The document discusses several measures of a robot's precision of movement:
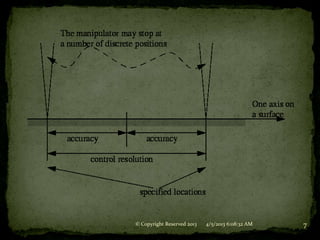
1. Spatial resolution refers to the smallest increment of movement the robot can make and depends on control resolution and mechanical inaccuracies like elastic deflection.
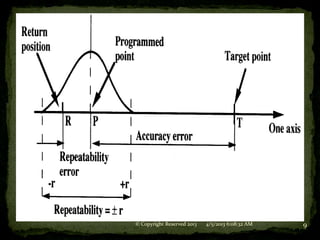
2. Accuracy refers to the robot's ability to position its wrist at a desired target point within its work volume and is one-half the spatial resolution.
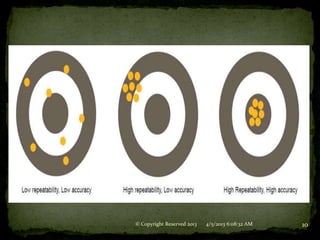
3. Repeatability refers to the robot's ability to return to a previously taught point in space when commanded.