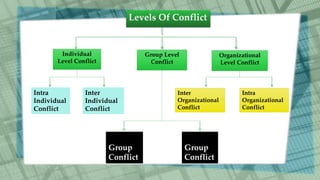
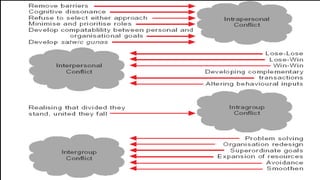
This document discusses conflict, including its sources, types, and levels. It defines conflict as a struggle between interdependent parties with incompatible goals. Conflict can originate from differences in information, beliefs, values, interests, desires, or scarce resources. The document outlines traditional, human relations, and integrationist views of conflict. It also describes latent, perceived, felt, manifest, functional, and dysfunctional types of conflict, as well as individual, group, organizational, inter-individual, inter-group, and inter-organizational levels of conflict. Finally, it lists five ways to manage conflicts: forcing, avoiding, accommodating, compromising, and collaborating.