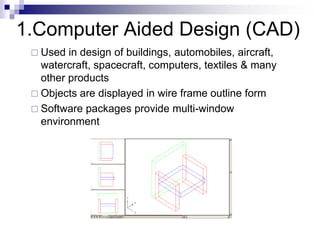
Computer graphics involves the creation and manipulation of images through modeling and rendering. It has applications in computer-aided design, presentations, computer art, entertainment like animation and games, education and training through simulations, communication, image processing, and graphical user interfaces. Common graphics packages provide functions for 2D drawing and access to graphics standards.