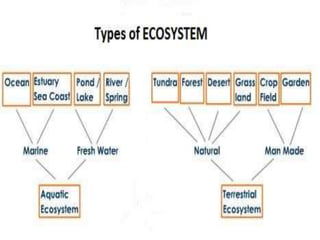
1. The document provides information about various types of ecosystems including terrestrial, aquatic, forest, grassland, desert, pond, lake, marine and ocean ecosystems.
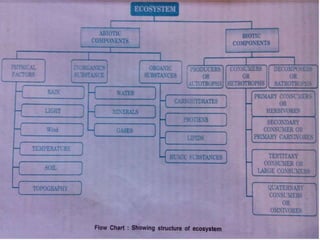
2. It describes the key components of an ecosystem as biotic factors (living organisms) and abiotic factors (non-living physical components).
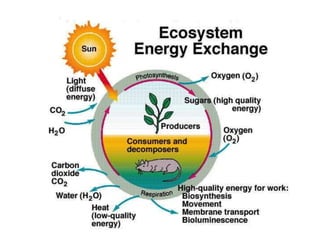
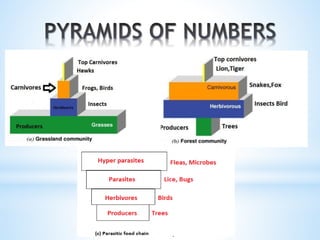
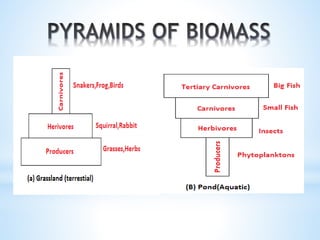
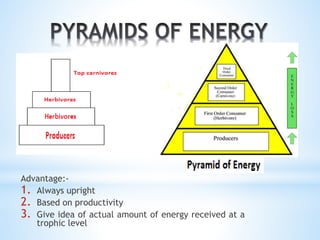
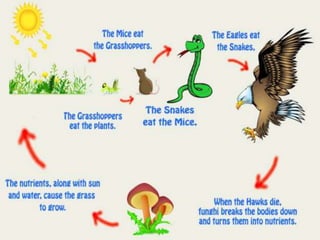
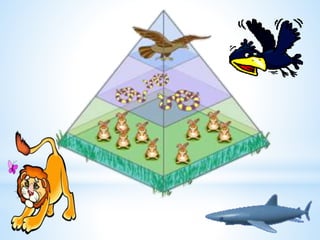
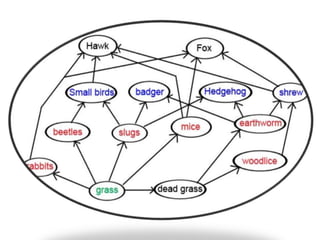
3. Energy flows through ecosystems via food chains and food webs with plants at the base converting solar energy to chemical energy which is then transferred between trophic levels.