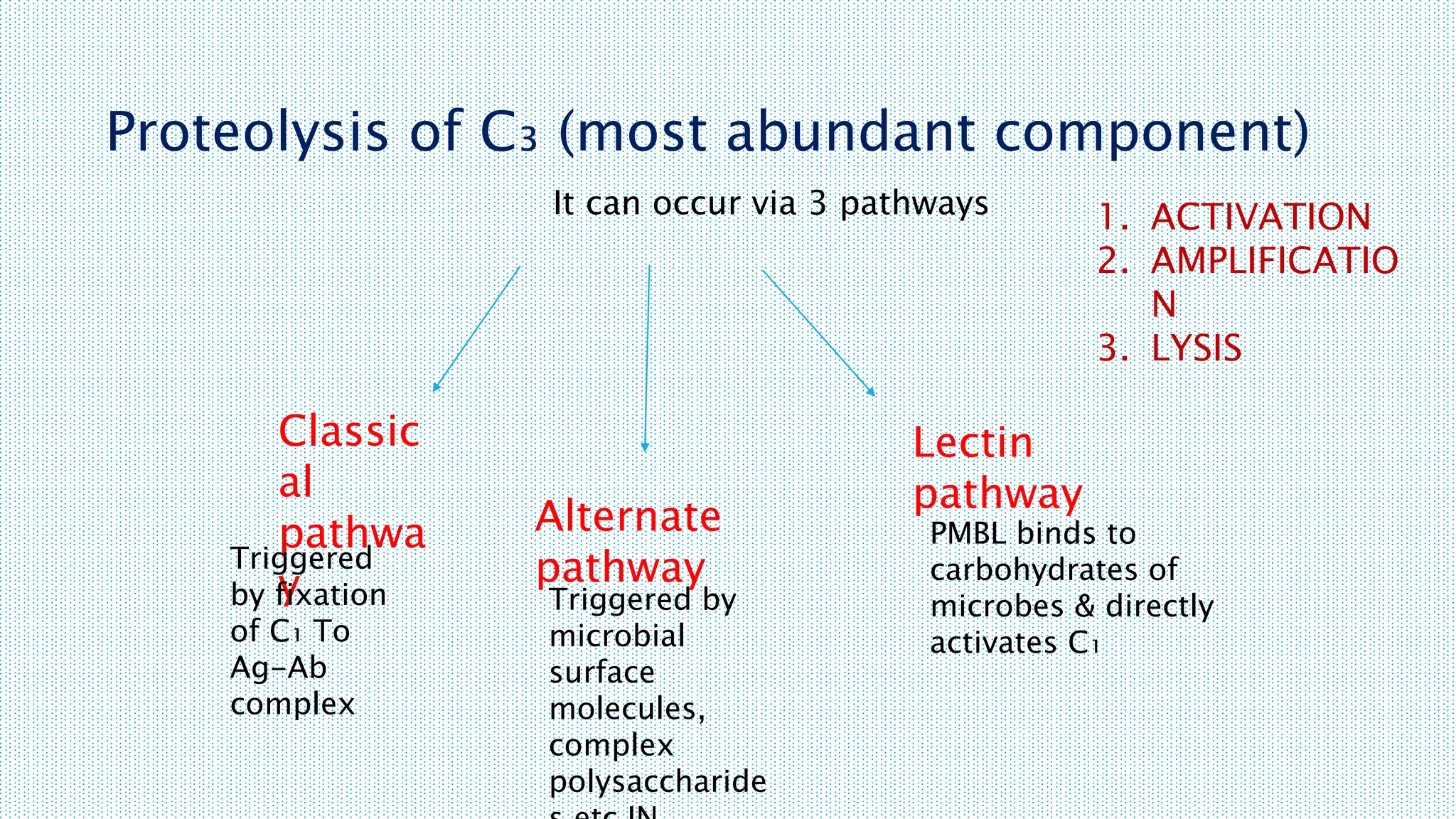
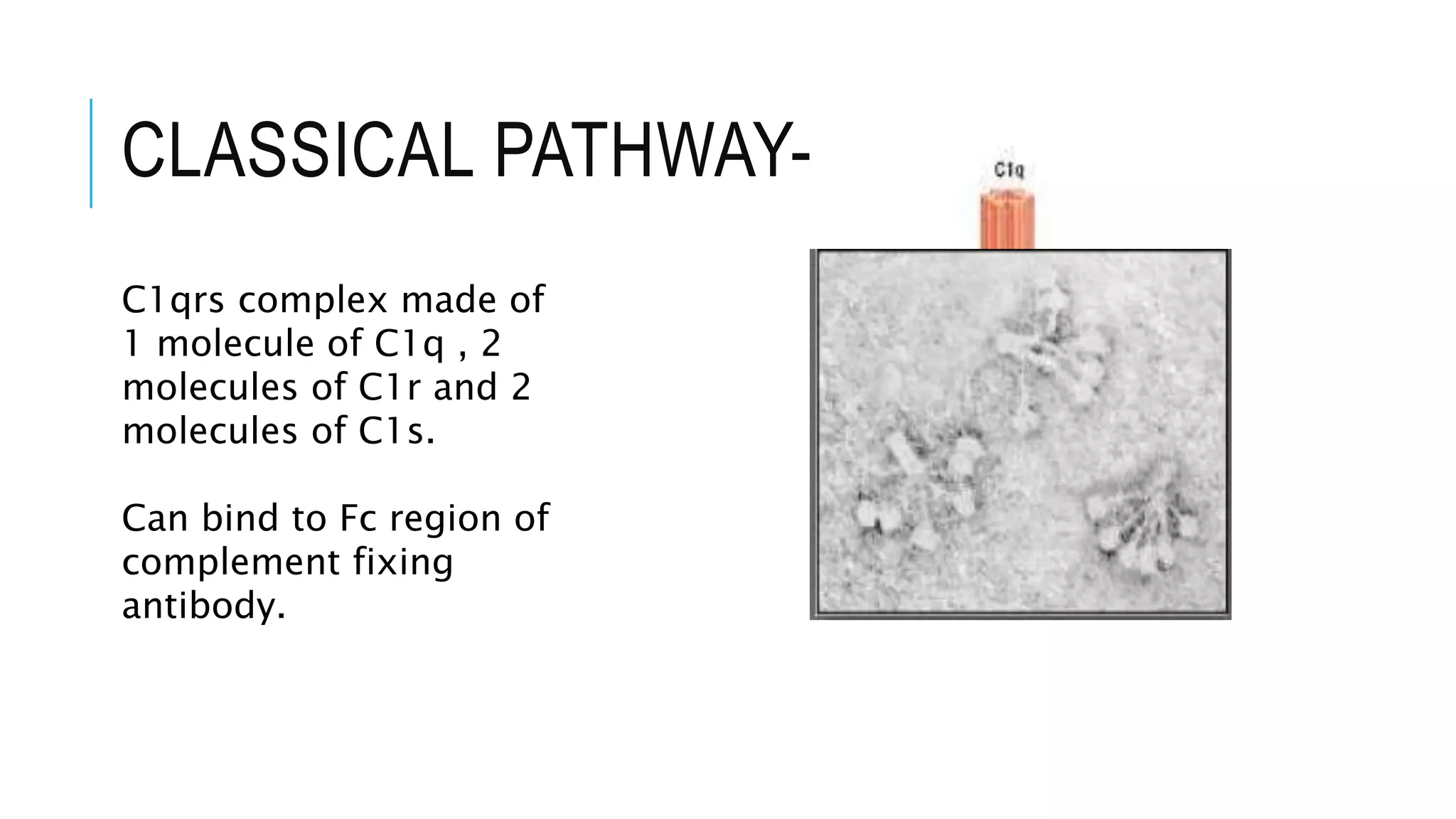
