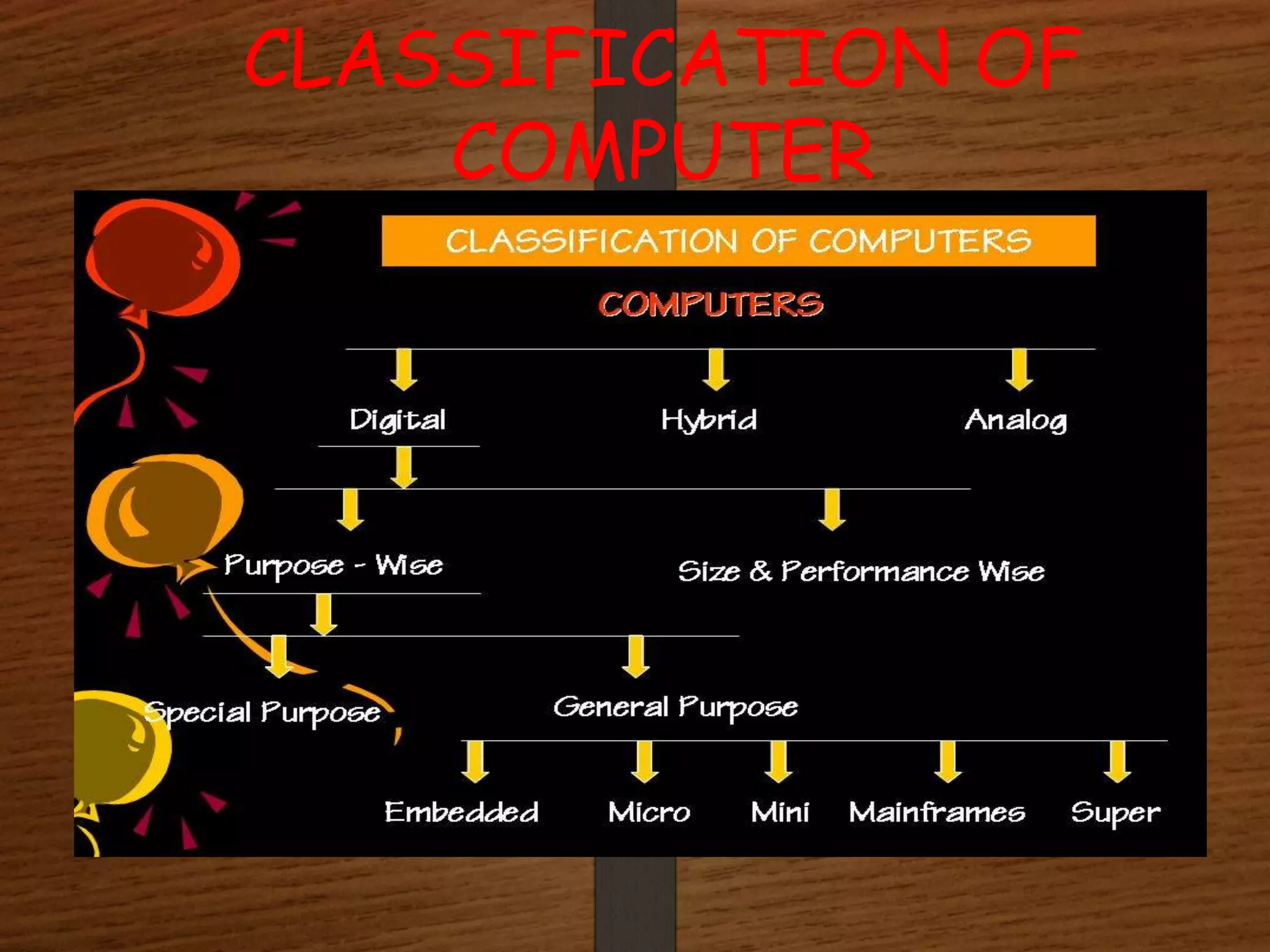
This document classifies computers into four main types: analog computers, digital computers, hybrid computers, and micro computers. It provides details on each type, including that analog computers represent variables as physical quantities and solve problems through related circuits, digital computers represent quantities with digits and perform calculations, hybrid computers combine analog and digital characteristics, and micro computers are the smallest with all circuitry on a chip. It also mentions super computers and mini computers.