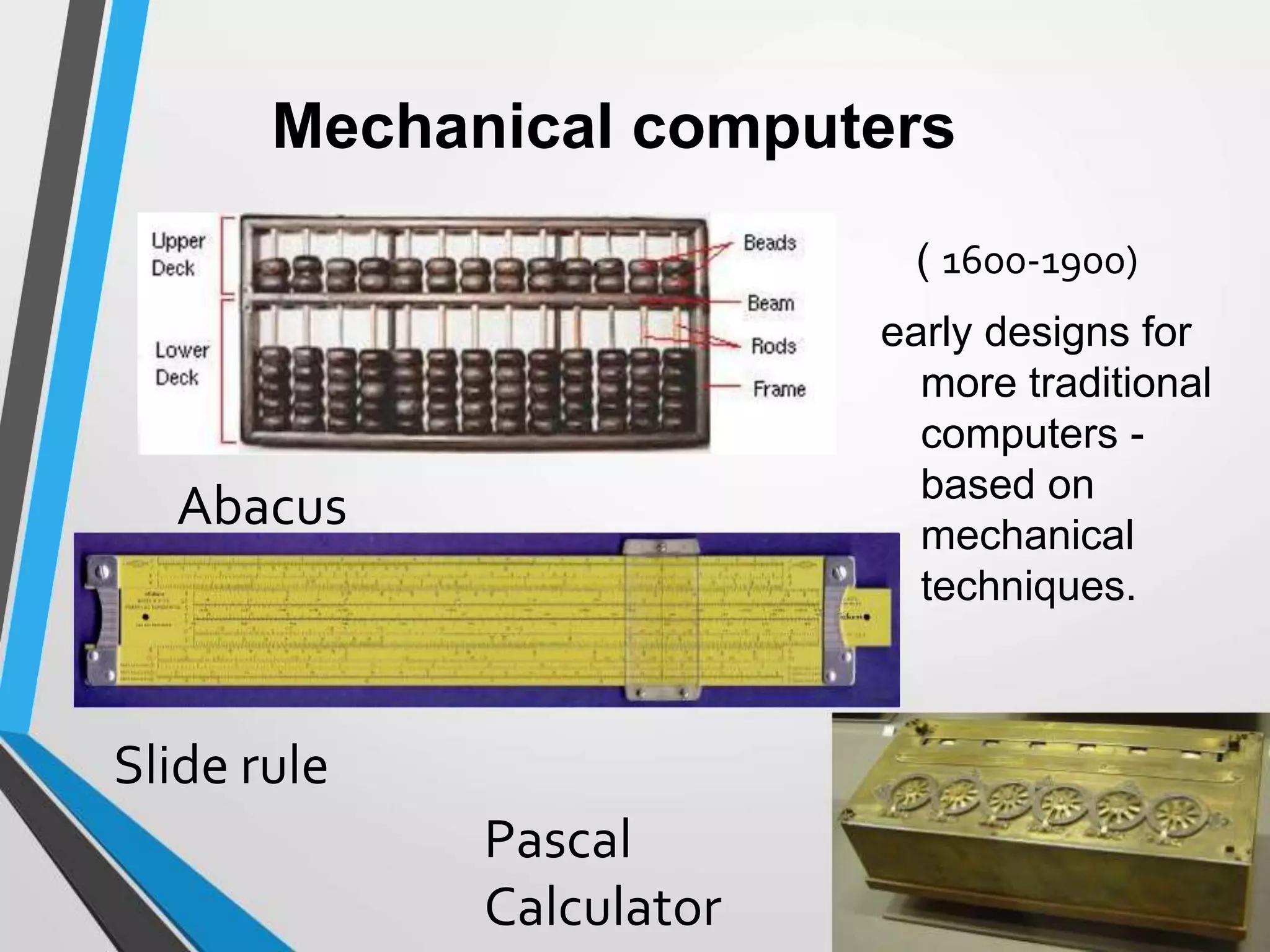
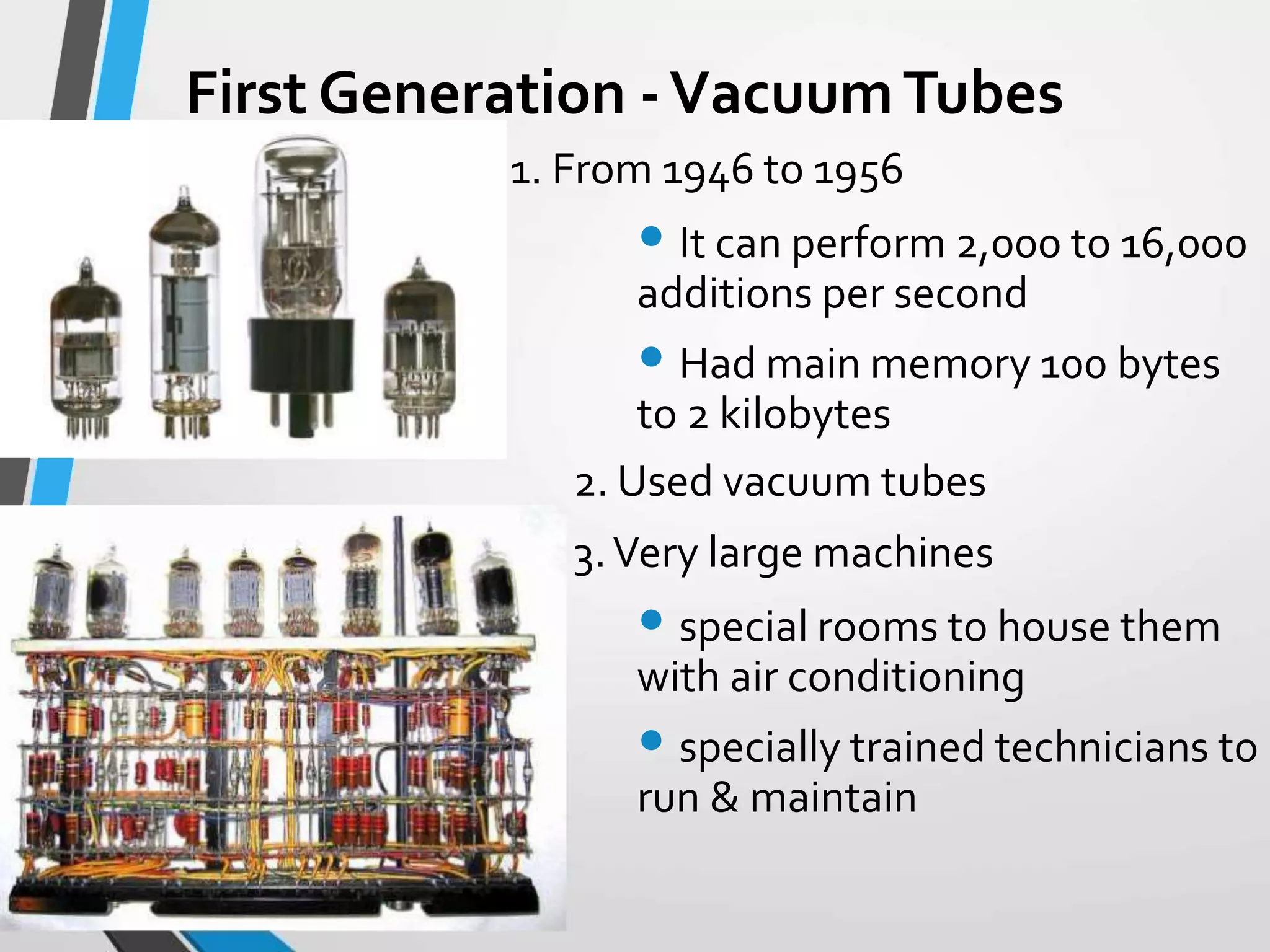
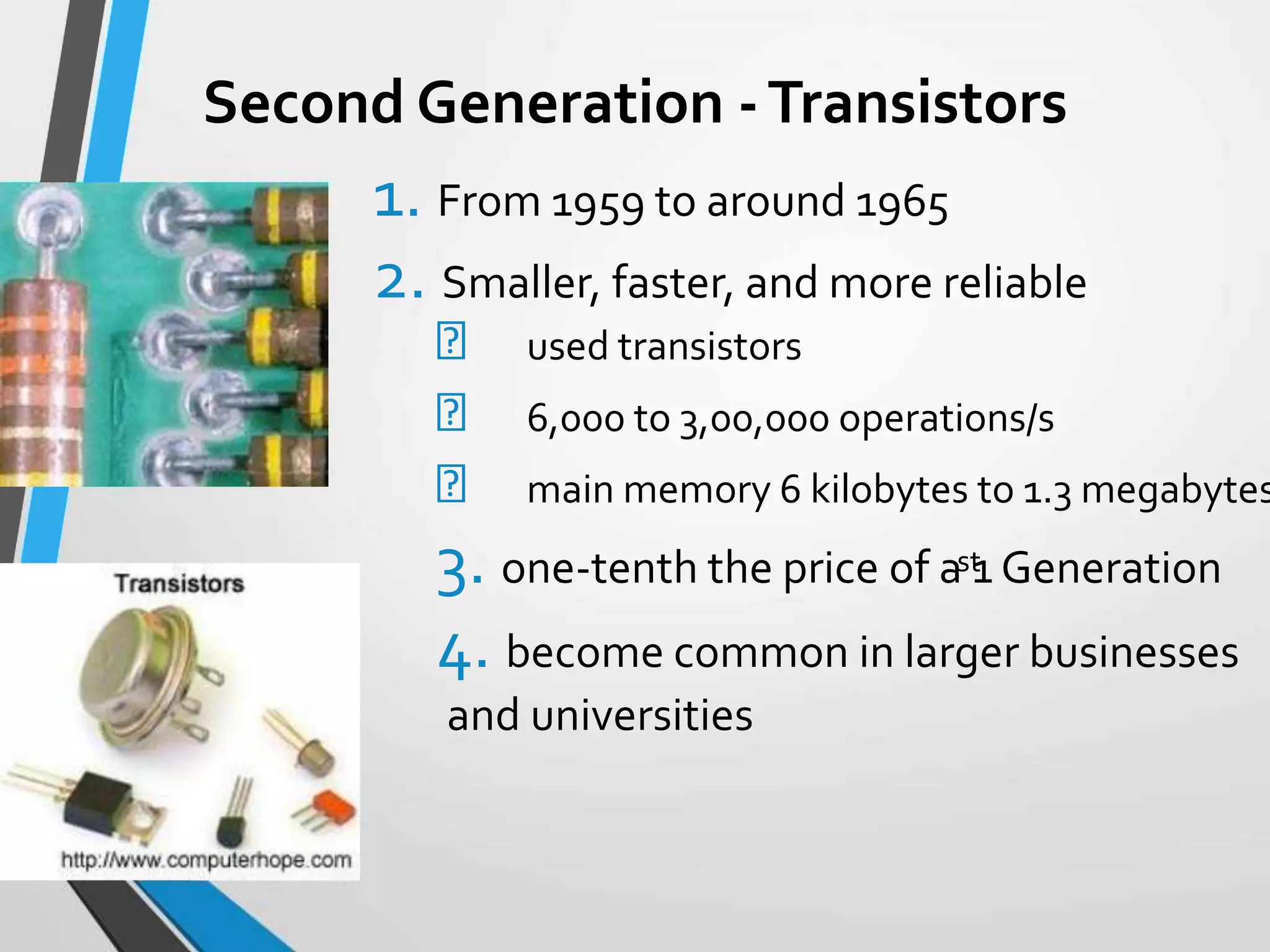
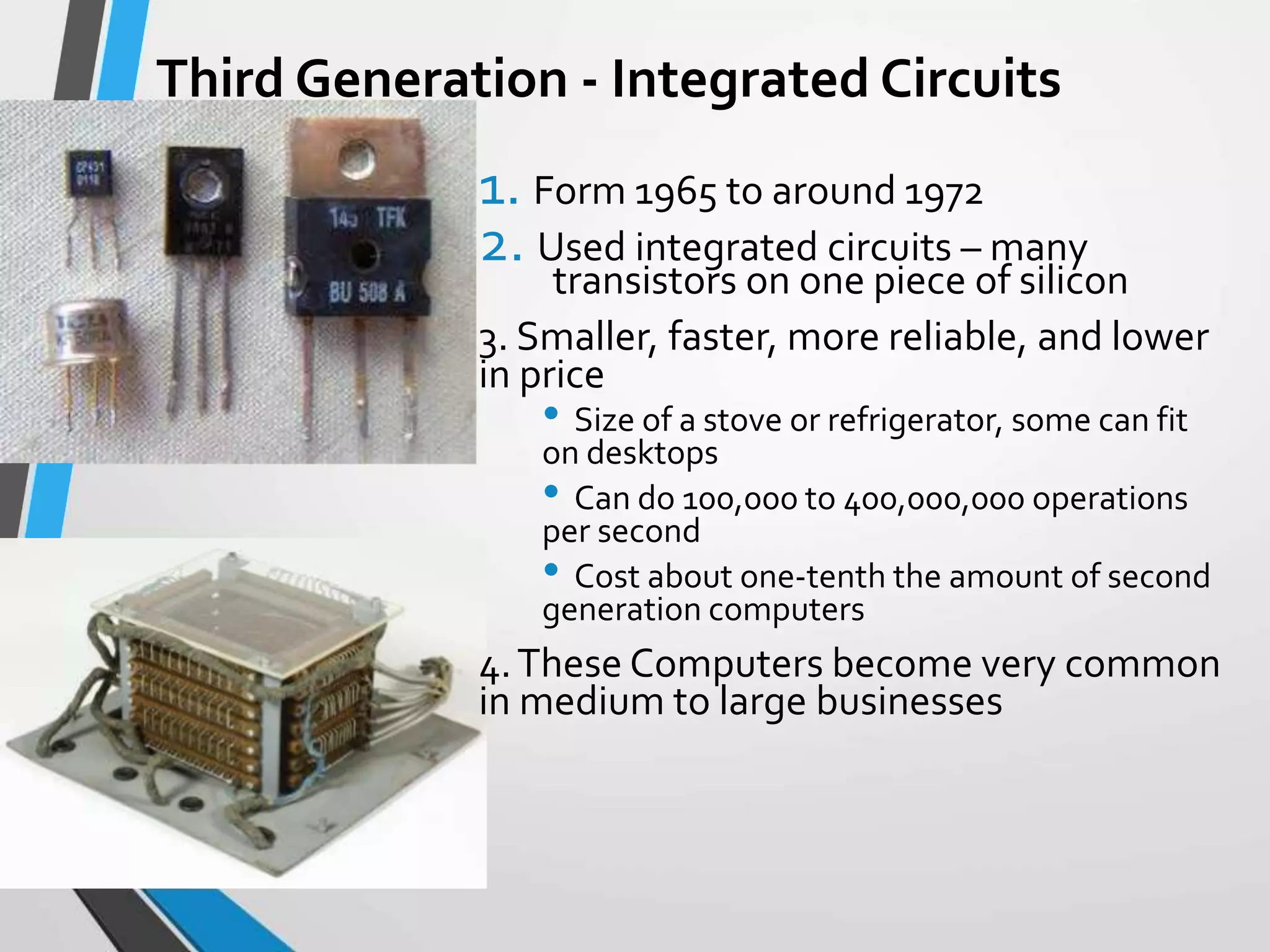