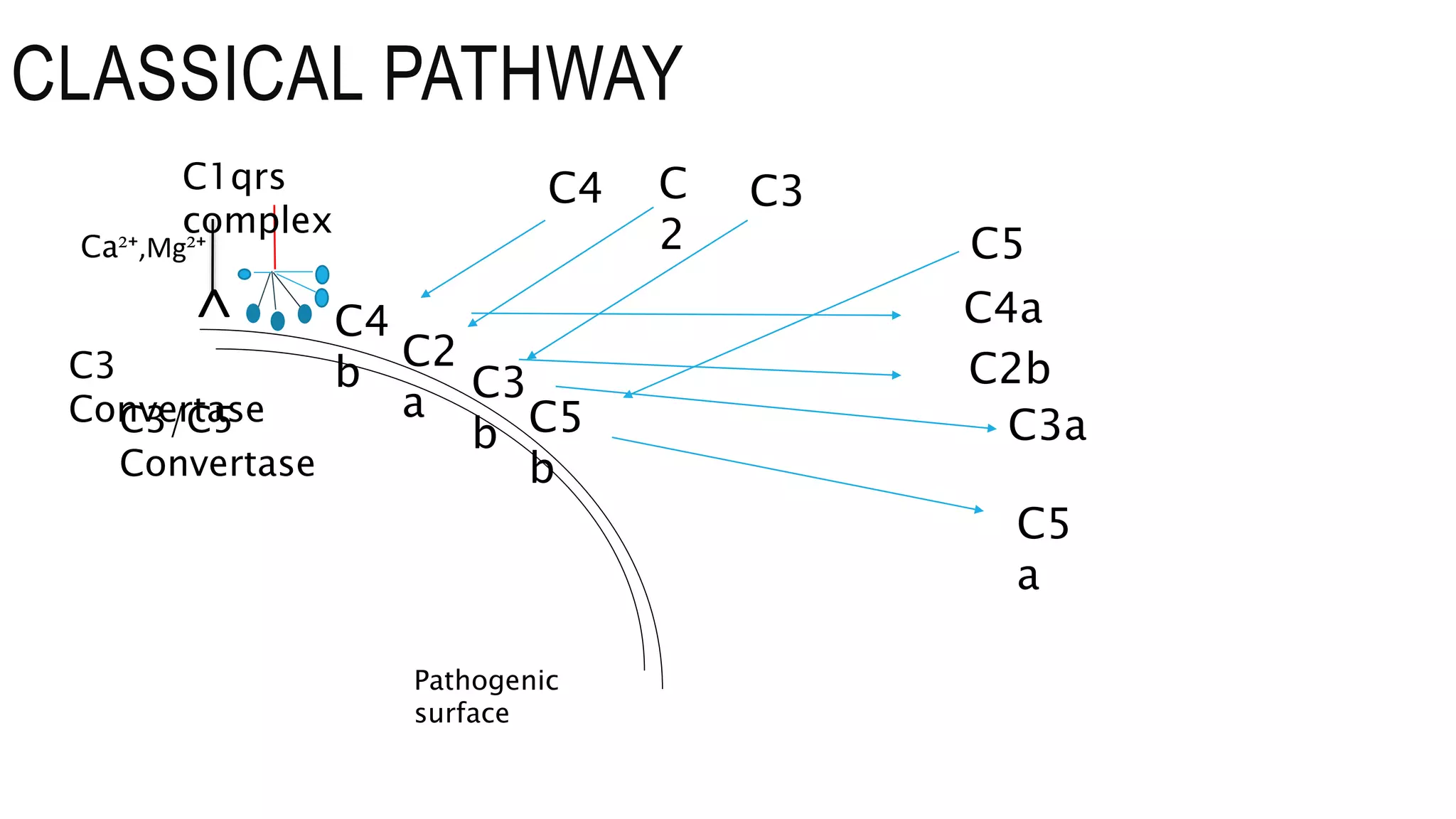
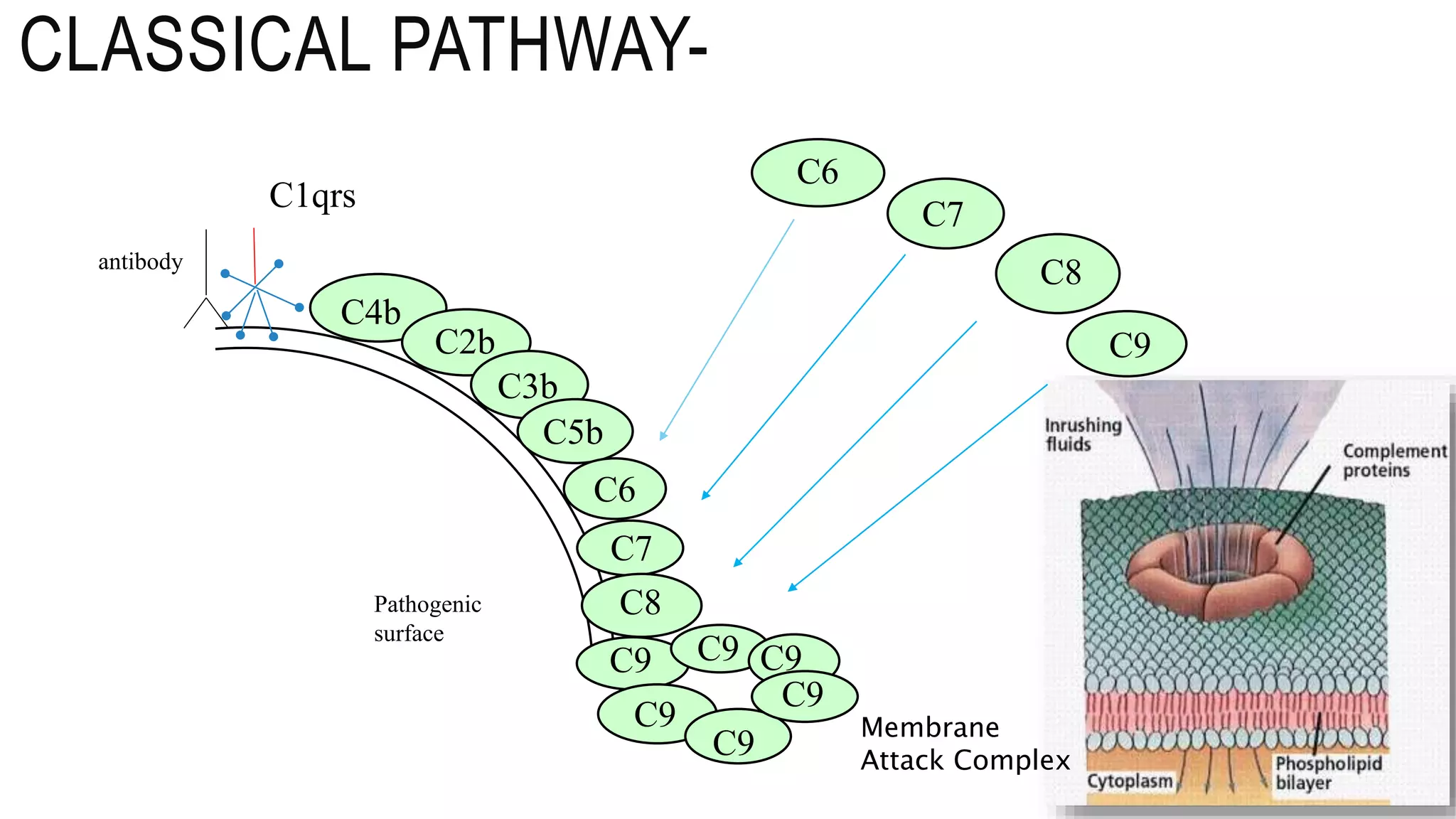
