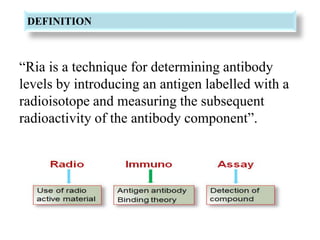
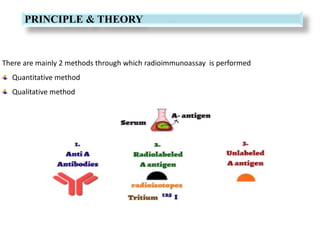
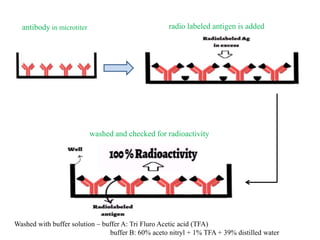
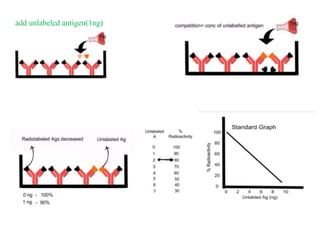
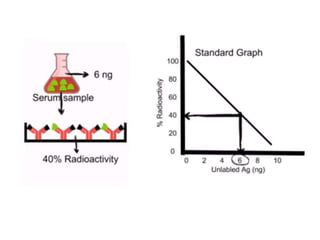
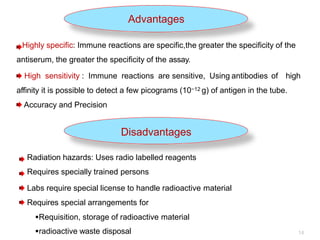
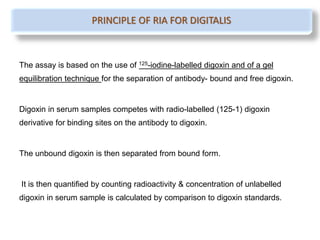
Radioimmunoassay (RIA) is a sensitive technique for detecting small quantities of substances using the principle of competitive binding between labeled and unlabeled antigens or ligands to an antibody. RIA of digitalis involves using radioactively labeled digoxin to compete with digoxin in serum samples for binding sites on anti-digoxin antibodies. The bound and unbound fractions are then separated, and the radioactivity counted to quantify the concentration of unlabeled digoxin in the serum sample. RIA of digitalis is used to monitor digoxin levels in patients receiving the drug to treat heart conditions. RIA provides high sensitivity and specificity for detection of biological substances and is used in various fields including endocrinology, pharmac