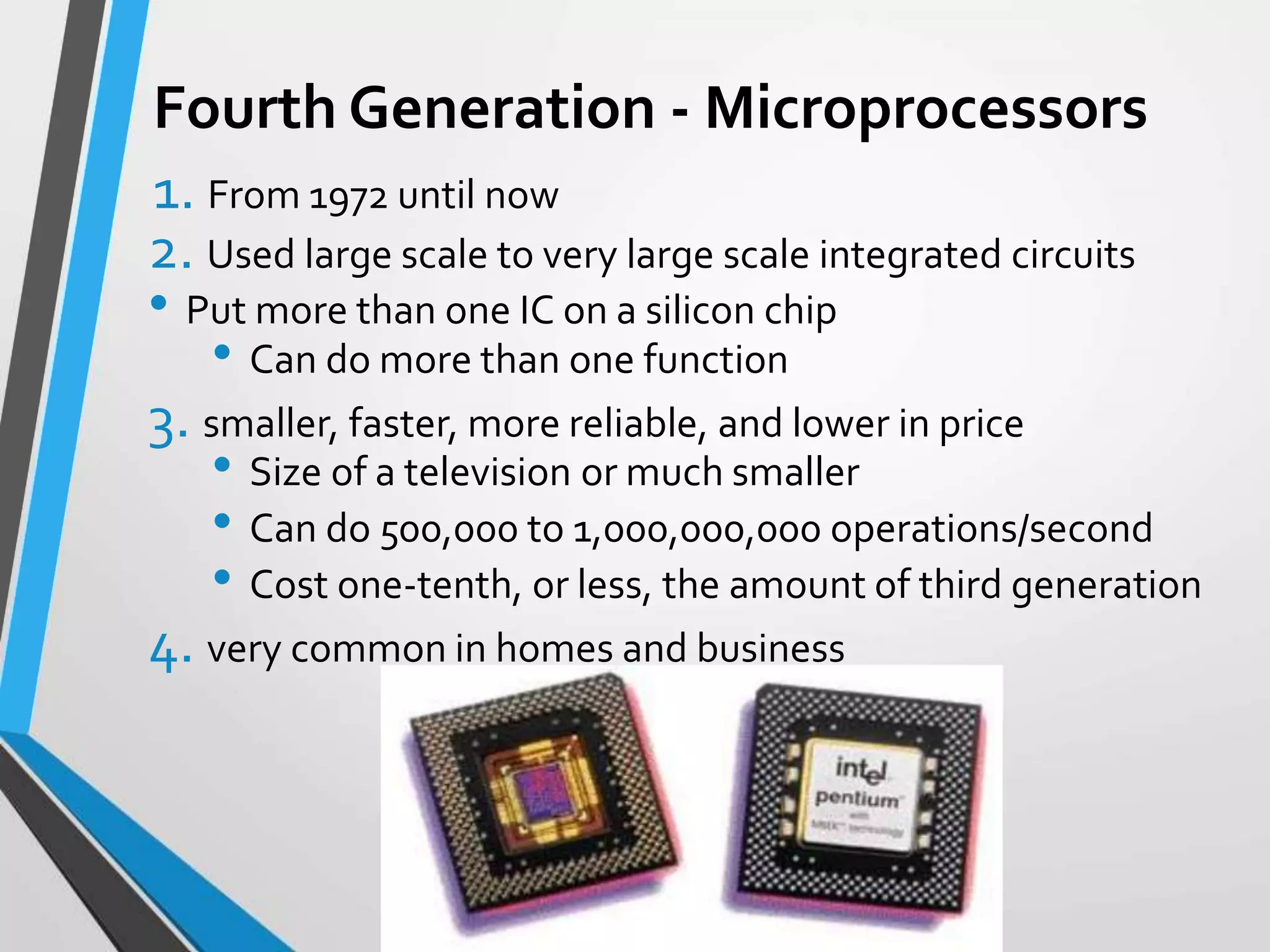
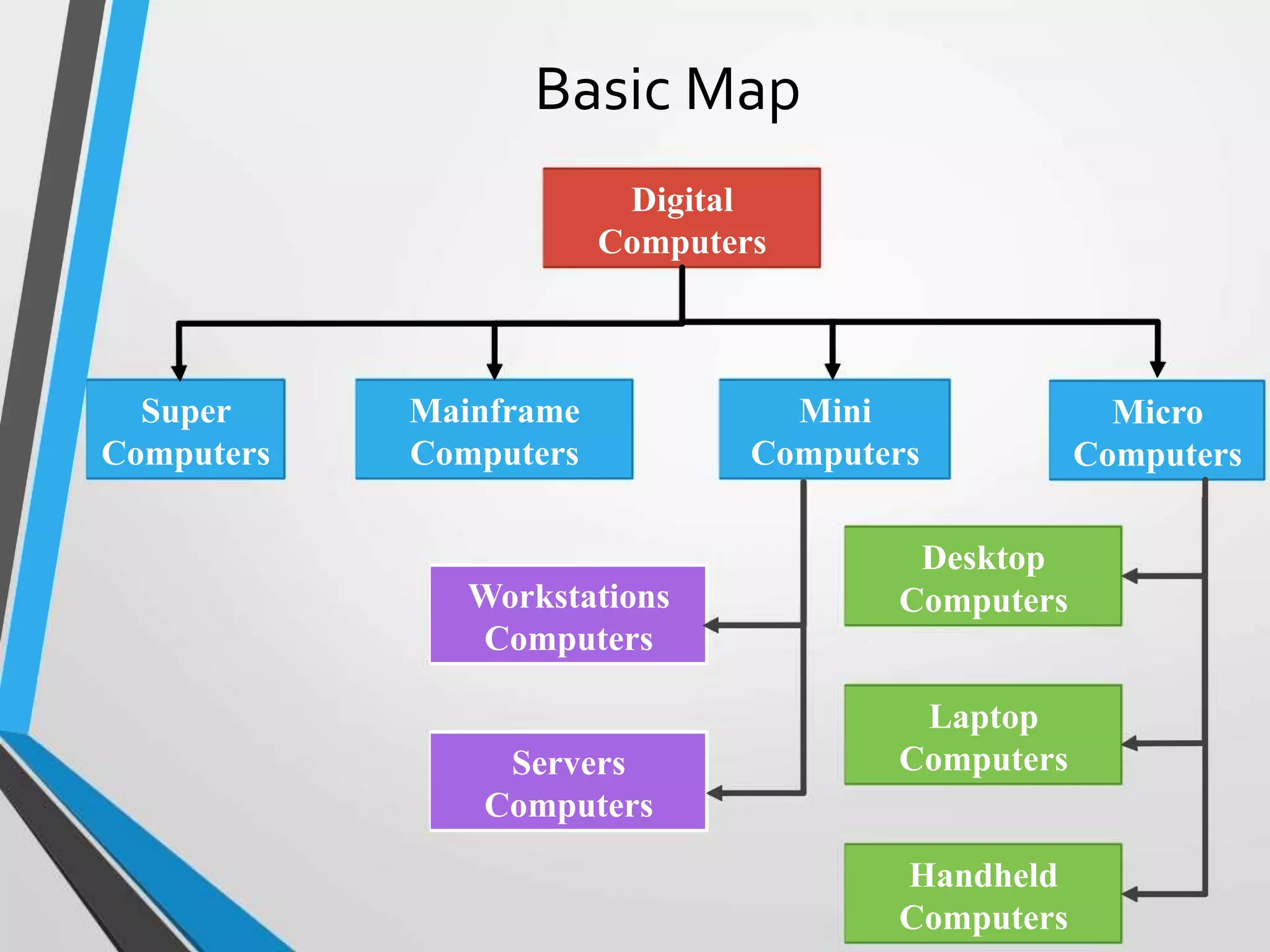
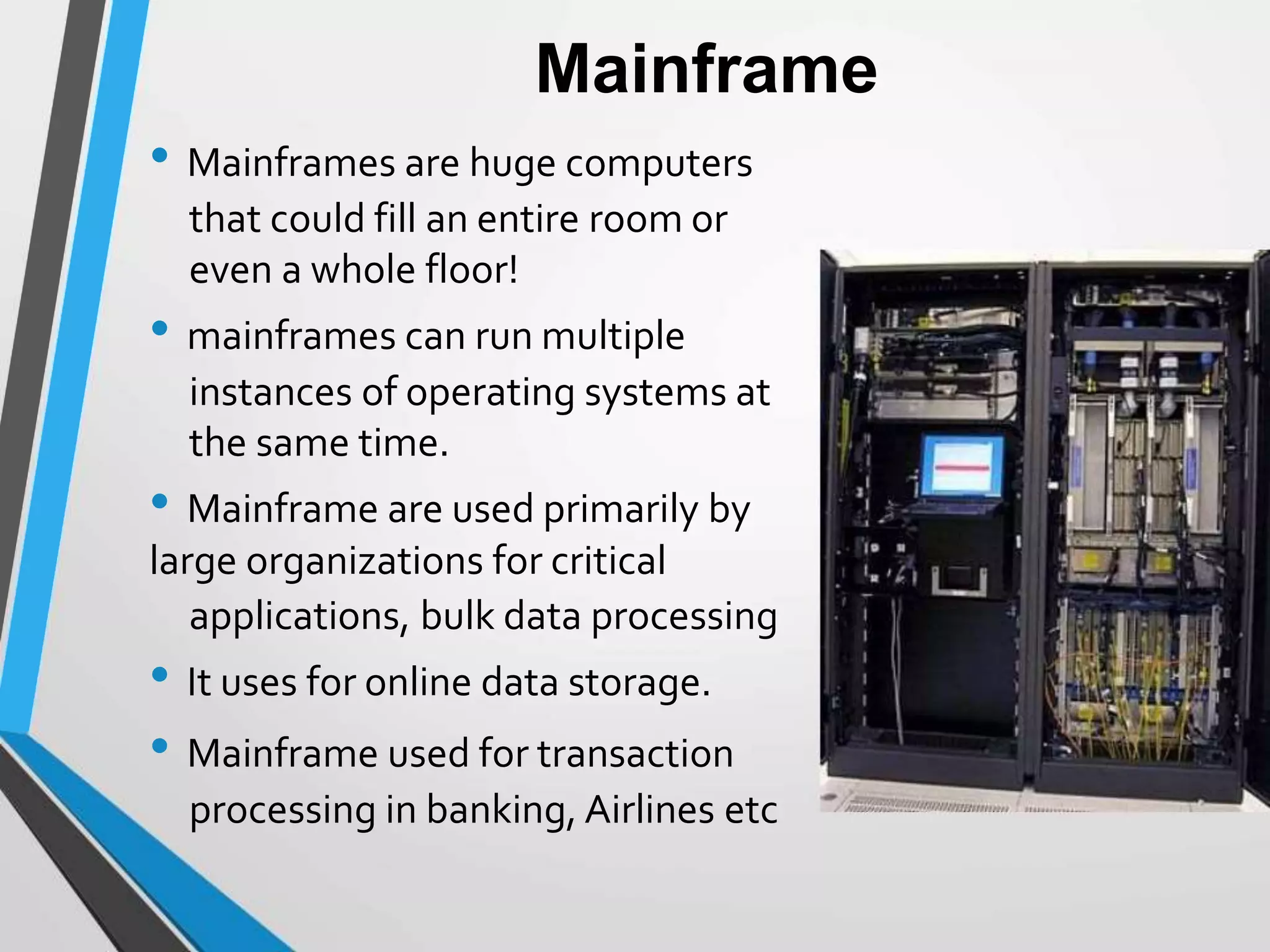
This document provides an introduction and history of computers, their applications, and types. It defines a computer as an electronic device that accepts input, processes data into information, produces output, and stores information. A user is someone who interacts with a computer. The history of computers is outlined in generations from mechanical computers in the 1600s to the current fourth generation of microprocessors. Computers are classified as analog, which represent continuous values, or digital, which use binary numbers. Types include supercomputers, mainframes, workstations, servers, desktops, laptops, and palmtops/handhelds. Each type has distinct features regarding size, power, and common applications.