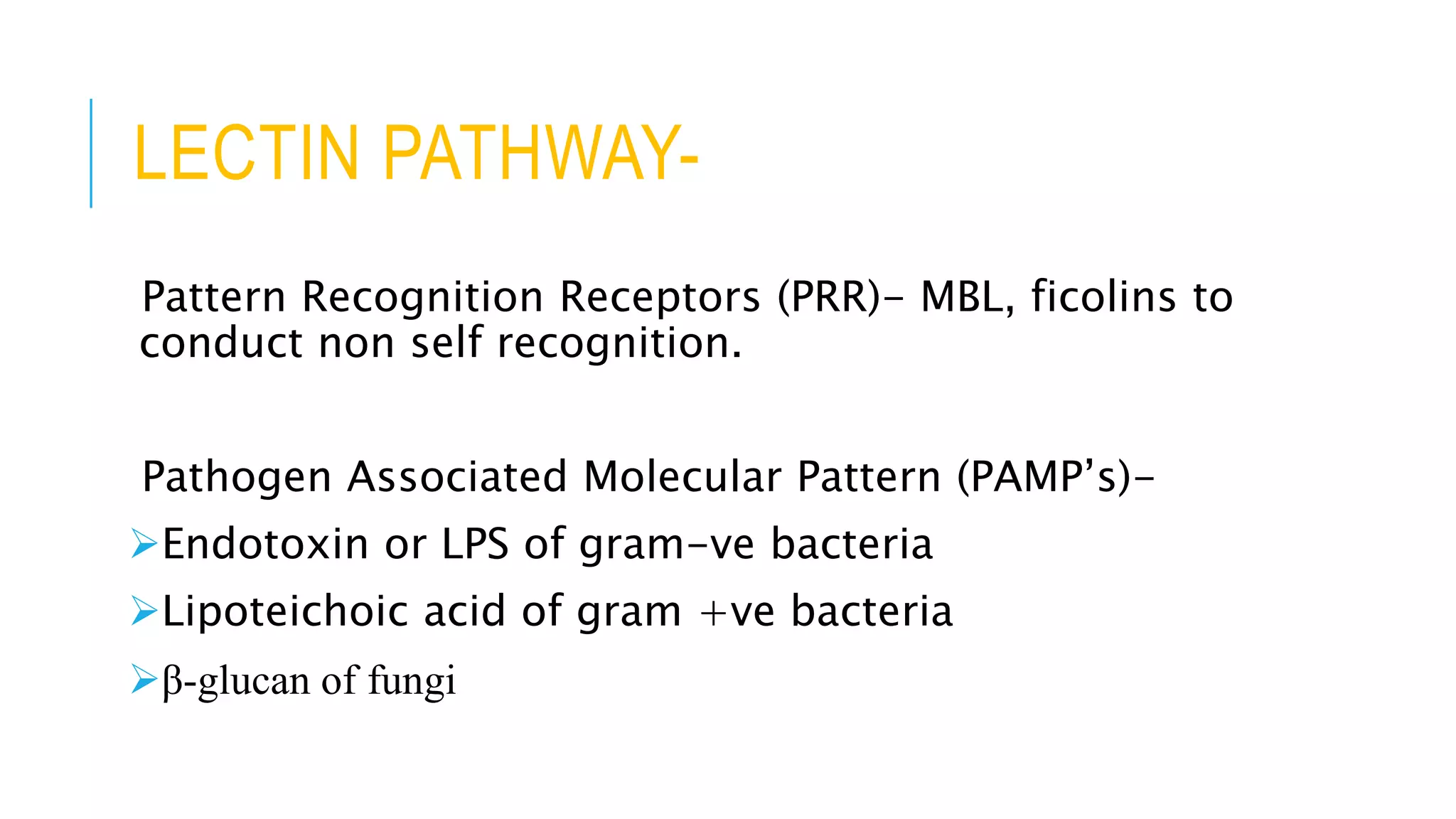
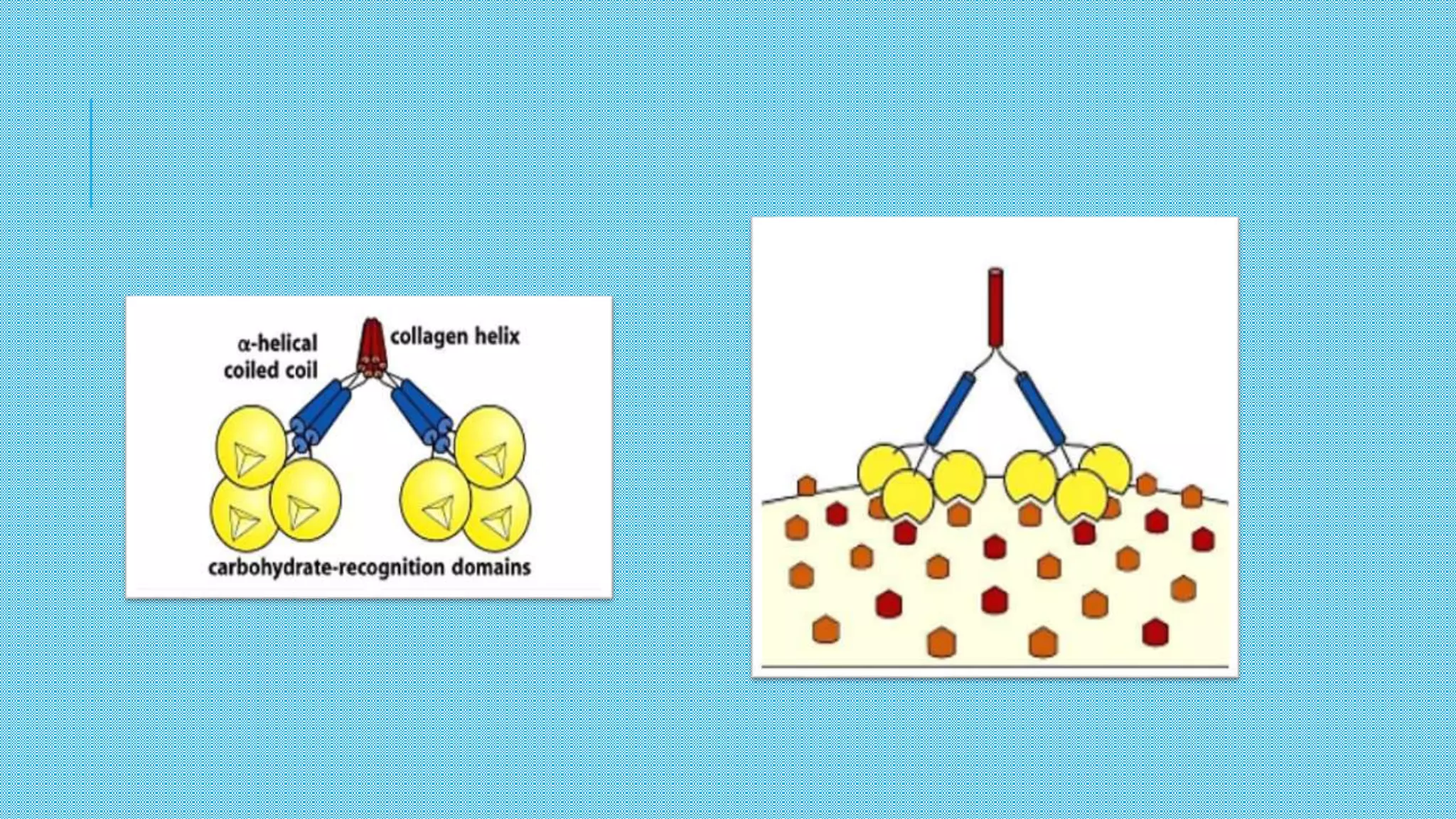
