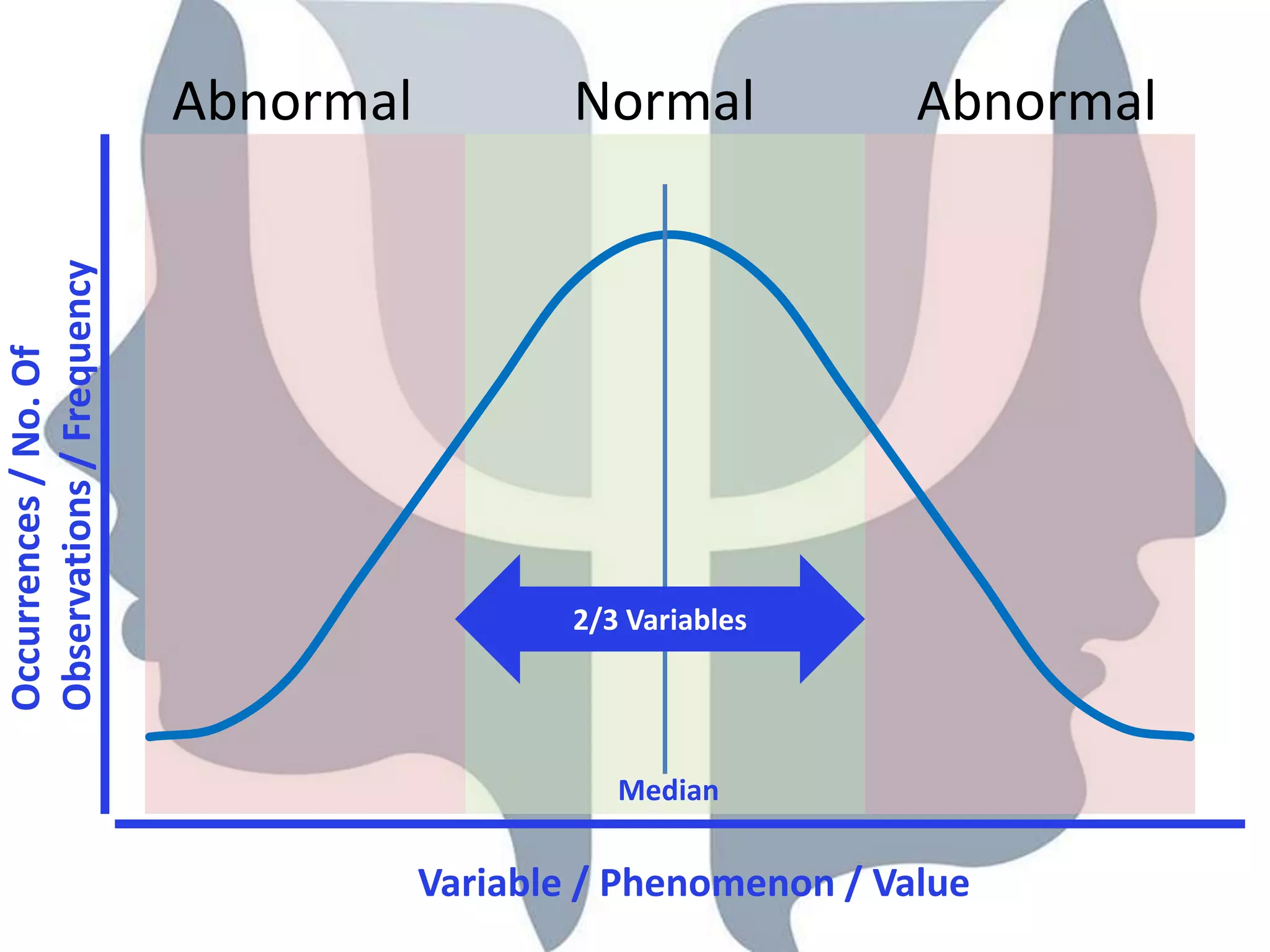
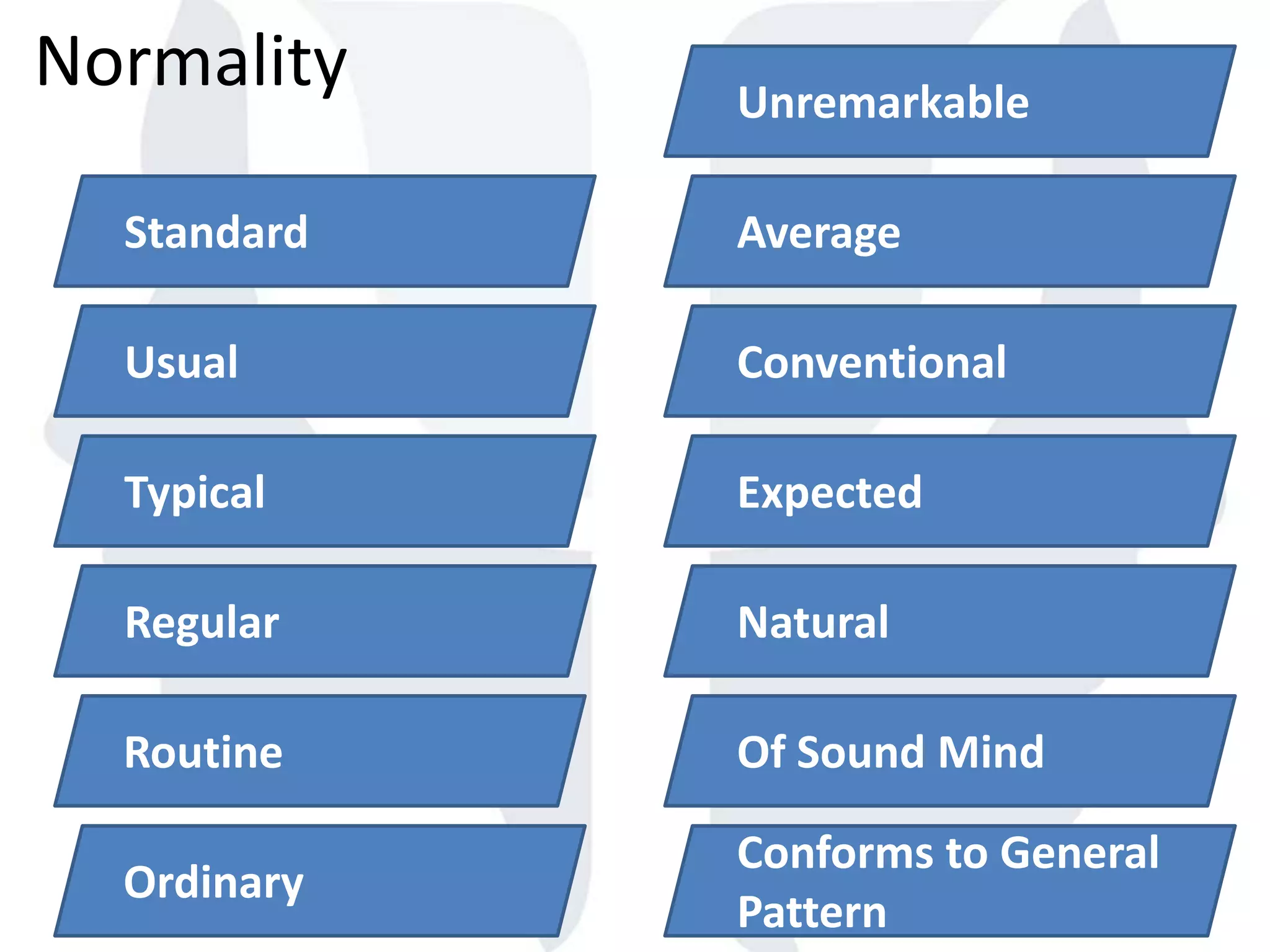
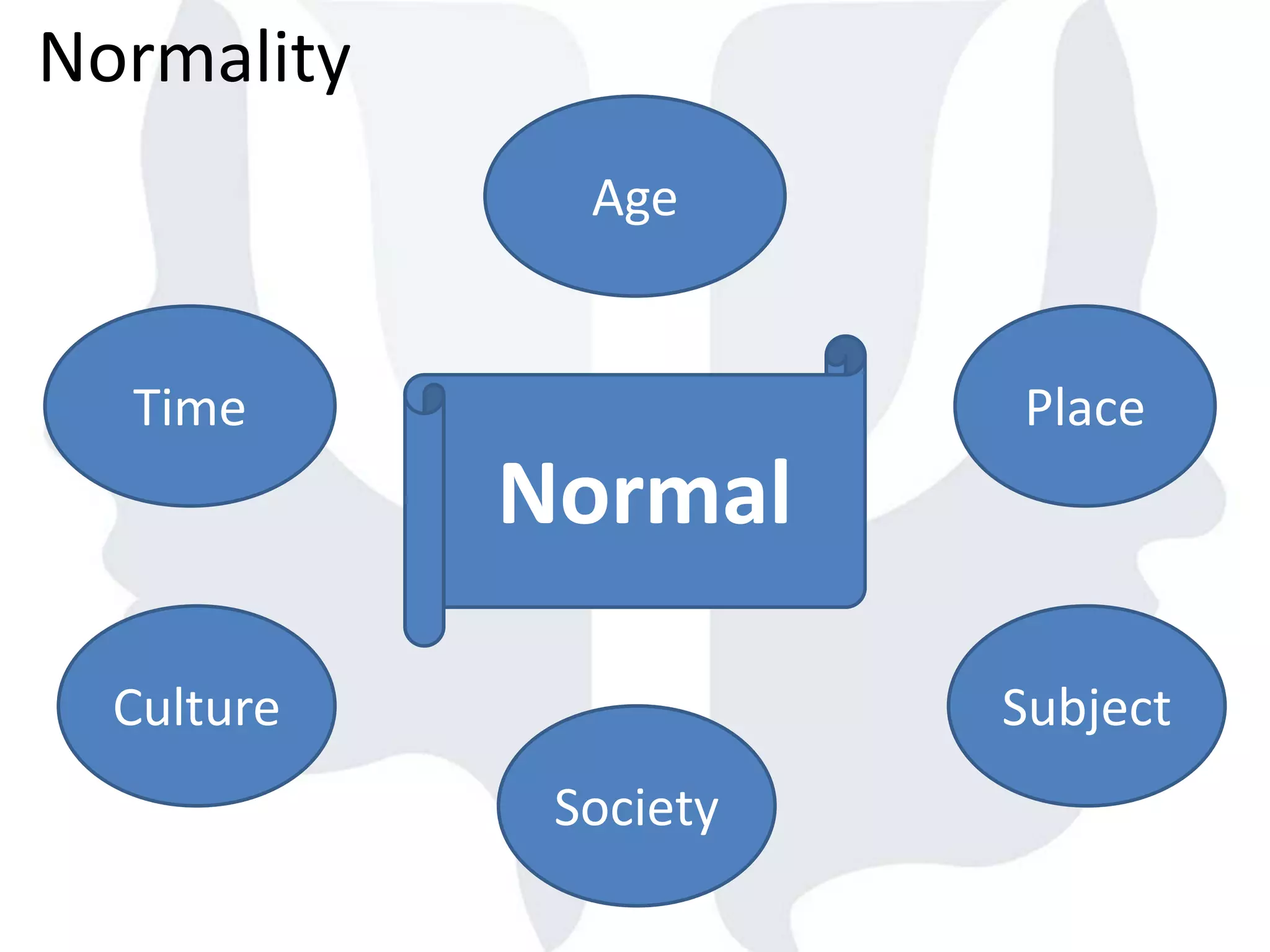
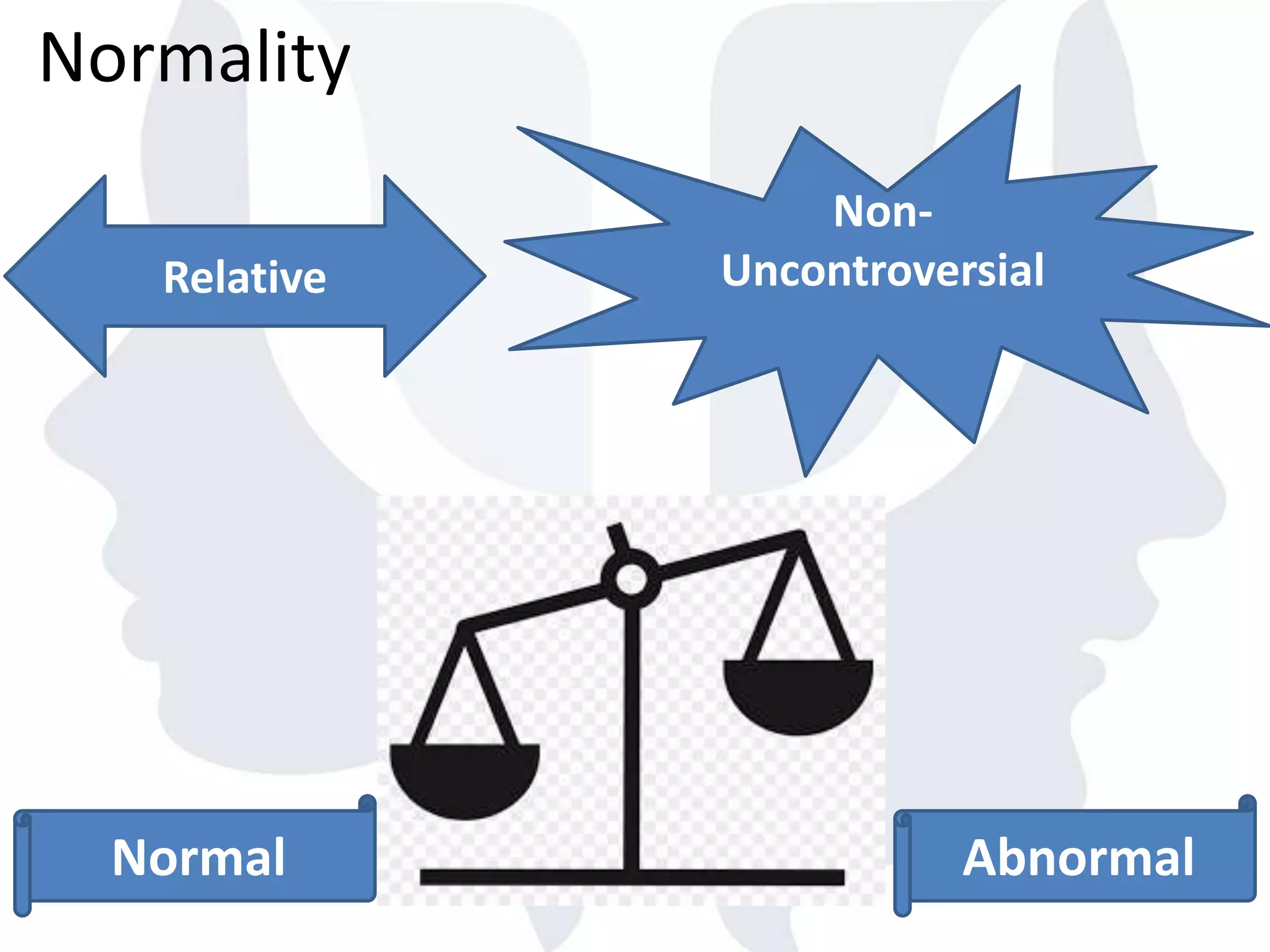
