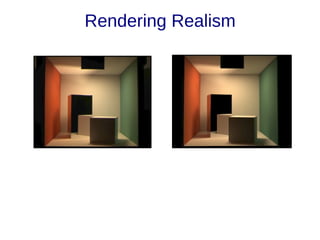
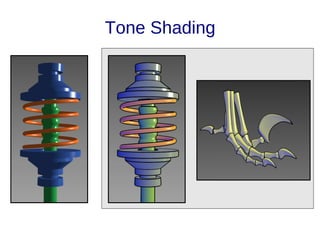
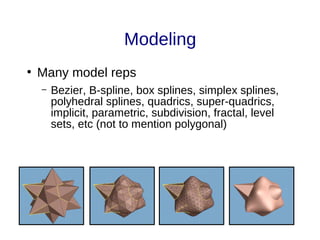
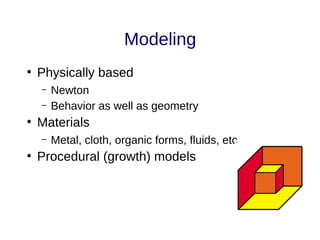
The document discusses the fundamentals and driving forces behind computer graphics, including its applications in the movie and game industries, medical imaging, and computer-aided design. It highlights advancements in hardware, rendering techniques, and the need for improved interaction methods. Key areas explored are modeling, different rendering methods, and their implications for various industries.