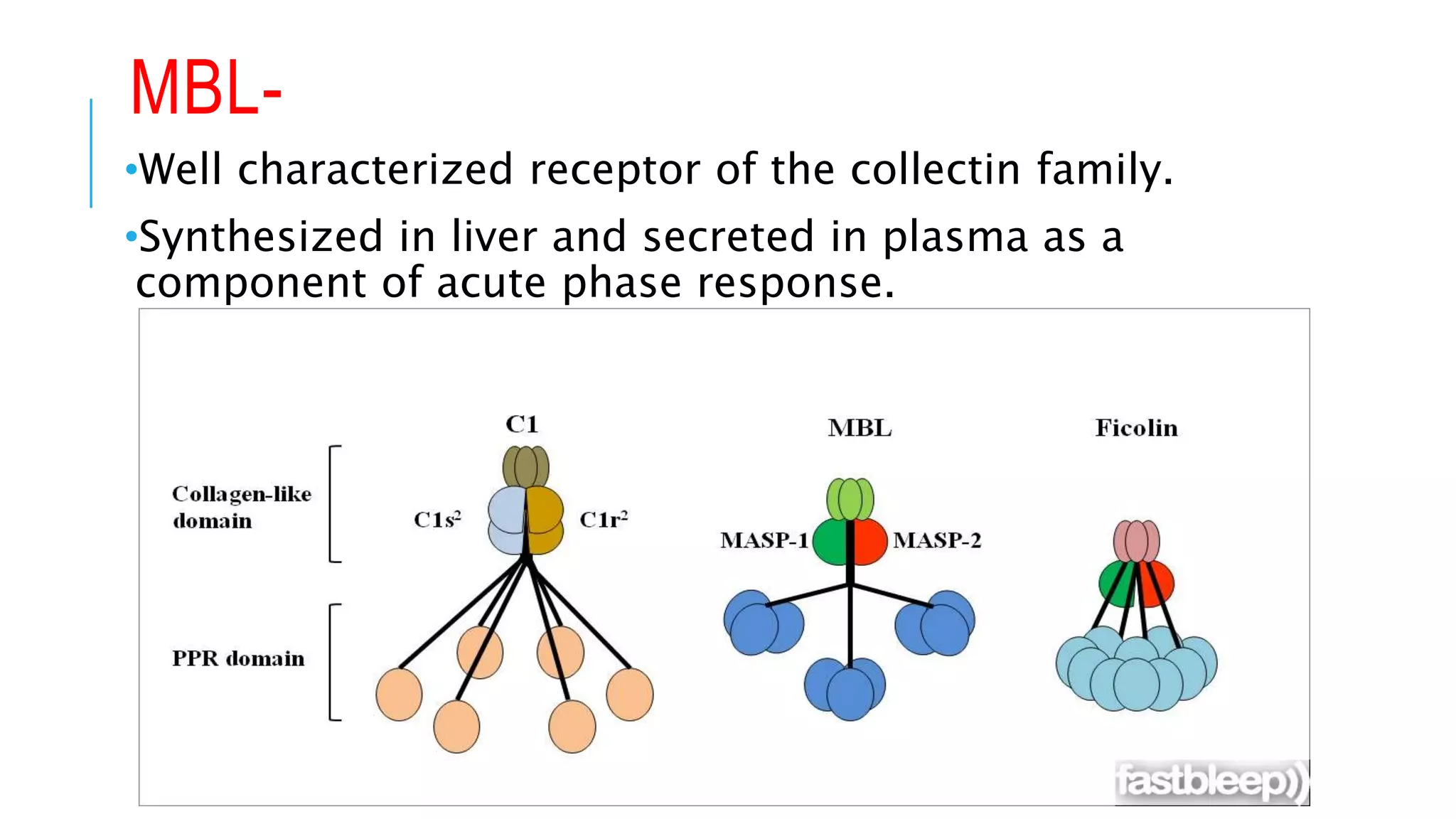
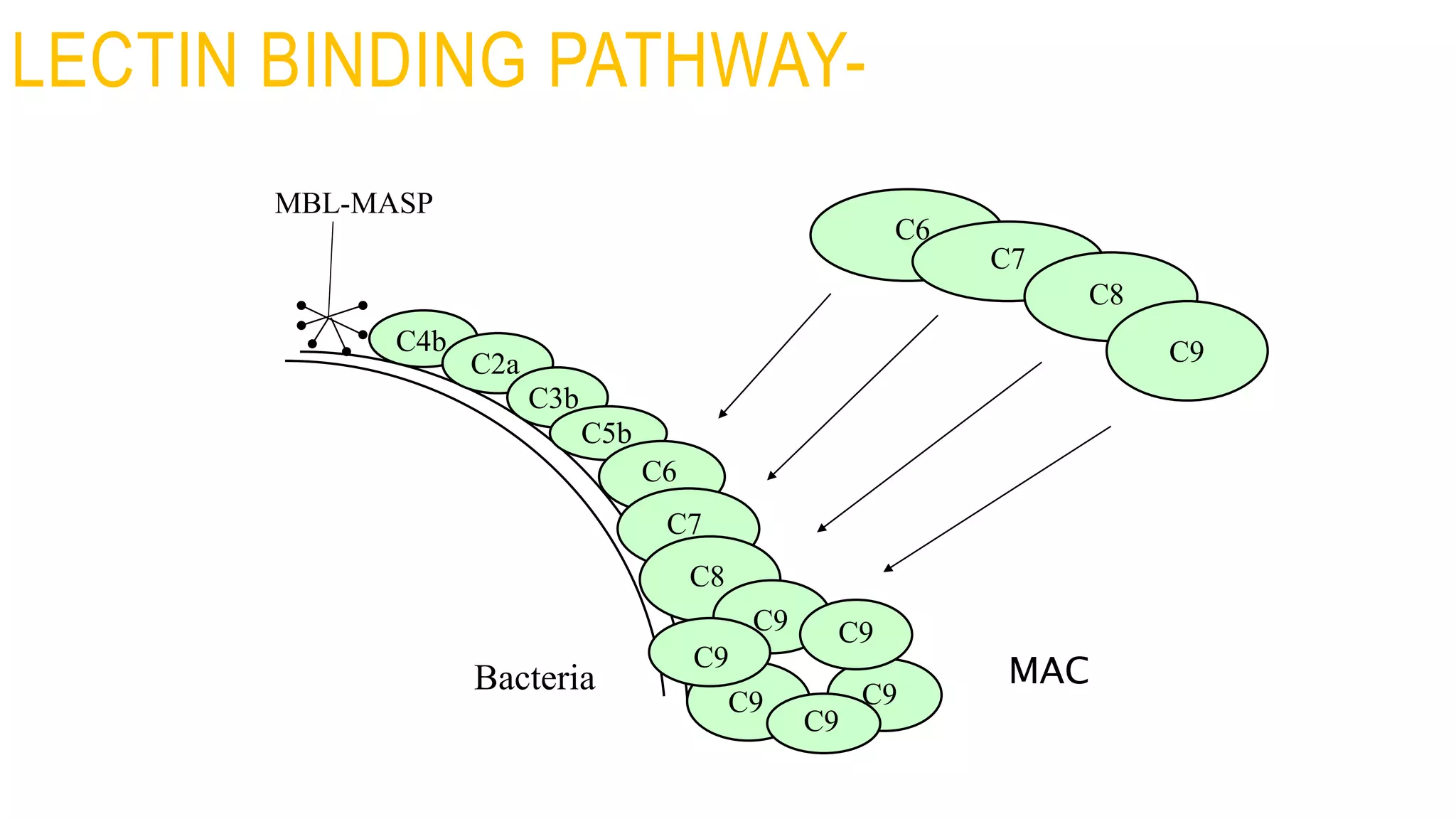
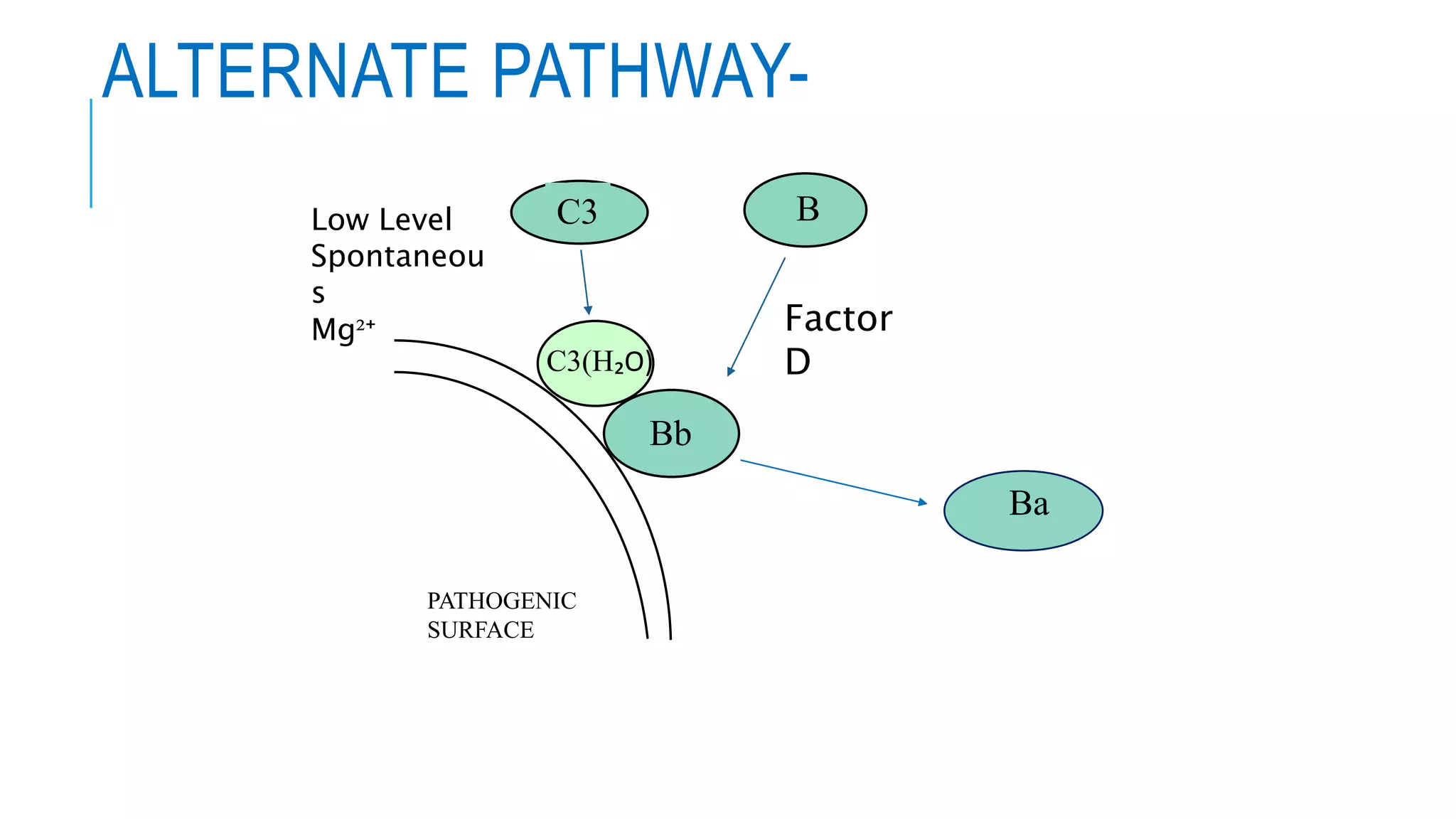
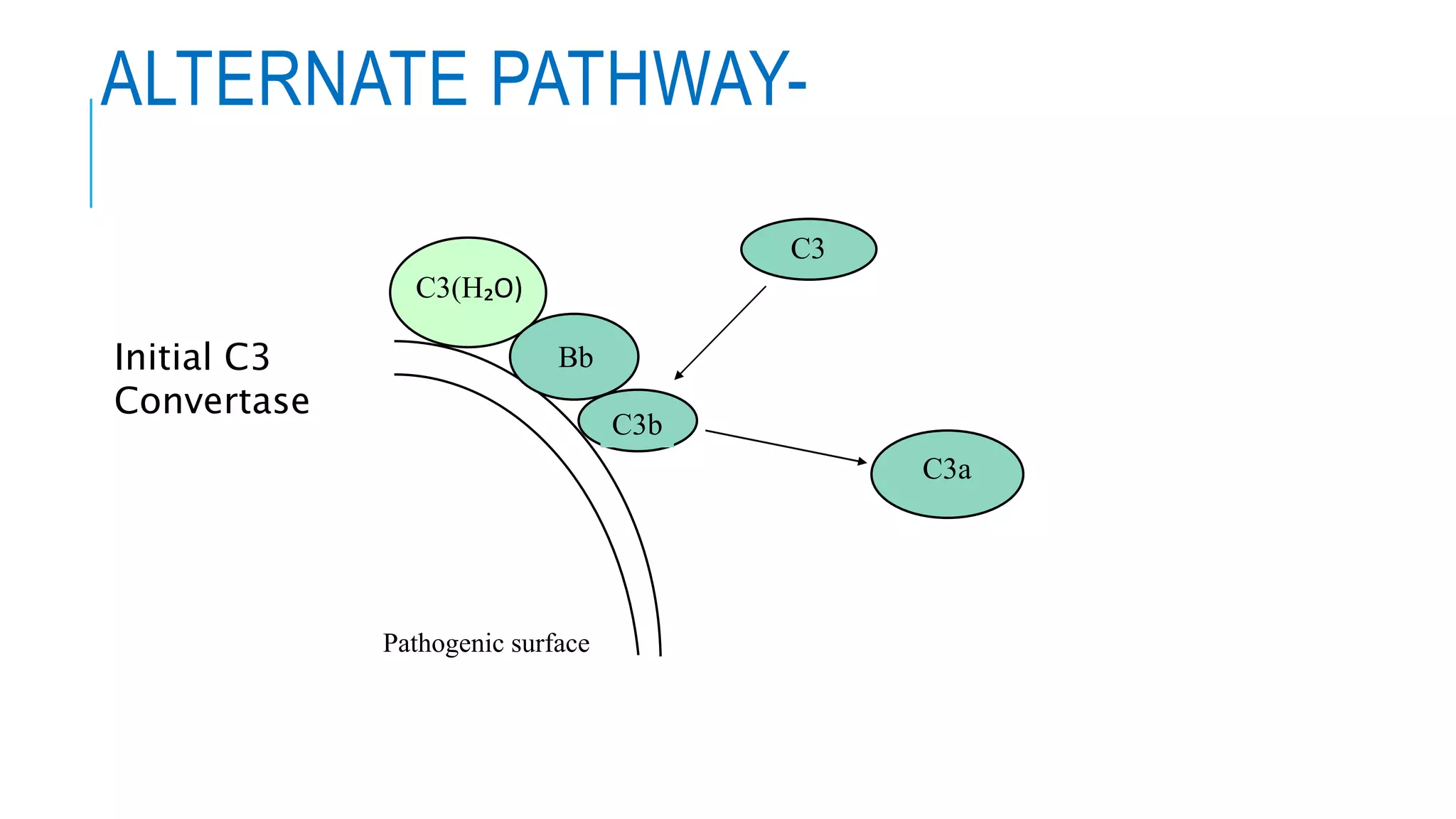
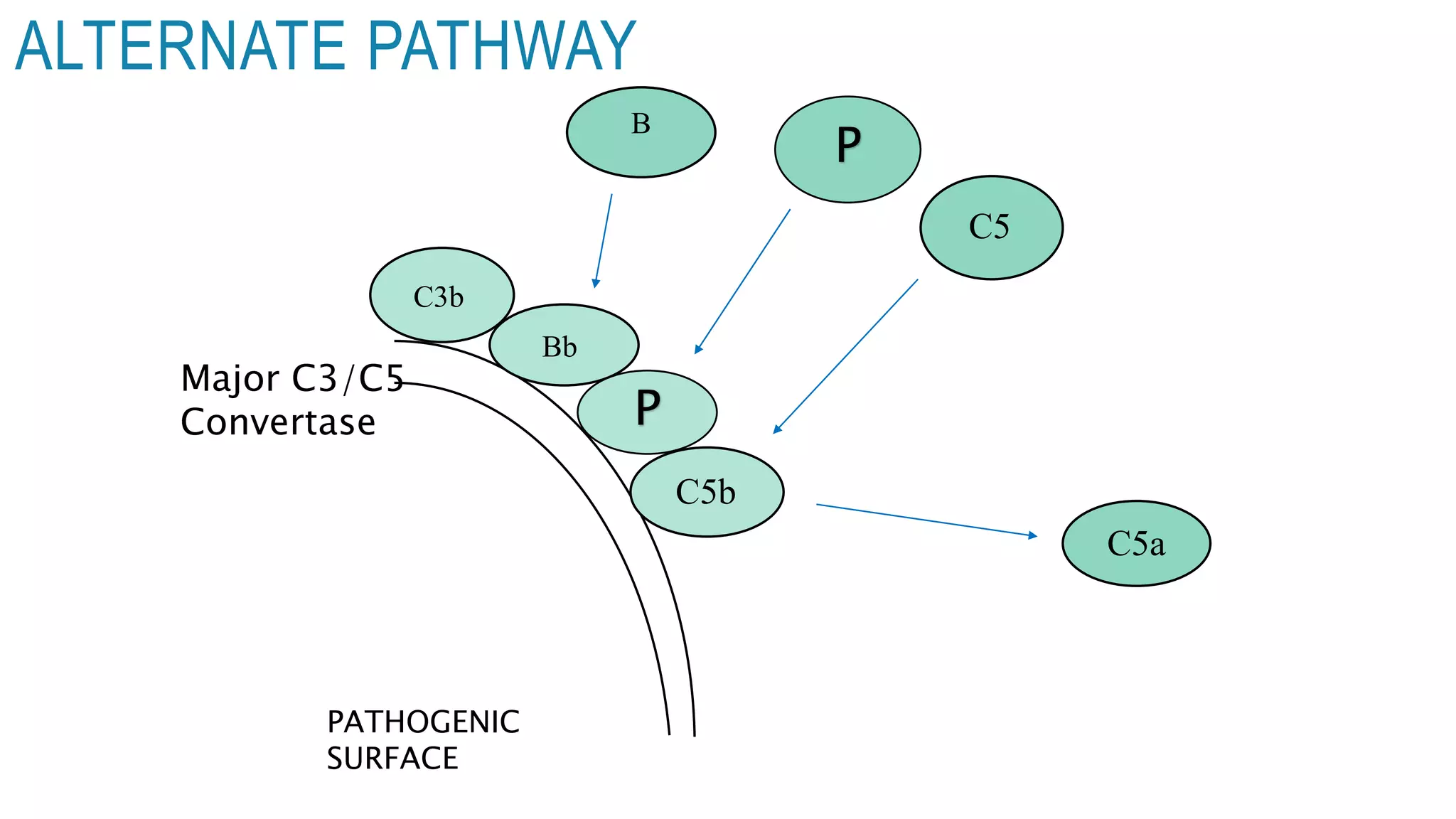
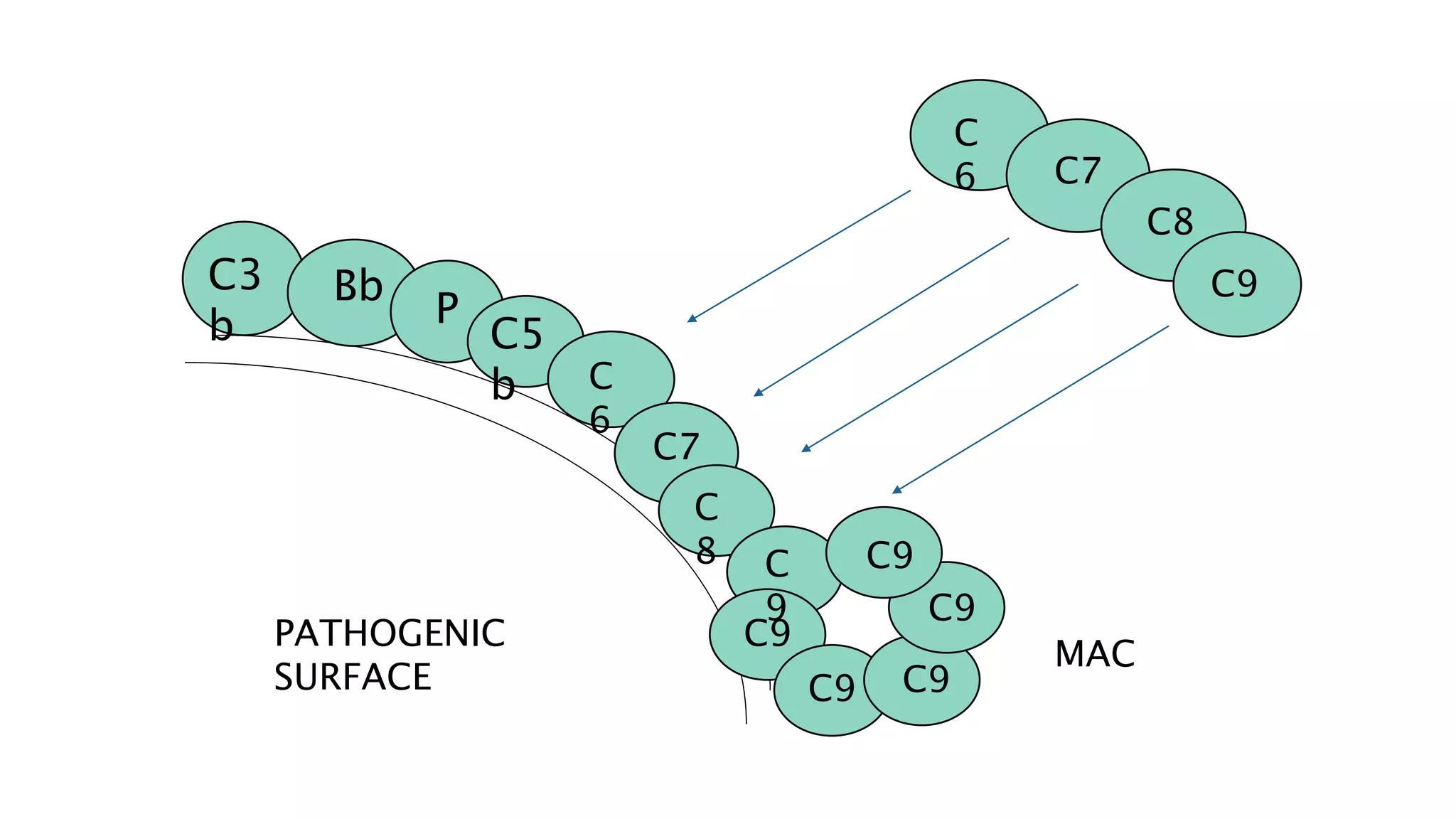