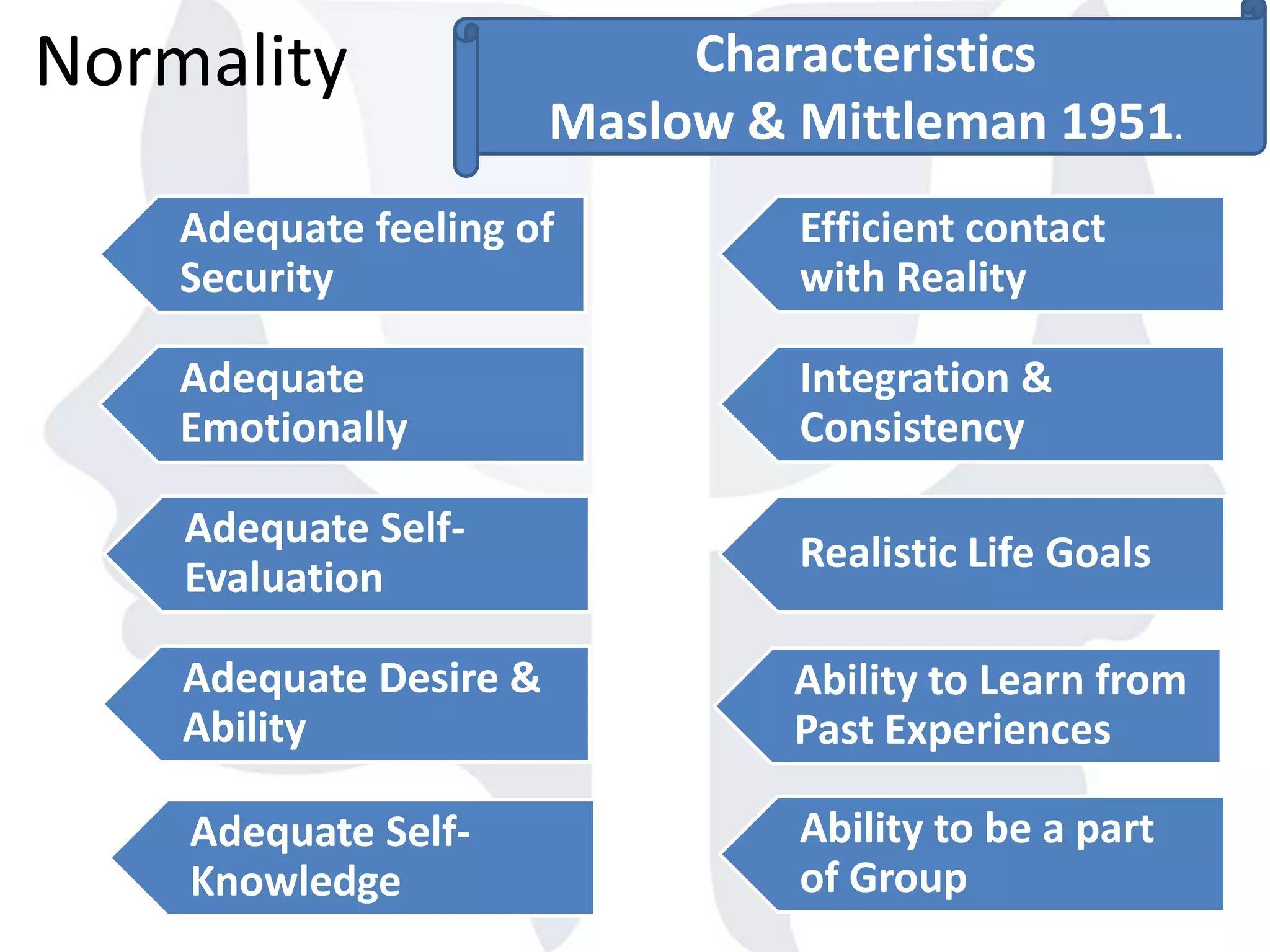
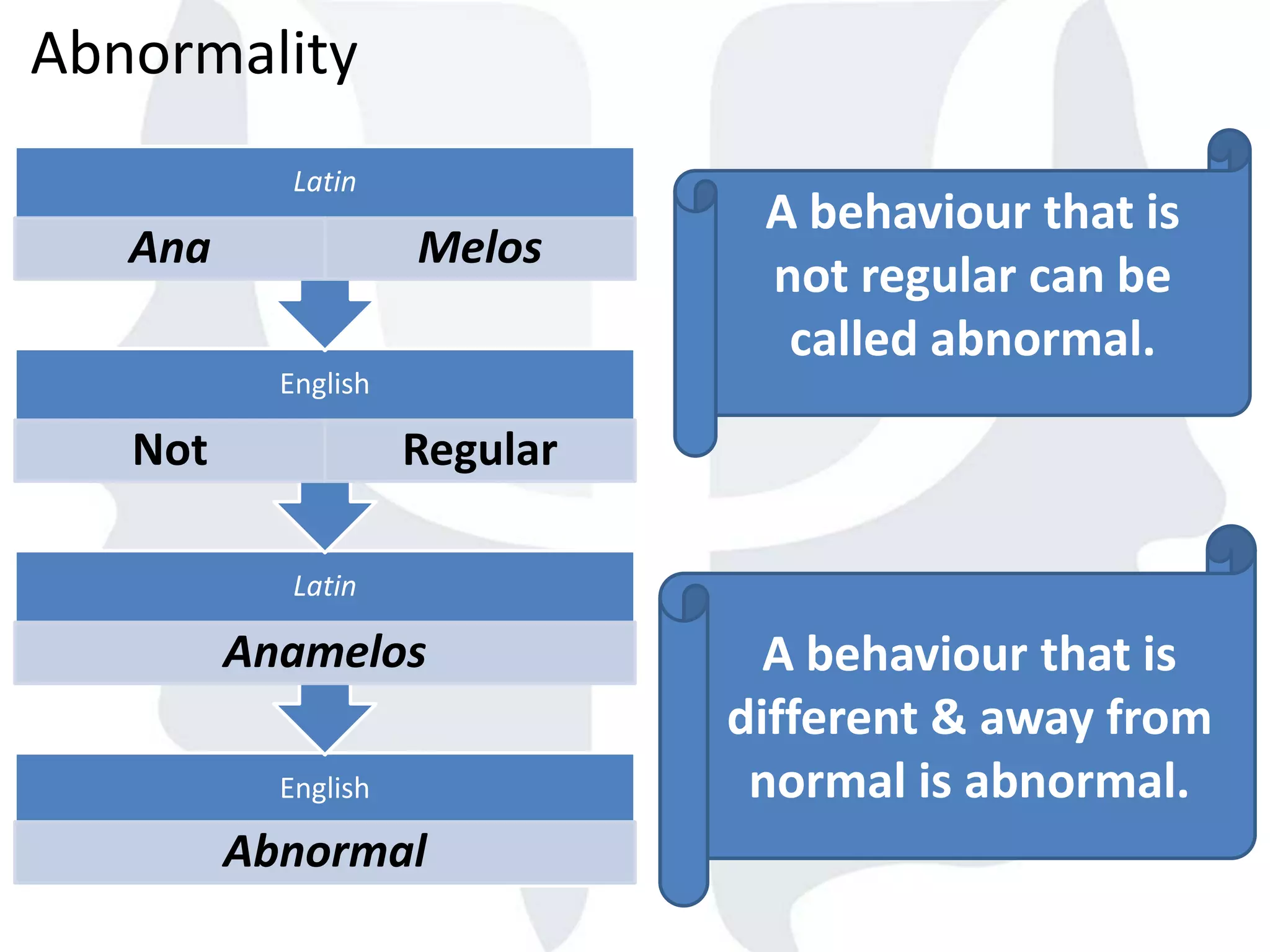
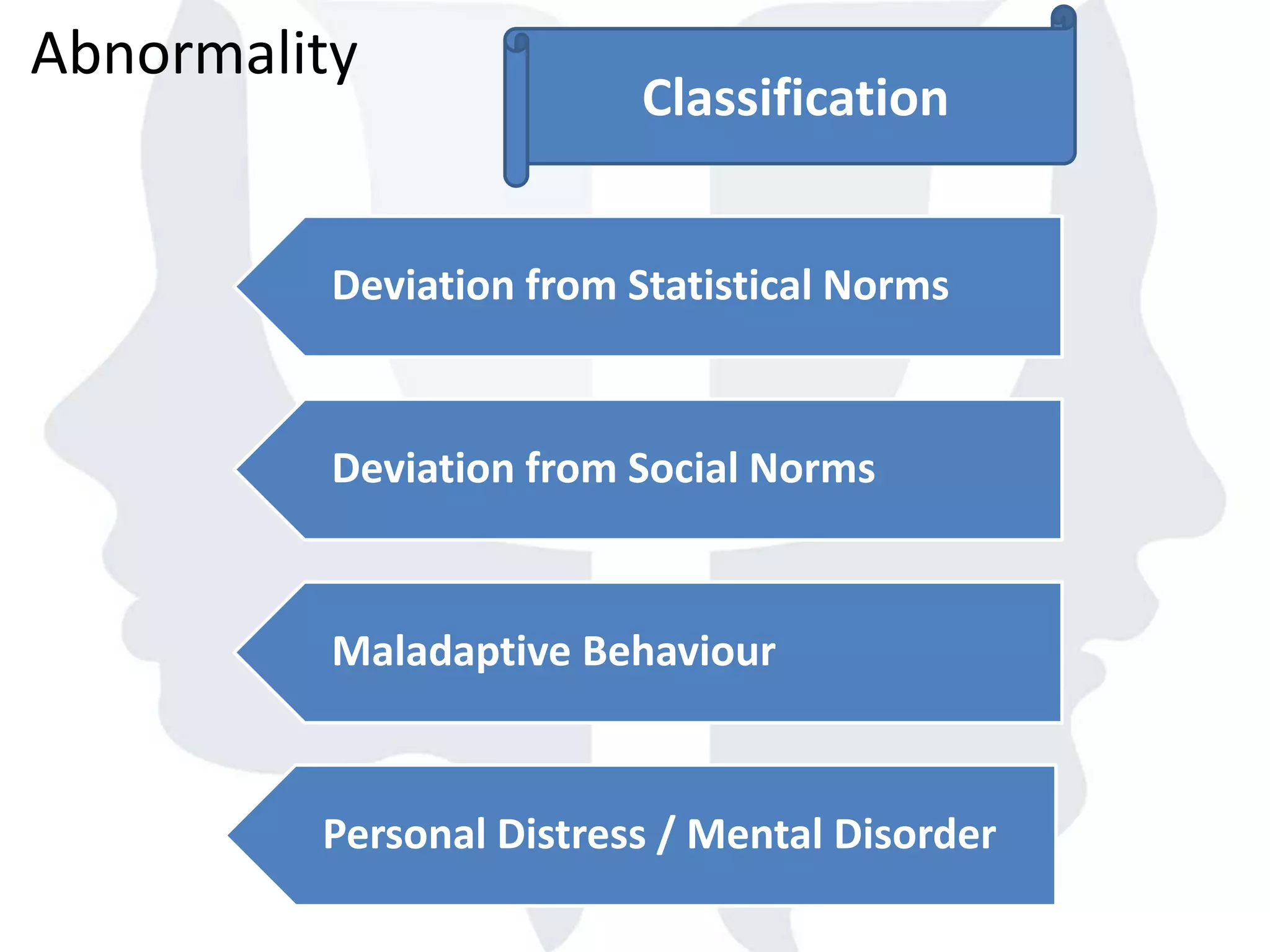
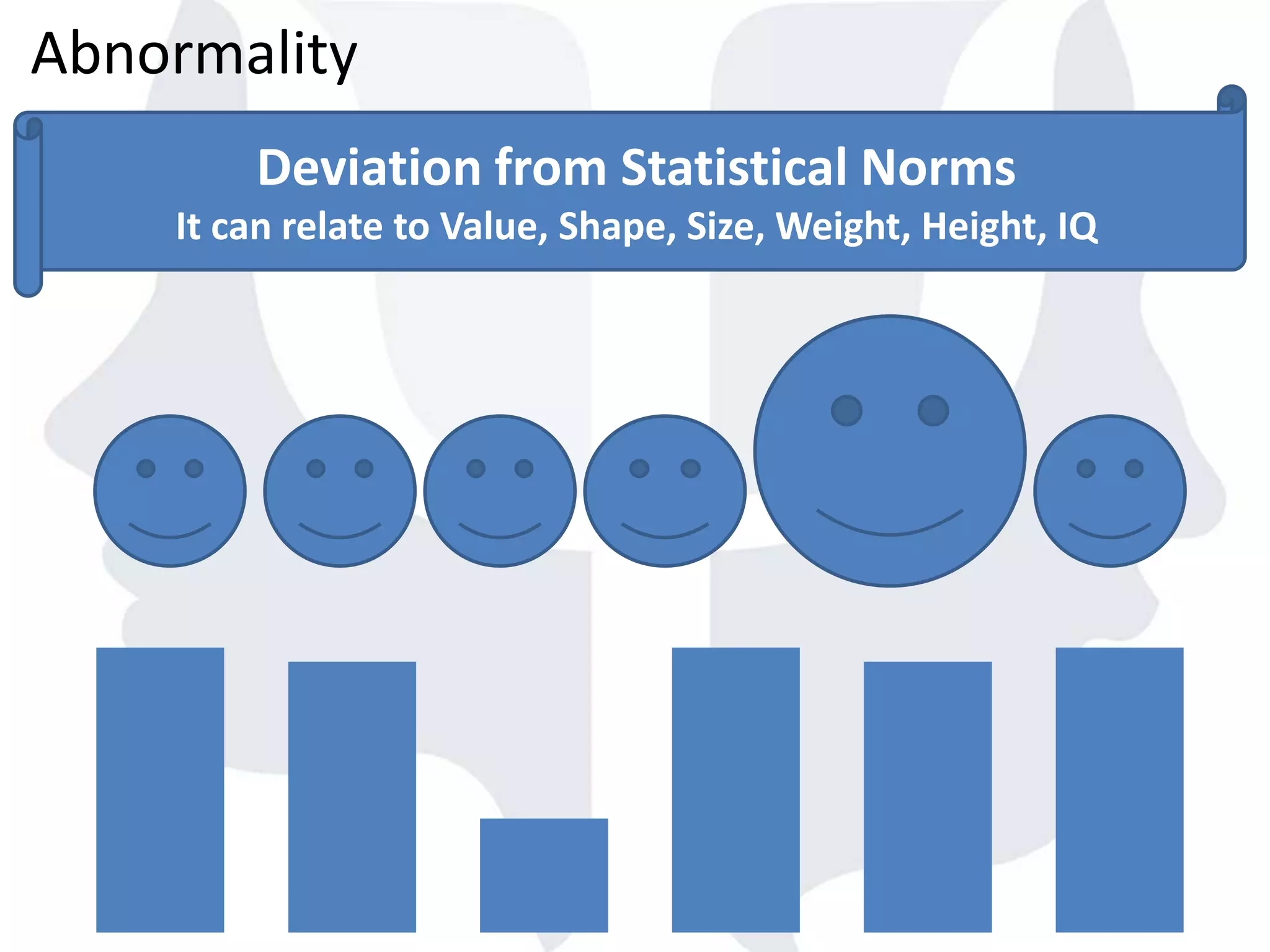
