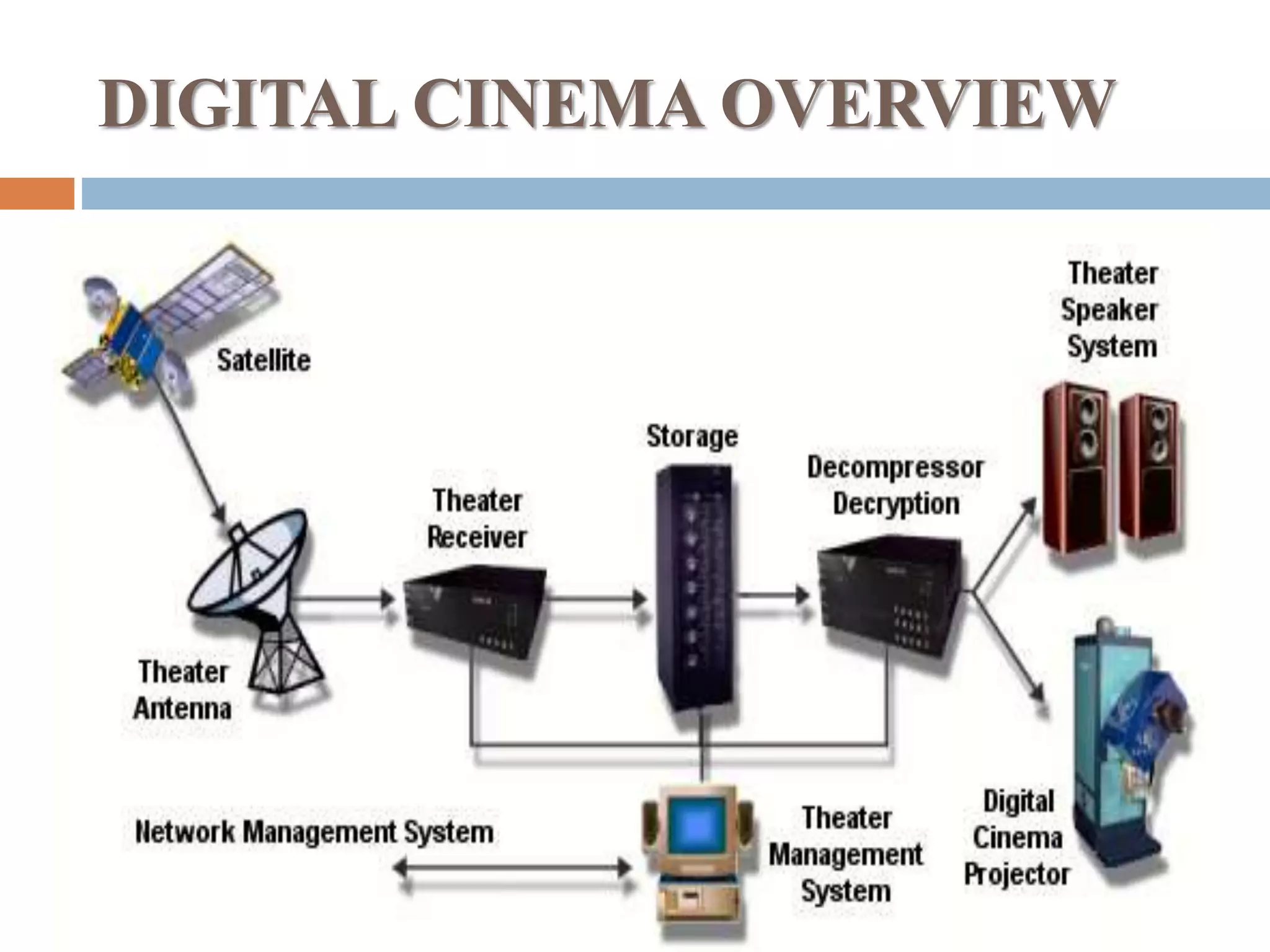
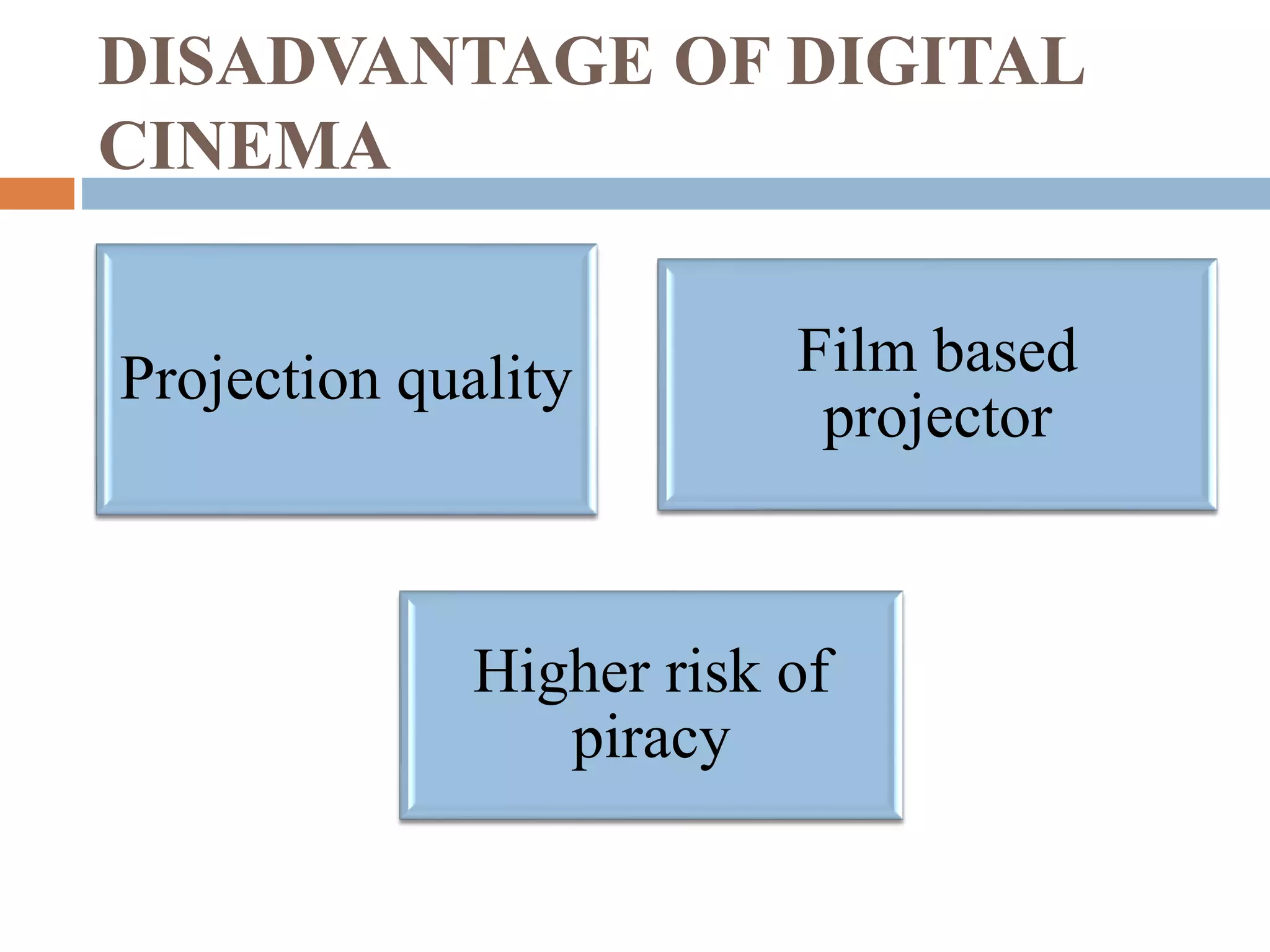
The document provides a comprehensive overview of digital cinema, discussing its history, components, advantages, disadvantages, and future scope. It highlights key developments in digital cinema from its inception in 1999 to the expected prevalence of digital screens by 2012. Various types of digital cinema, including 2D, 3D, 4D, and 5D, are explained along with their unique characteristics.