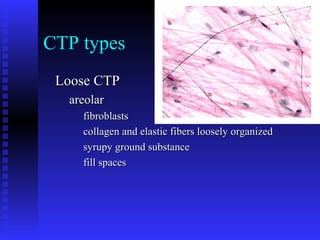
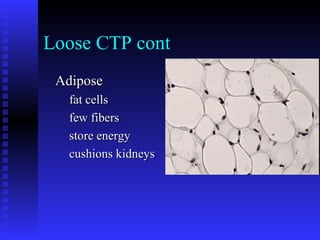
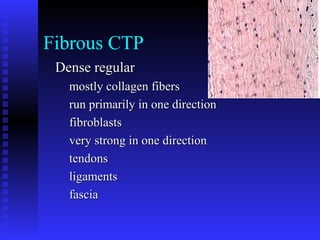
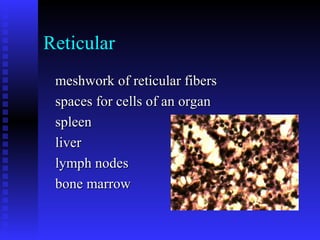
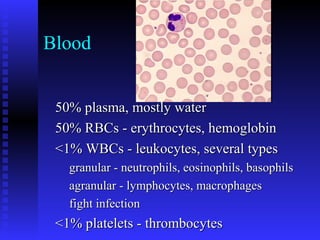
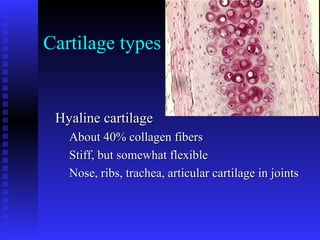
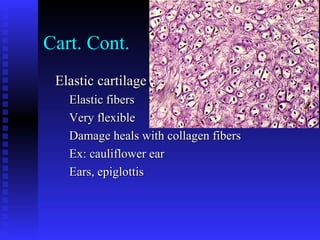
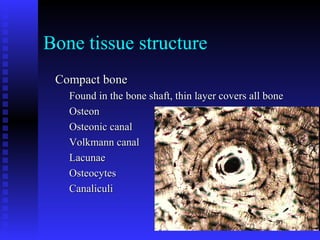
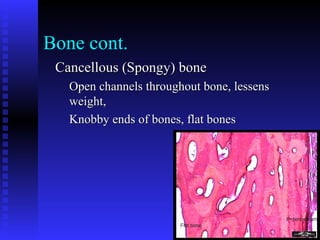
This document summarizes the four main types of connective tissue: connective tissue proper, blood and lymph, cartilage, and bone. It describes their characteristics, functions, subtypes, and tissue structures. Connective tissues provide structure and support, defense, nutrient storage and transport, and cushioning/protection. They contain cells, fibers, and ground substance and include areolar, adipose, dense regular, dense irregular, elastic, and reticular connective tissue proper; blood and lymph fluid; hyaline, elastic, and fibrocartilage; and compact and cancellous bone tissue.