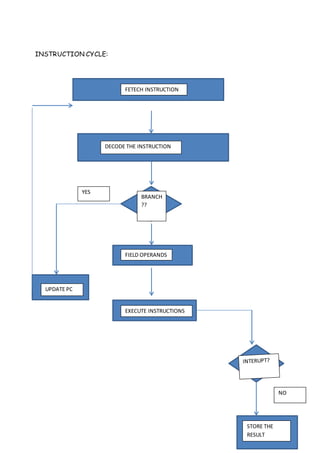
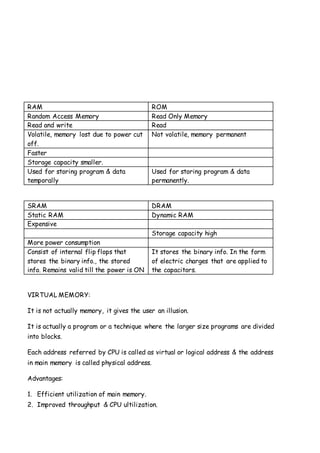
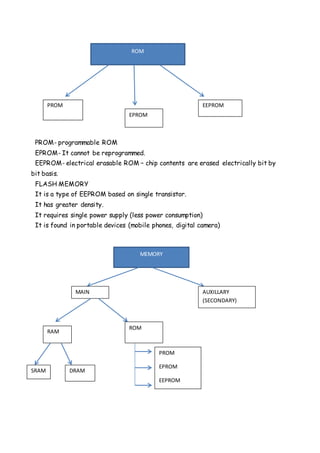
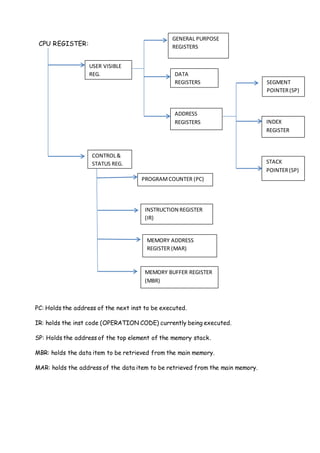
This document discusses computer organization and architecture. It defines key concepts like the central processing unit (CPU), bus, cache memory, registers, memory, and interrupts. The CPU fetches and executes instructions, and processes data with functions like fetching instructions, interpreting instructions, fetching and processing data, and writing results. The document also compares characteristics of CISC and RISC architectures.