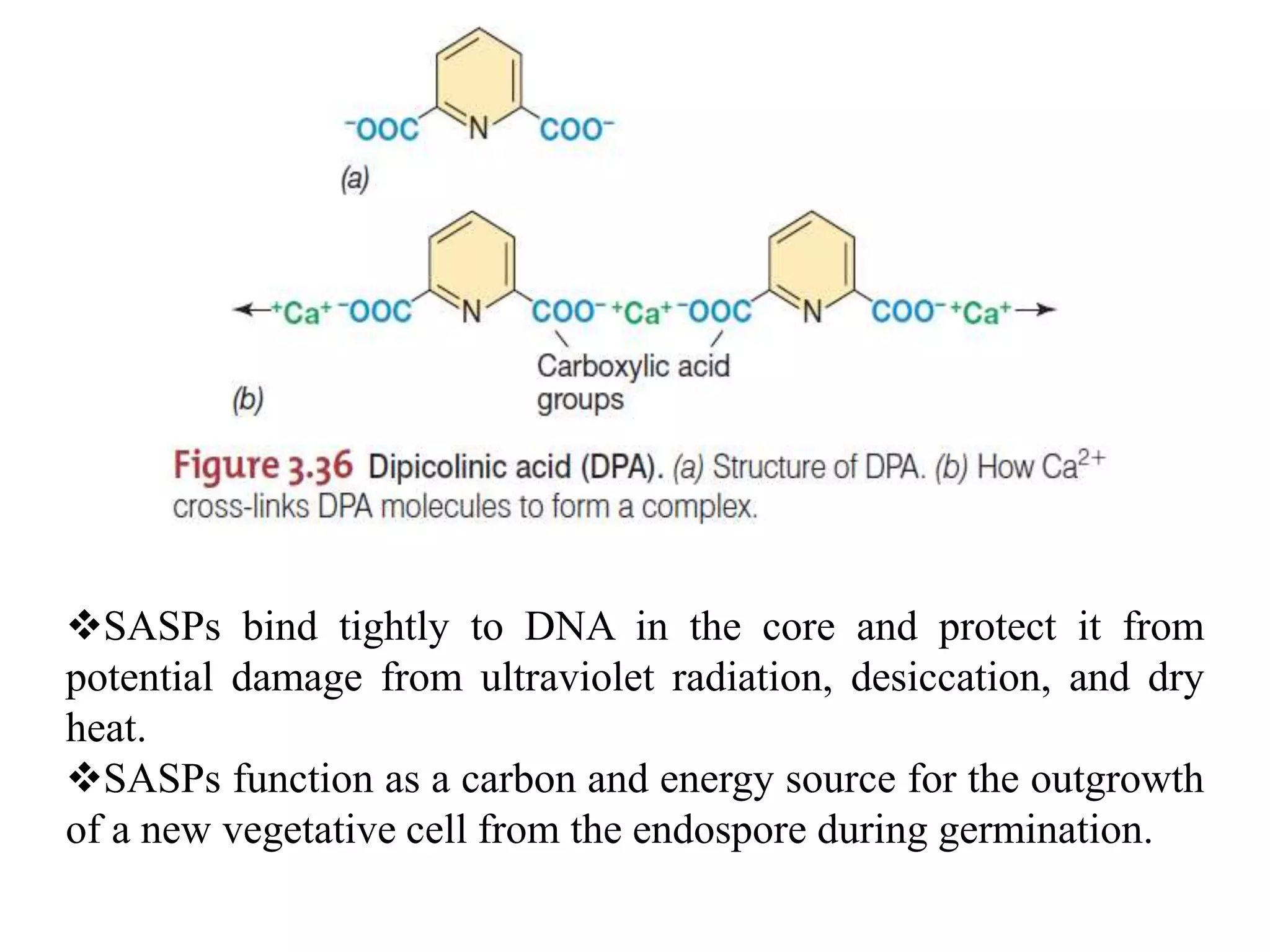
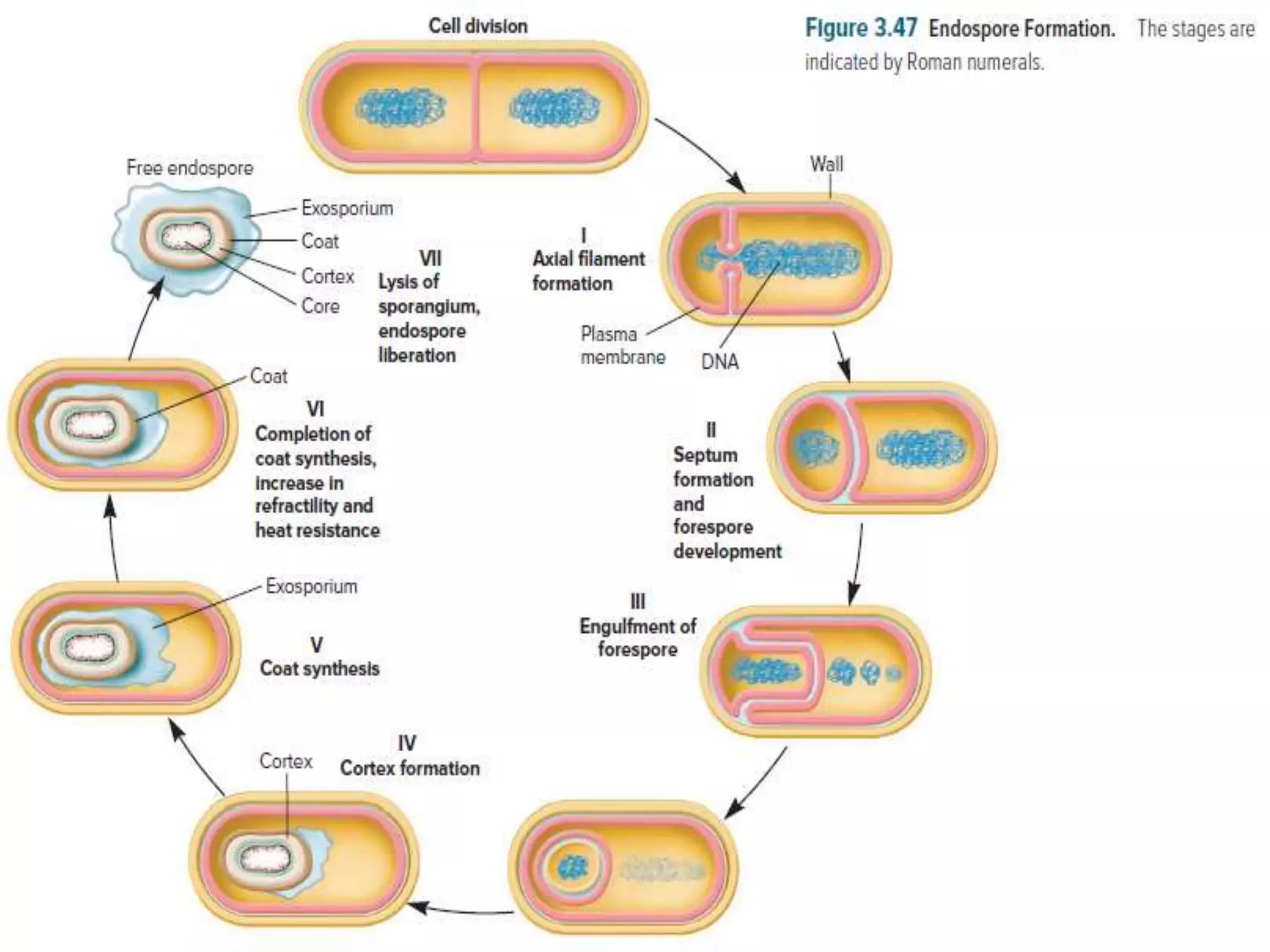
Bacterial endospores are highly durable, dehydrated structures formed by certain Firmicutes bacteria during times of nutrient stress. Endospores are formed inside the mother cell and consist of multiple protective layers, including an impermeable cortex and core containing dipicolinic acid and small acid-soluble proteins. This specialized structure allows endospores to survive extreme environmental conditions until nutrients become available again to trigger germination. Important pathogens like Clostridium botulinum and Bacillus anthracis are able to form resistant endospores, posing challenges for food safety and medicine.