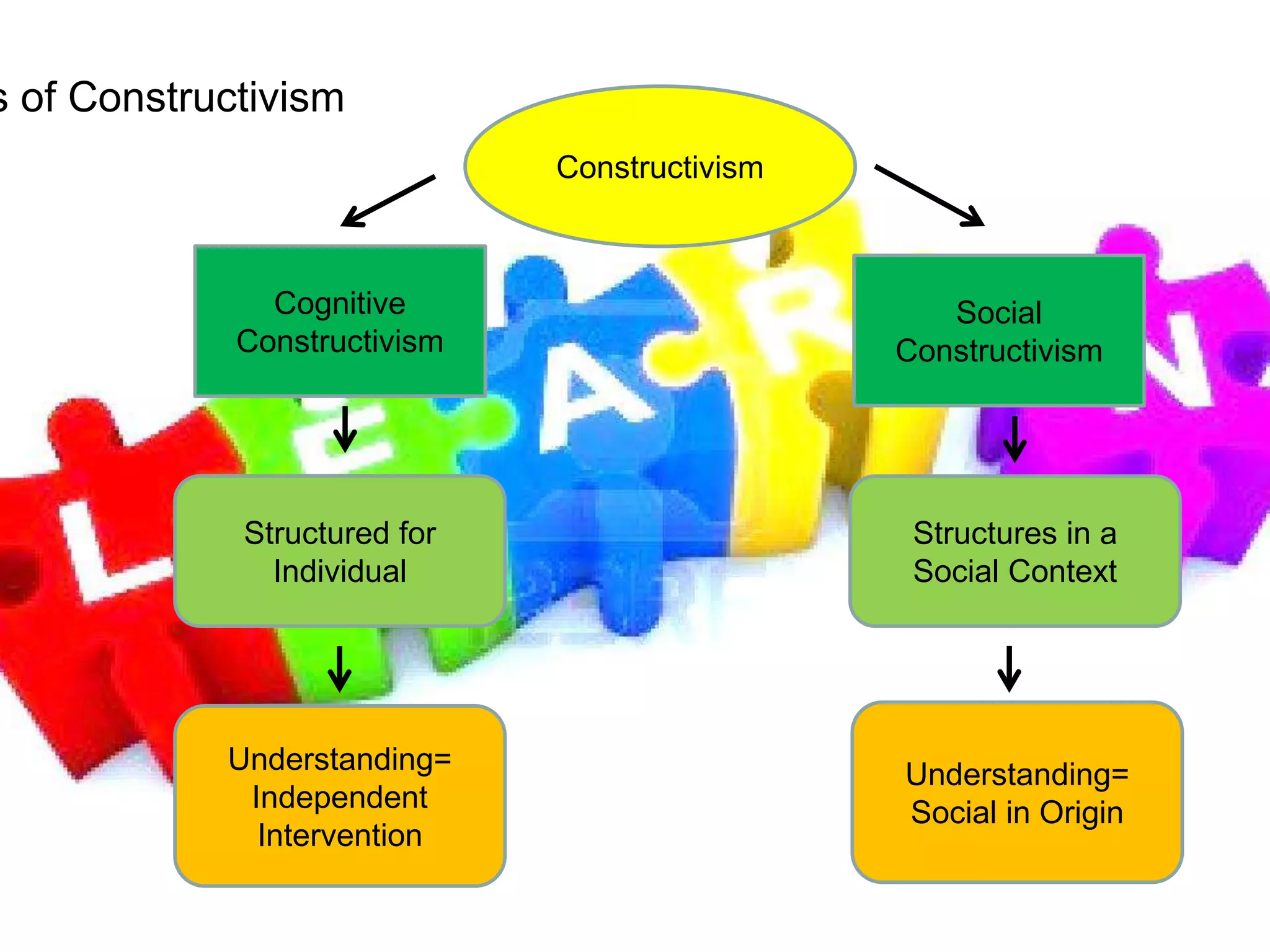
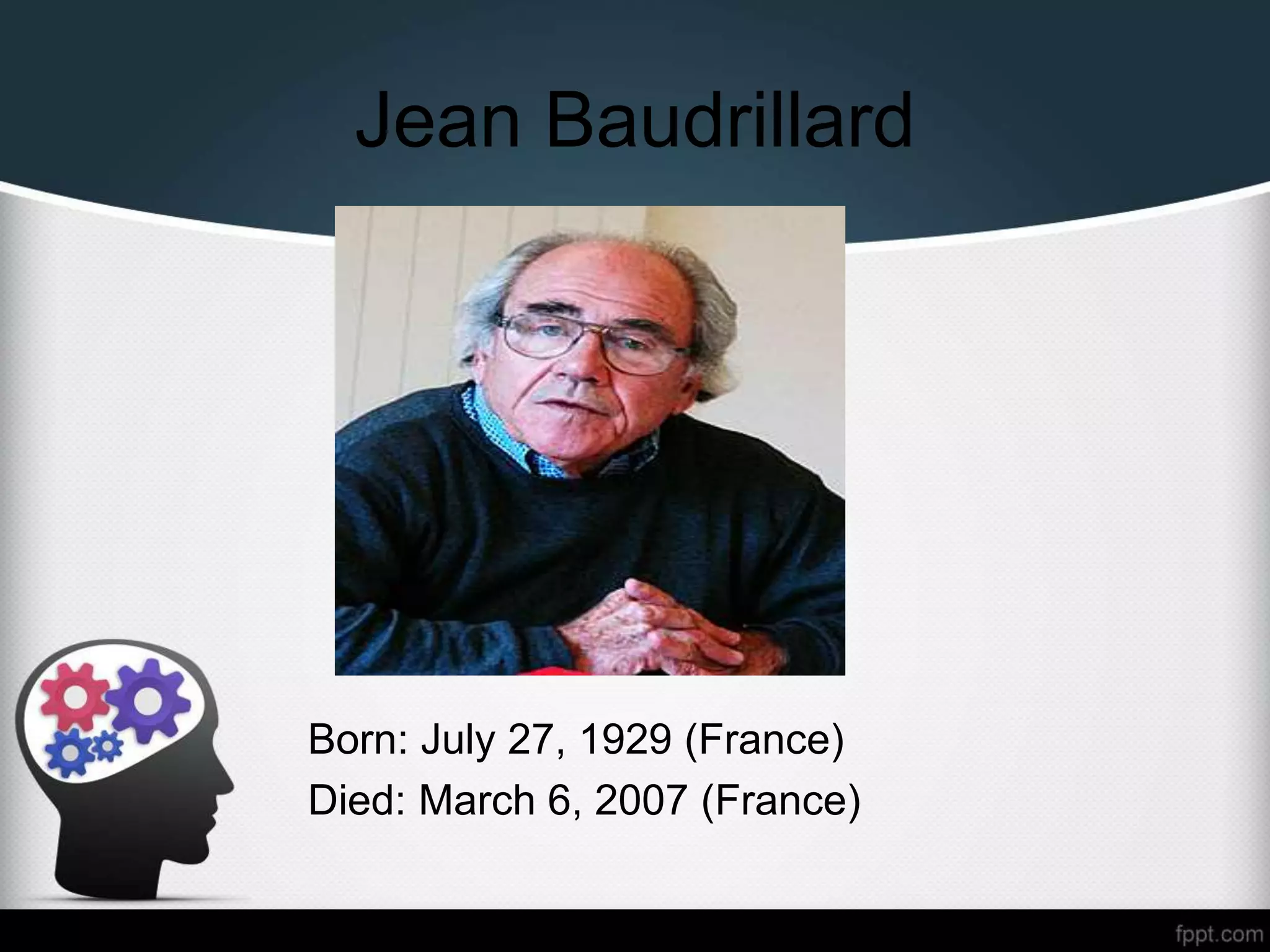
This document provides an overview of constructivism and postmodernism. It defines constructivism as the philosophy that learners need to build their own understanding of new ideas. Key proponents mentioned include Jean Piaget, Lev Vygotsky, and Gaston Bachelard. Different types of constructivism are outlined such as cognitive, social, and radical constructivism. Postmodernism is then defined as the belief that there is no true objectivity and authentic scientific method is impossible. Key assumptions of postmodernism include that all truth is constructed and reality is socially constructed rather than objectively mirrored in human understanding.