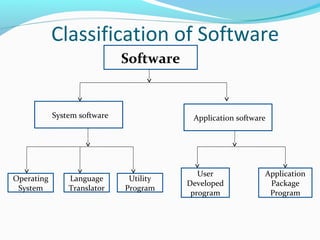
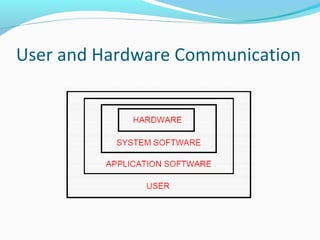
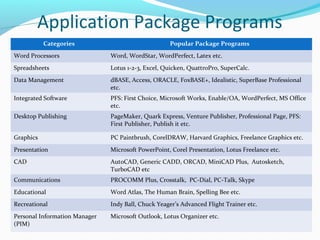
The document provides an overview of computer software, detailing its classifications into system software and application software, and the different types within those categories, such as operating systems and utility programs. It also discusses application software, distinguishing between horizontal and vertical applications, and introduces the concepts of commercial, shareware, freeware, and firmware. Additionally, it mentions popular application package programs and their advantages for users.