Types of computer on the basis of sizes:
Mainframe Computer
Super Computer
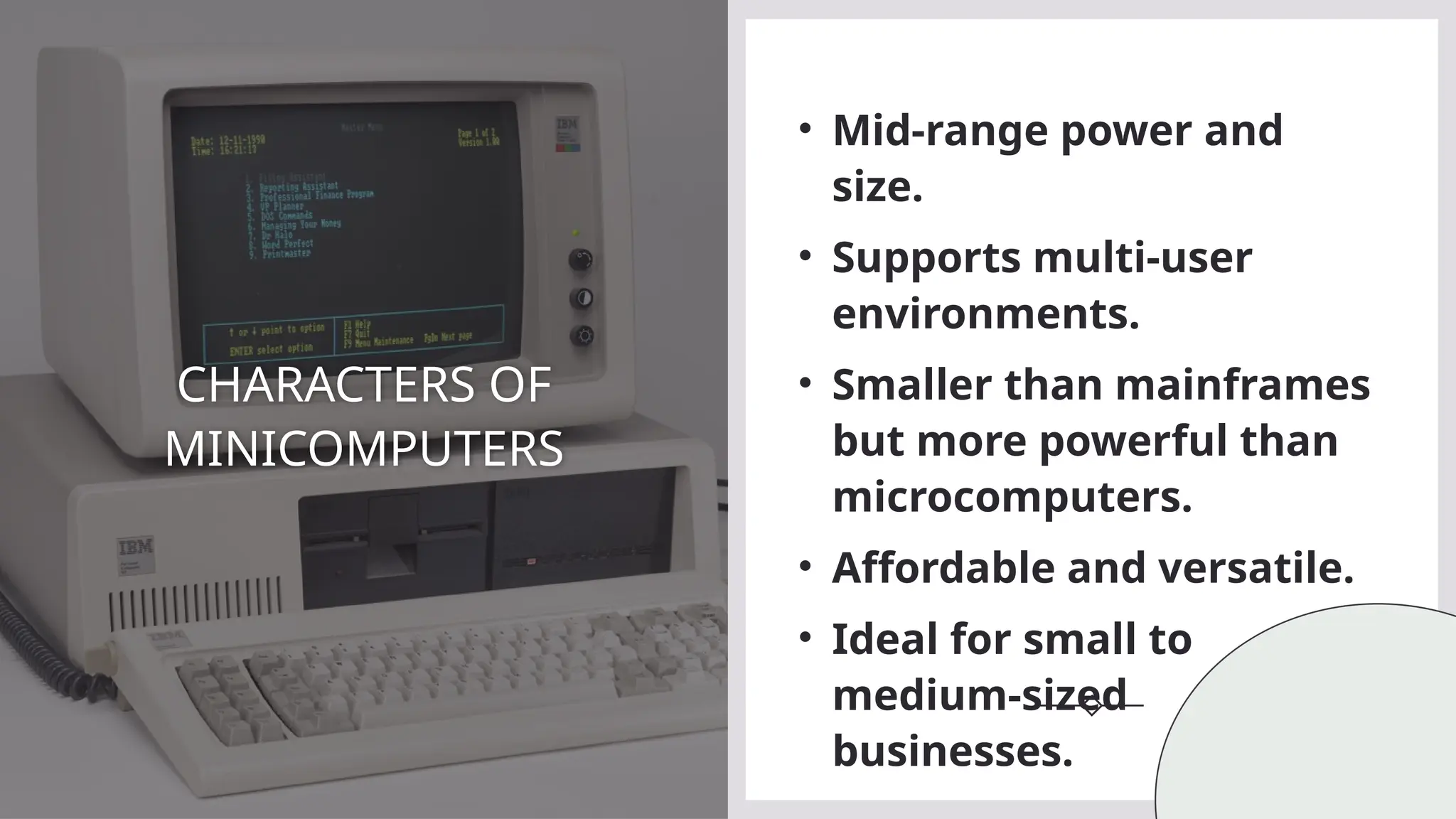
Mini Computer
Micro Computer
Computers can be classified based on size into four main types:
1. Supercomputers – These are the most powerful and fastest computers, used for complex tasks like weather forecasting, scientific simulations, and cryptography.
2. Mainframe Computers – Large and powerful, mainframes handle massive data processing for banks, government agencies, and large enterprises.
3. Minicomputers – Also called mid-range computers, they are smaller than mainframes but still serve multiple users, often used in business and research.
4. Microcomputers – Also known as personal computers (PCs), these are the most common, including desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones.
Each type serves different purposes, from high-performance computing to personal use.