied and