This document outlines the concept of compound distributions. It defines a compound distribution as a random variable Y that is the sum of random variables X1 + X2 + ... + XN, where N is a random variable representing the number of terms. The document discusses the assumptions about N and the Xi, provides an example, and outlines the key properties of compound distributions including distribution function, expected value, variance, and moment generating function. It also includes a numerical example to demonstrate calculating the expected value and variance of a compound distribution.





![1. Distribution function
By the total law of probability, the distribution function of Y
is given by
𝐹𝑌(y)= 𝑛=0
∞
𝐺 𝑛(y)P[N=n]
Where
For n=0 ,𝐺0(y) is the distribution function of the point
mass at y=0
For n ≥ 1 , 𝐺 𝑁 (y) is the distribution function of the
independent sum 𝑋1+𝑋2+…….+𝑋 𝑁](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-160918163750/85/compound-distribution-7-320.jpg)
![2. Expected value
The mean aggregate claim is :
E[Y]=E[N]E[X]
The expected value of the aggregate claims has a natural
interpretation .
It is the product of the expected number of claims and the
expected individual claim amount](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-160918163750/85/compound-distribution-8-320.jpg)
![Expected value (cont…)
proof: E[Y] = 𝐸 𝑁[E(Y|N=n)]
= 𝐸 𝑁[ E[ 𝑖=1
𝑁
𝑋𝑖]]
= 𝐸 𝑁[∑E[X]]
= 𝐸 𝑁[NE[X]]
= E[N]E[X]
The higher moments of the aggregate claims Y
do not have a intuitively clear formula as the
first moment .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-160918163750/85/compound-distribution-9-320.jpg)
![3. Higher moment
We can obtain the higher moments by using the first
principle
E[𝑌 𝑛
] = 𝐸 𝑁[E(𝑌 𝑛
|N)]
= 𝐸 𝑁[E({𝑋1+𝑋2+…….+𝑋 𝑁} 𝑛|N)]
=E[𝑍1
𝑛
]P N = 1 +E[𝑍2
𝑛
]P N = 2 +…….
Where
𝑍 𝑛 = 𝑋1+𝑋2+…….+𝑋 𝑁](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-160918163750/85/compound-distribution-10-320.jpg)
![4. Variance
The variance of the aggregate claims var[Y] is:
var[Y] = E[N] var[X]+ var[N]𝐸[𝑋]2
The variance of the aggregate claims also has a
natural interpretation
It is the sum of two components such that the first
component stems from the variability of the individual
claim amount and the second component stems from
the variability of the number of claims](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-160918163750/85/compound-distribution-11-320.jpg)
![Variance (cont…)
The variance of the aggregate claims ,by using the total
variance formula
var[Y] = 𝐸 𝑁[𝑣𝑎𝑟(Y|N)]+𝑣𝑎𝑟 𝑁 [E(Y|N)]
= 𝐸 𝑁[𝑣𝑎𝑟(𝑋1+𝑋2+…….+𝑋 𝑁|N)]
+ 𝑣𝑎𝑟 𝑁 [E(𝑋1+𝑋2+…….+𝑋 𝑁|N)]
= 𝐸 𝑁[N𝑣𝑎𝑟(X)]+𝑣𝑎𝑟 𝑁 [NE(X)]
var[Y] = E N Var X + Var N 𝐸[𝑋]2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-160918163750/85/compound-distribution-12-320.jpg)
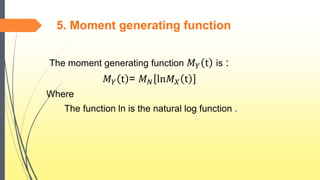
![Steps for m.g.f.
𝑀 𝑌 t = E[𝑒 𝑡𝑌 ]
= 𝐸 𝑁[E𝑒 𝑡( 𝑋1+ 𝑋2+…….+ 𝑋 𝑁) |N]
= 𝐸 𝑁[E(𝑒 𝑡𝑋1…….. 𝑒 𝑡𝑋 𝑁)|N]
= 𝐸 𝑁[E(𝑒 𝑡𝑋1)…….. E(𝑒 𝑡𝑋 𝑁)|N]
= 𝐸 𝑁[𝑀 𝑋(𝑡) 𝑁
]
= 𝐸 𝑁[𝑒 𝑁𝑙𝑛𝑀 𝑋(𝑡)
]
𝑀 𝑌 t = 𝑀 𝑁[ln𝑀 𝑋(t)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-160918163750/85/compound-distribution-14-320.jpg)
![Numerical Problem
𝑋𝑖 = Numbers of the 𝑖 𝑡ℎ patient has
𝑋𝑖 is distributed as a possion
E[𝑋𝑖] = 1.6
N = Number of patients seen by a doctor in an hour
N is also possion distributed
E[N] = 4.7
Problem :
1. What are the expected number of symptoms
diagnosed in an hour by a doctor ?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-160918163750/85/compound-distribution-15-320.jpg)
![Numerical (cont…)
2. What are the variance value of symptoms
diagnose in an hour by a doctor
Solution
S= Number of symptoms diagnosed in an hour by a
doctor
S= 𝑋1+𝑋2+…….+𝑋 𝑁
1. E[S]=E[N]E[ 𝑋𝑖]
E[S]=7.52
2. var[S] = E[N] var[ 𝑋𝑖]+ var[N]𝐸[ 𝑋𝑖]2
var[S] = 19.552](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-160918163750/85/compound-distribution-16-320.jpg)
