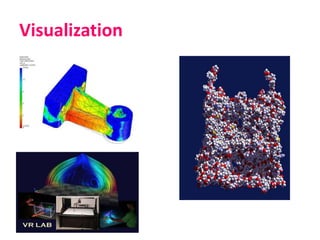
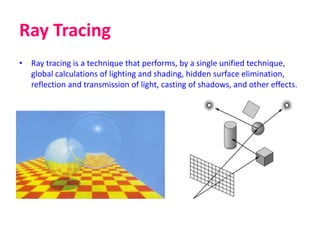
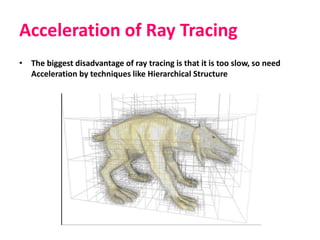
The document discusses the importance of computer graphics across various fields such as movies, games, and architecture, emphasizing the role of rendering in visualizing models into images. Key concepts in rendering include OpenGL, lighting, ray tracing, texture, shadows, and radiosity, which contribute to creating realistic graphics. Additionally, it highlights advanced research topics in rendering, computer animation, and geometry.