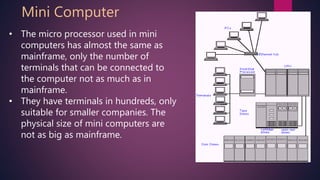
Digital computers can be classified into several types based on their size and capabilities. Supercomputers are the largest and most powerful, used for scientific applications. Mainframe computers are also very large and can handle vast amounts of data for large organizations. Mini computers have fewer terminals but more processing power than mainframes. Microcomputers include portable devices like laptops, tablets, and smartphones. Each type has differing processing speeds, memory capacities, and uses.