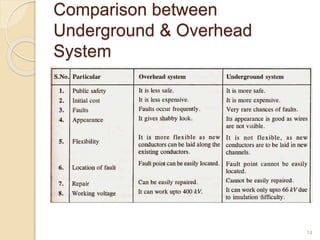
This document discusses underground cables, including their structure, construction, classification, insulating materials, and comparison to overhead systems. It provides details on the following:
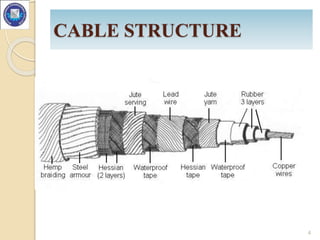
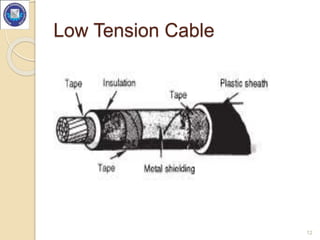
- Underground cables consist of one or more conductors covered with insulating material and a protective covering, and are buried directly in the ground or installed in underground ducts.
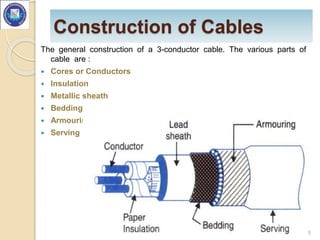
- Cable construction generally includes cores or conductors, insulation, a metallic sheath, bedding, armouring, and serving.
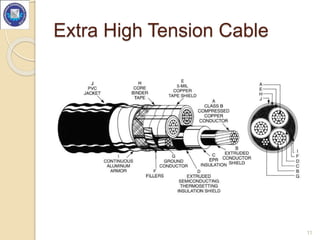
- Cables are classified based on voltage level as low, high, super, extra high, or extra super voltage cables.
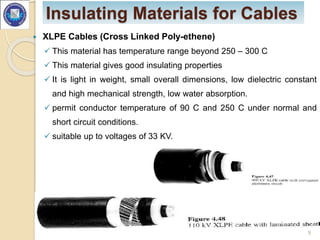
- Important properties of insulating materials include high resistivity, dielectric strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures. Common materials are