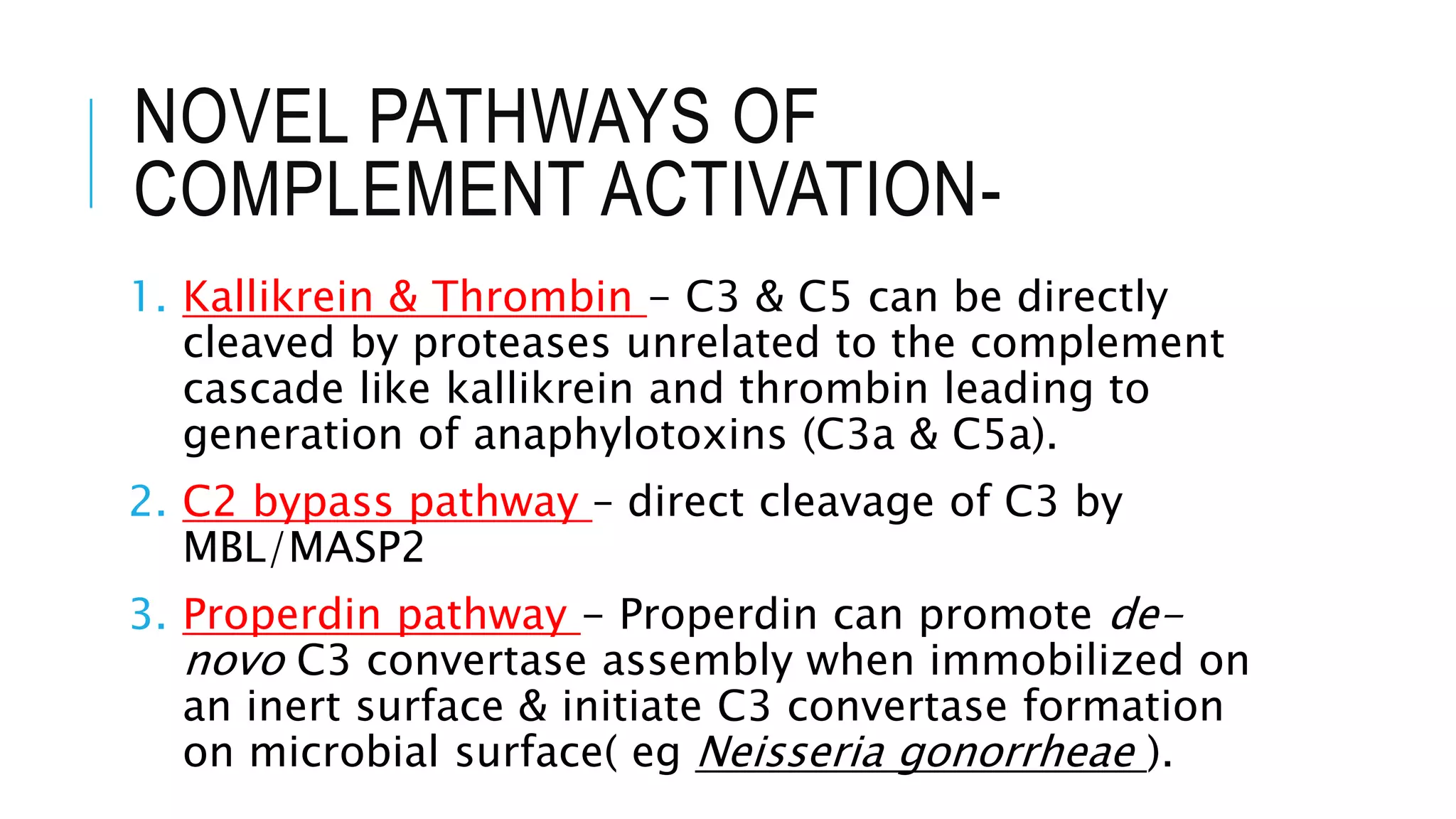
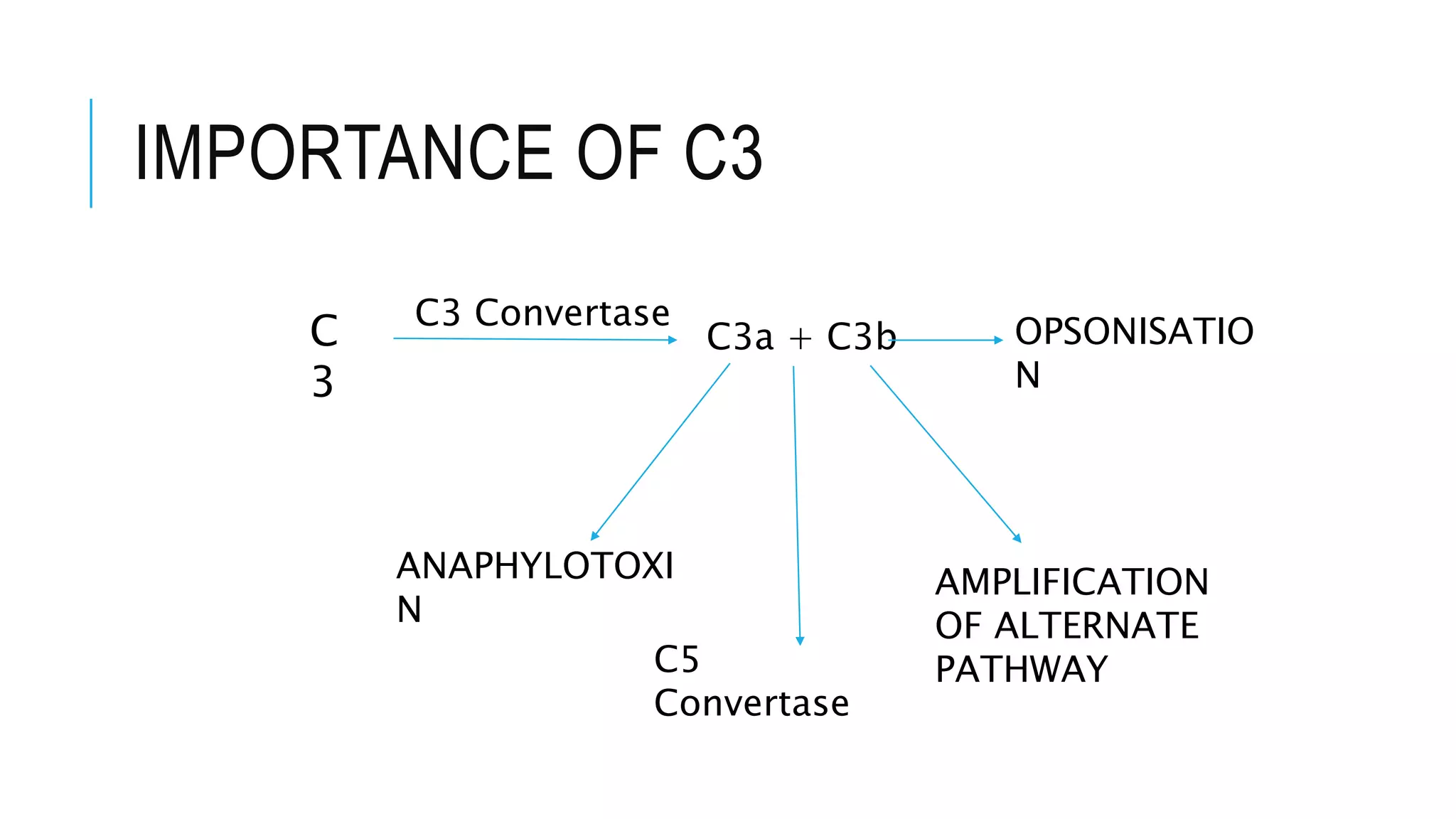
