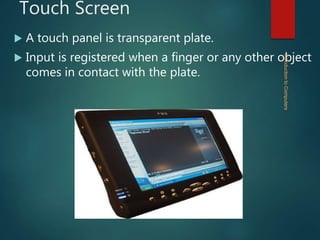
Peripheral devices that allow communication between the computer and outside world are called input/output devices. Input devices supply data and programs to the computer and include keyboards, mice, scanners, microphones. Output devices allow the computer to communicate information to users and include printers, monitors, speakers. Common input devices described are keyboards, mice, scanners, microphones. Common output devices described are printers, monitors, and speakers.