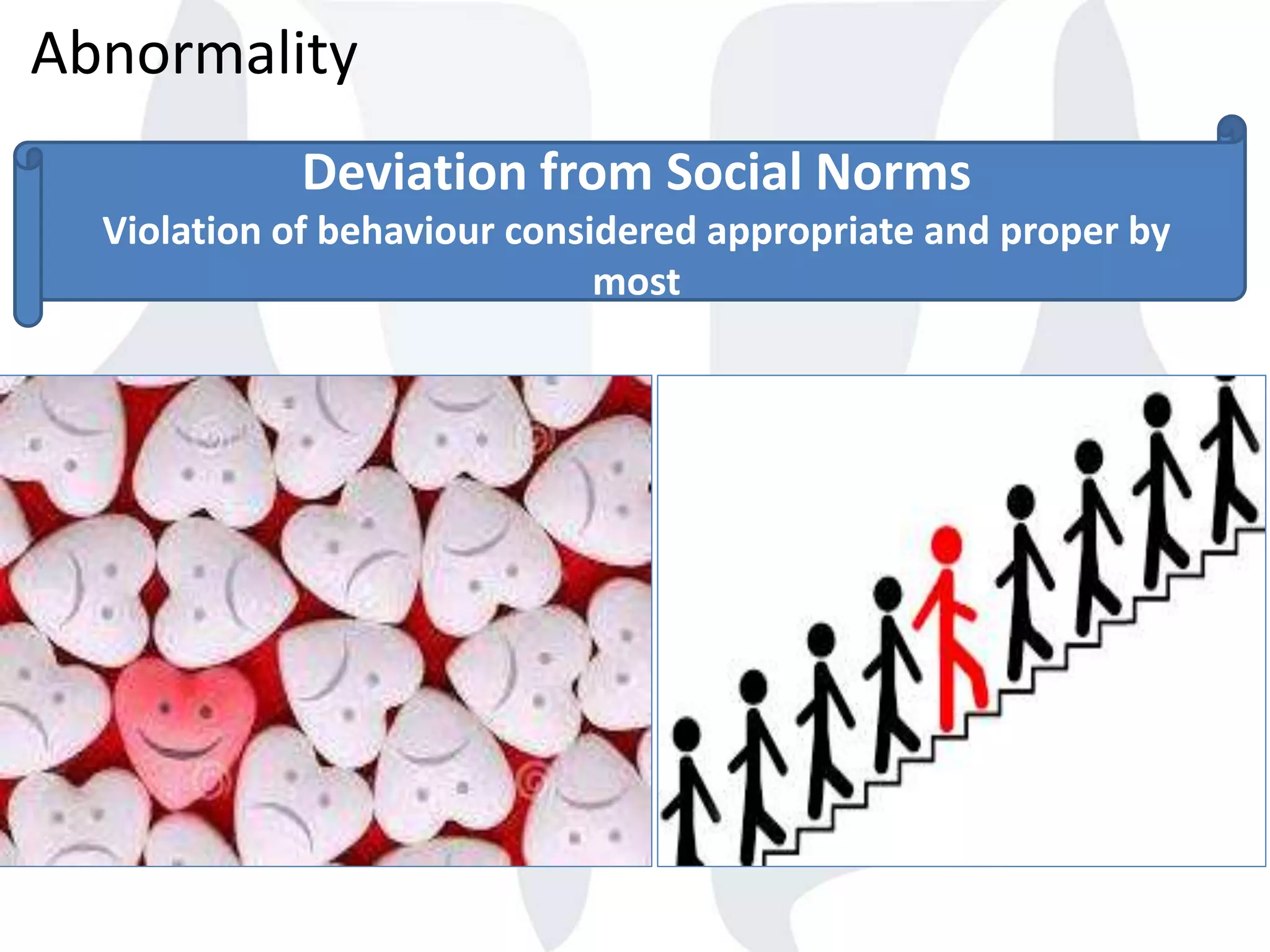
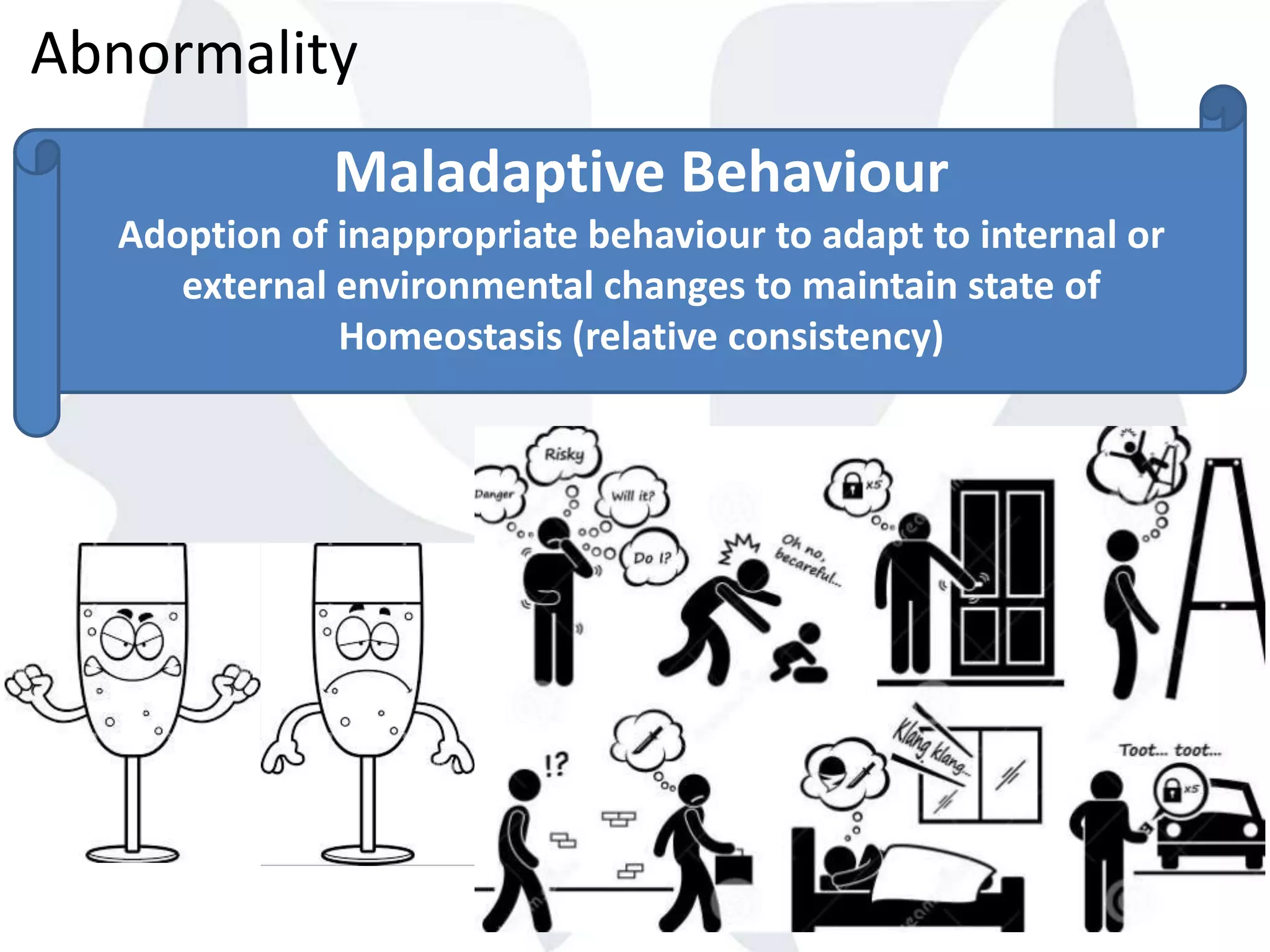
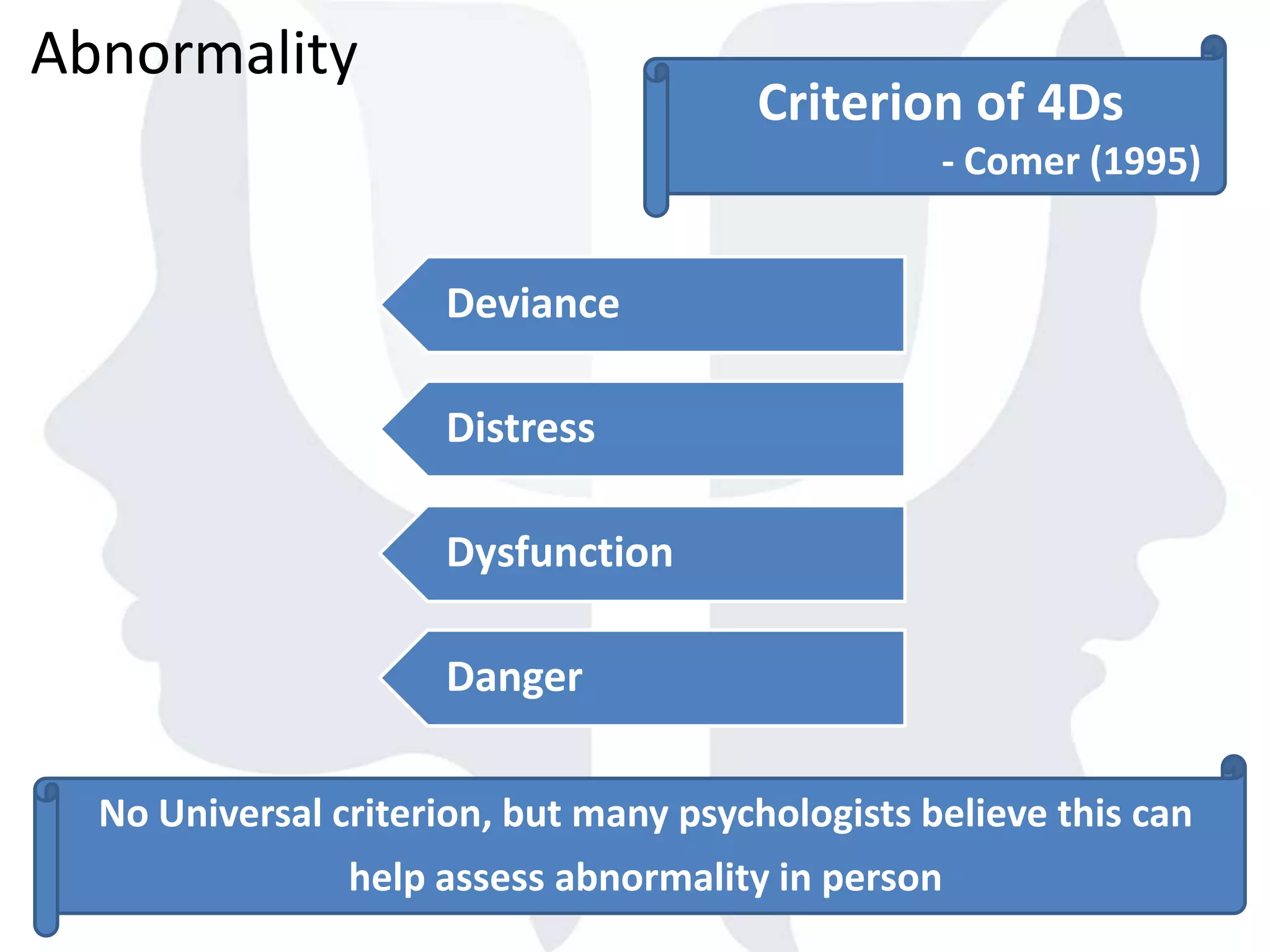
