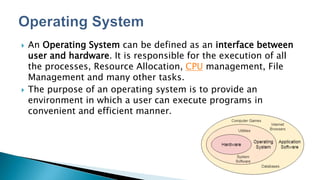
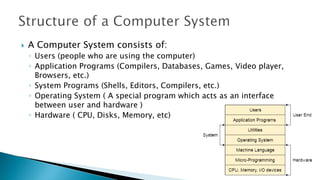
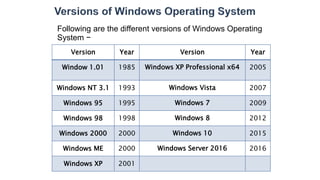
This lecture discusses operating systems. It defines an operating system as an interface between users and hardware that is responsible for executing processes, allocating resources, managing the CPU and files. It explains that an operating system provides an environment for users to run programs conveniently and efficiently. Major operating systems discussed include DOS, Windows, and Unix. Key functions of operating systems are also outlined such as memory management, process execution, file management, and interfacing with hardware.