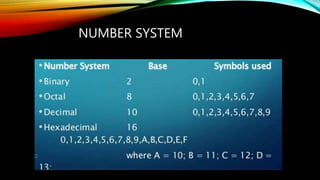
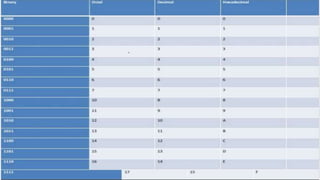
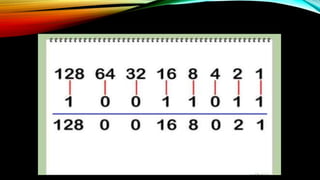
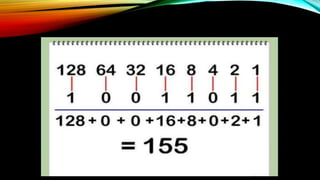
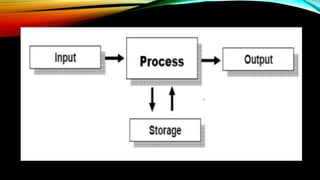
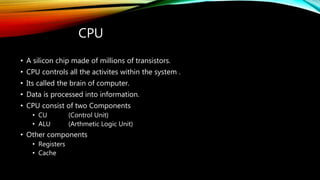
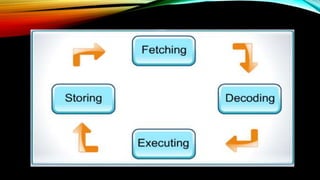
The document explains how computers represent and process data, detailing concepts like bits, bytes, and binary to decimal conversions. It covers text encoding with ASCII and Unicode, and describes the CPU's structure and operations, including input/output, calculations, and logical comparisons. Additionally, it discusses factors that affect processing speed, such as clock rate and memory size.