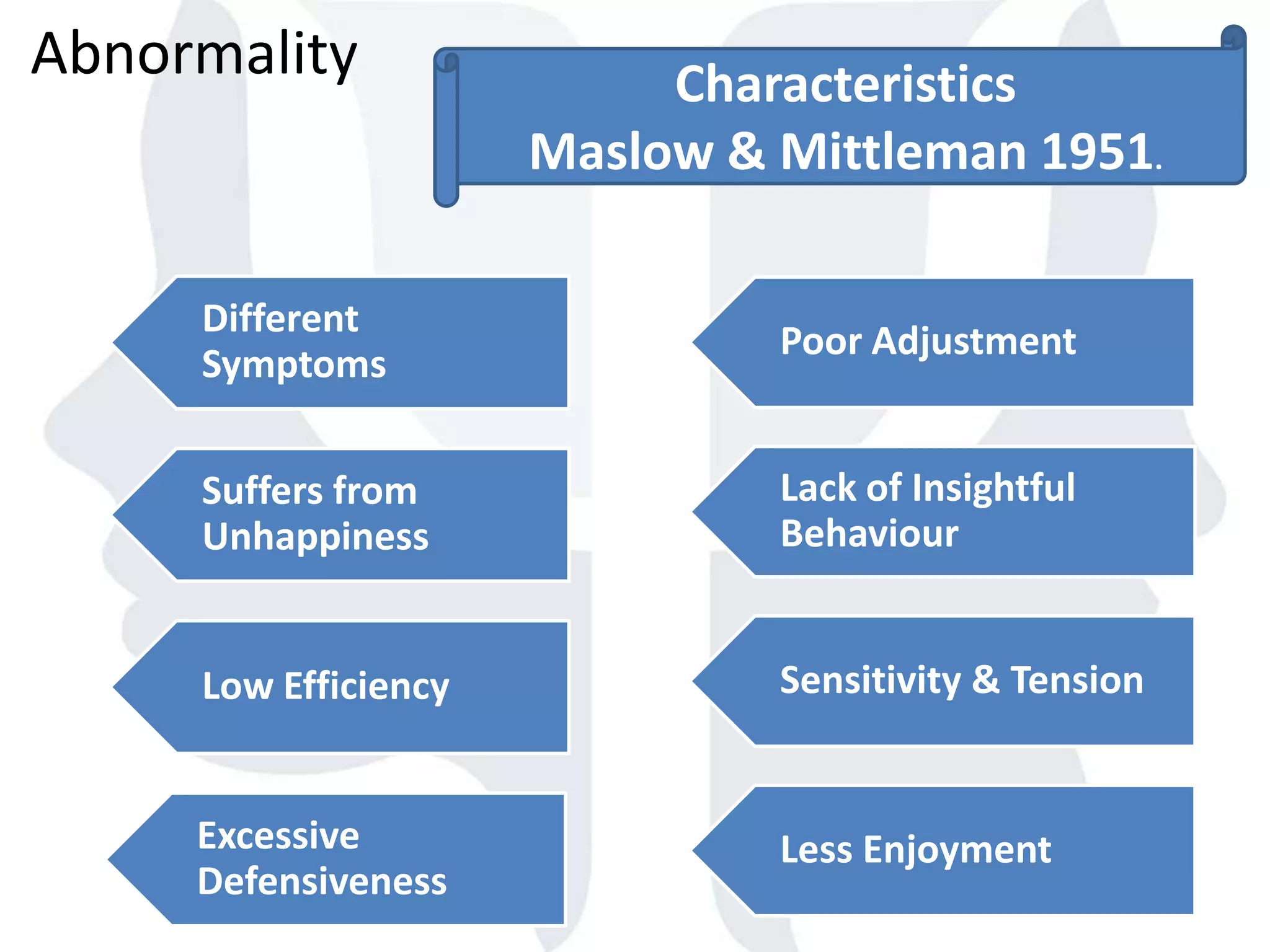
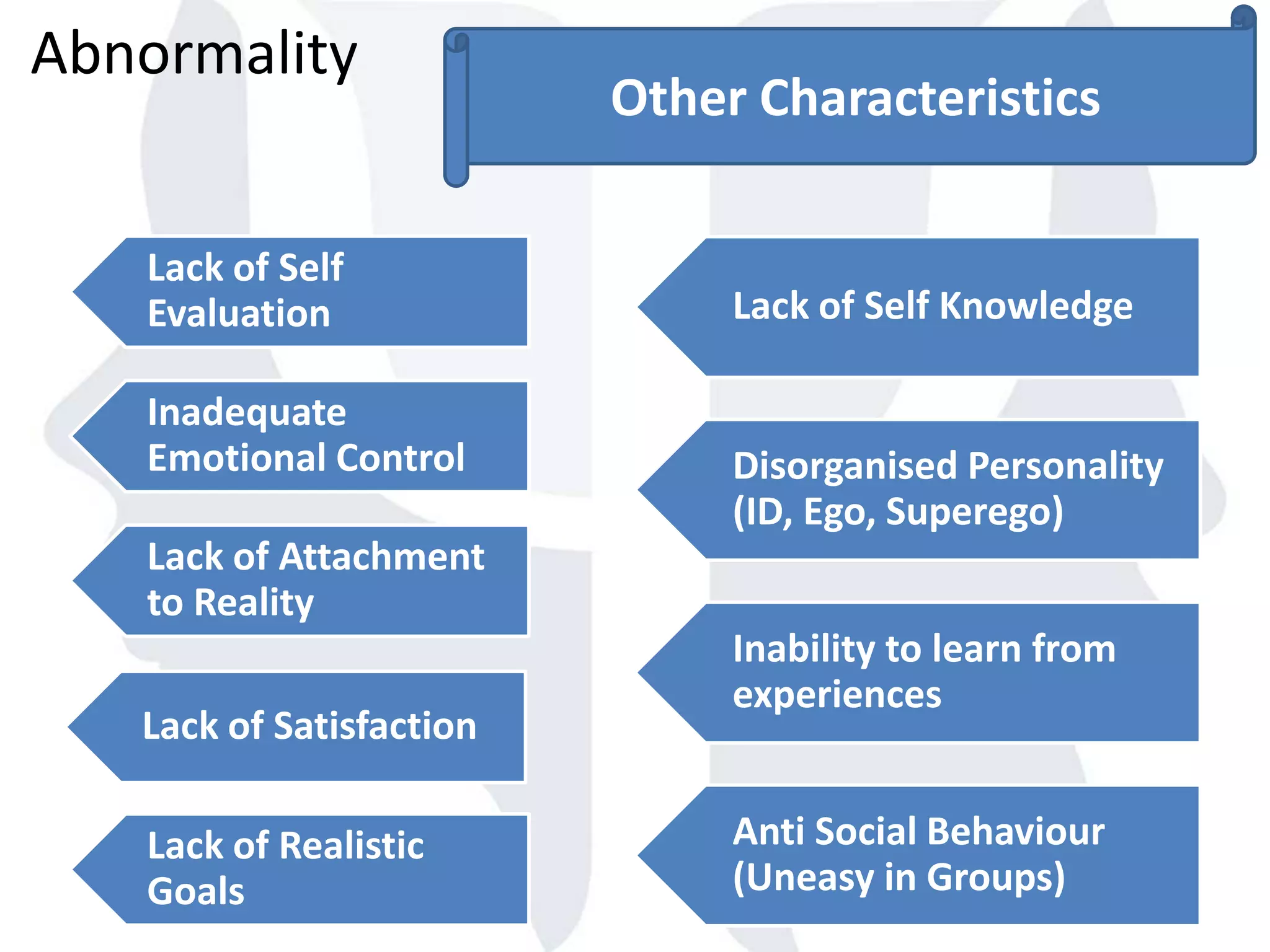
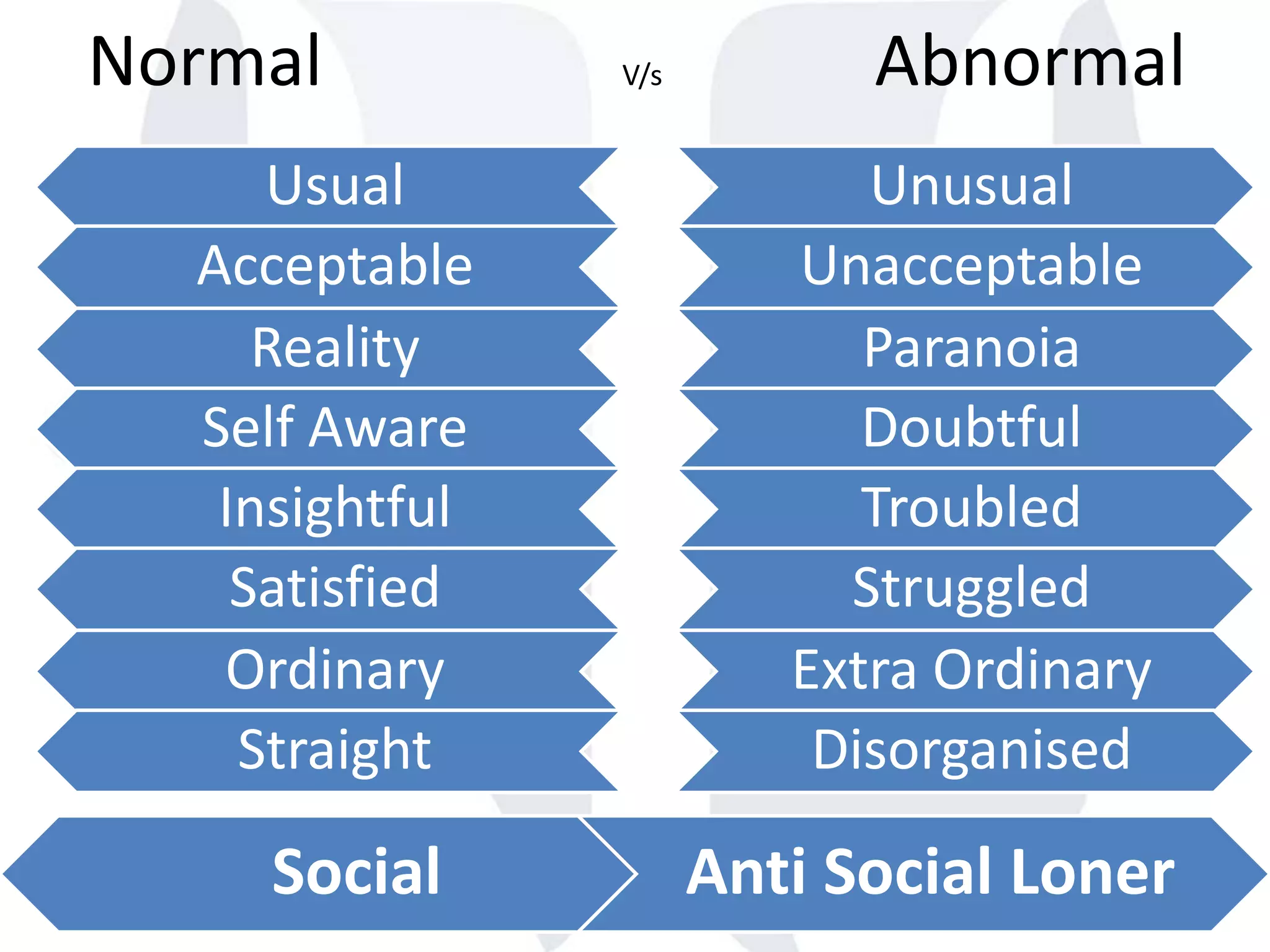
This document provides information about normality and abnormality in psychology. It defines normality as behaviors, traits, and mental well-being that conform to social and cultural standards. Abnormality is defined as behaviors or experiences that deviate from these standards in a way that causes personal distress or dysfunction. The document lists characteristics of normality, such as adequate self-evaluation and ability to learn from experiences. It also lists characteristics of abnormality, such as deviance from social norms, maladaptive behaviors, and traits like excessive defensiveness and lack of insight. The document compares normal and abnormal traits.