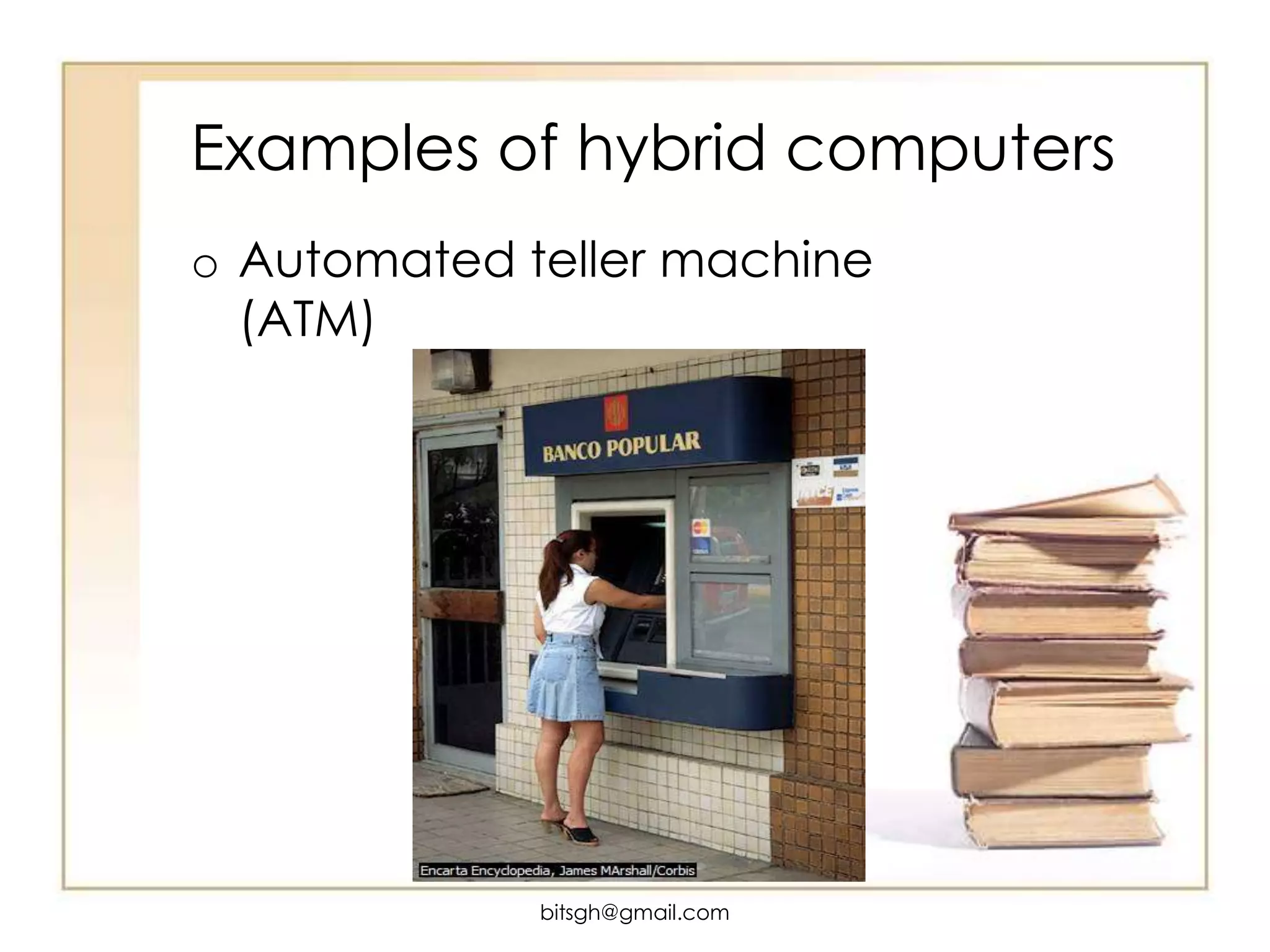
There are three main ways to classify computers: by type, by purpose, and by size/capacity. By type includes digital, analogue, and hybrid computers. Digital computers represent data using binary digits while analogue computers use continuous signals. Hybrid computers have elements of both. By purpose includes special purpose computers designed for specific tasks and general purpose computers with diverse applications. By size/capacity refers to a computer's processing power and includes macro, mini, and micro categories. Macro computers are the largest and most powerful while micro computers are the smallest, personal devices.