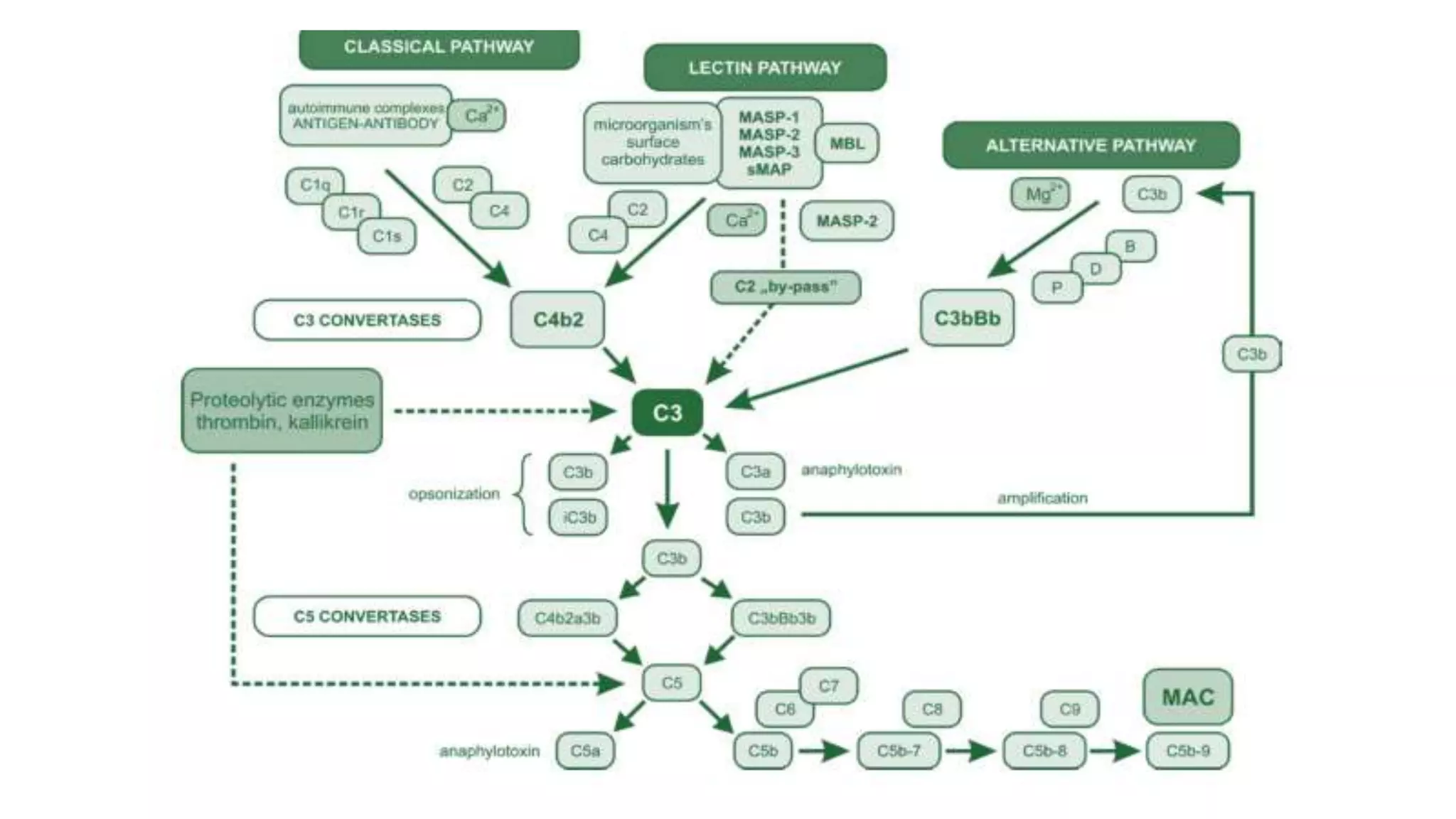
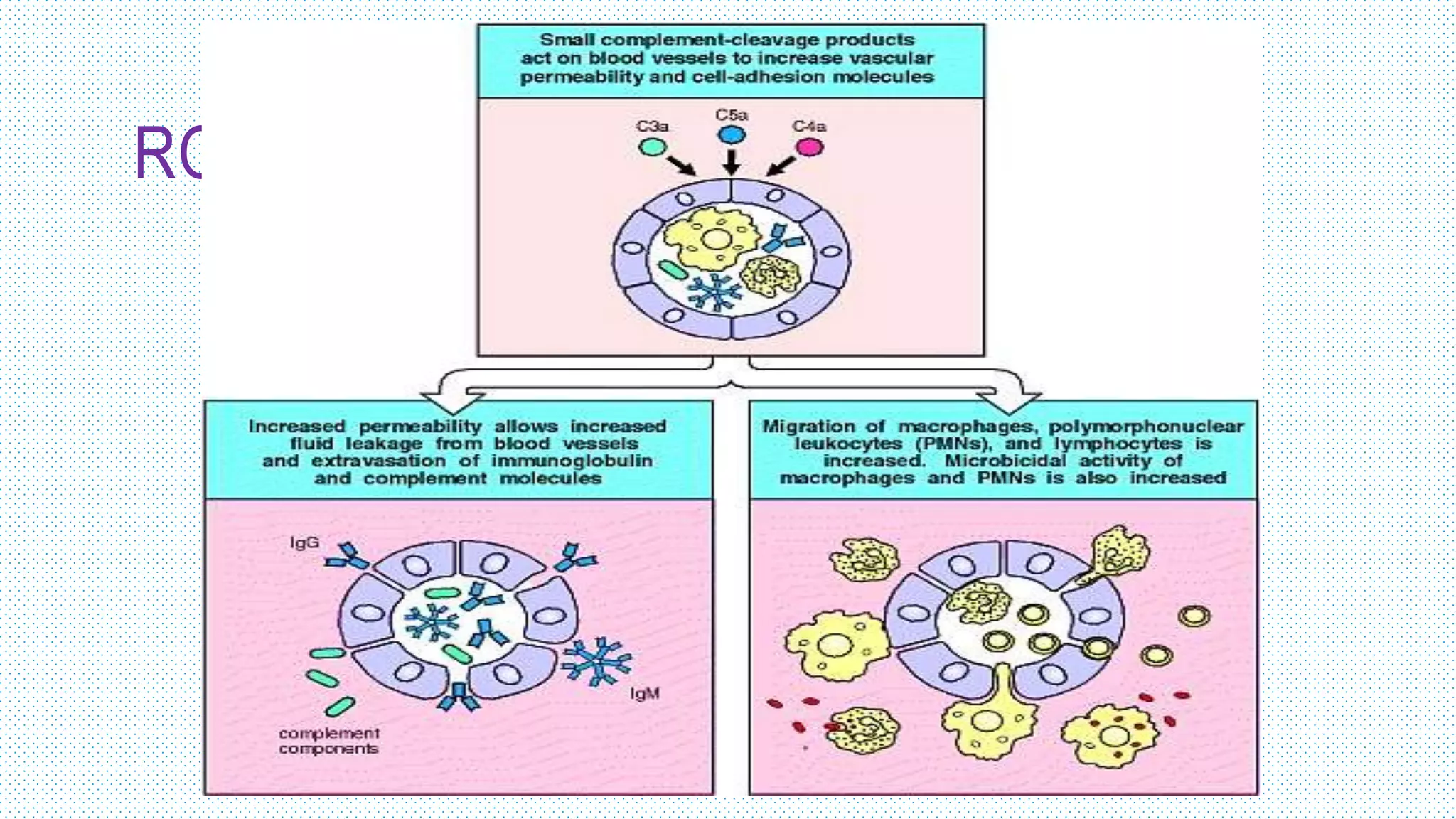
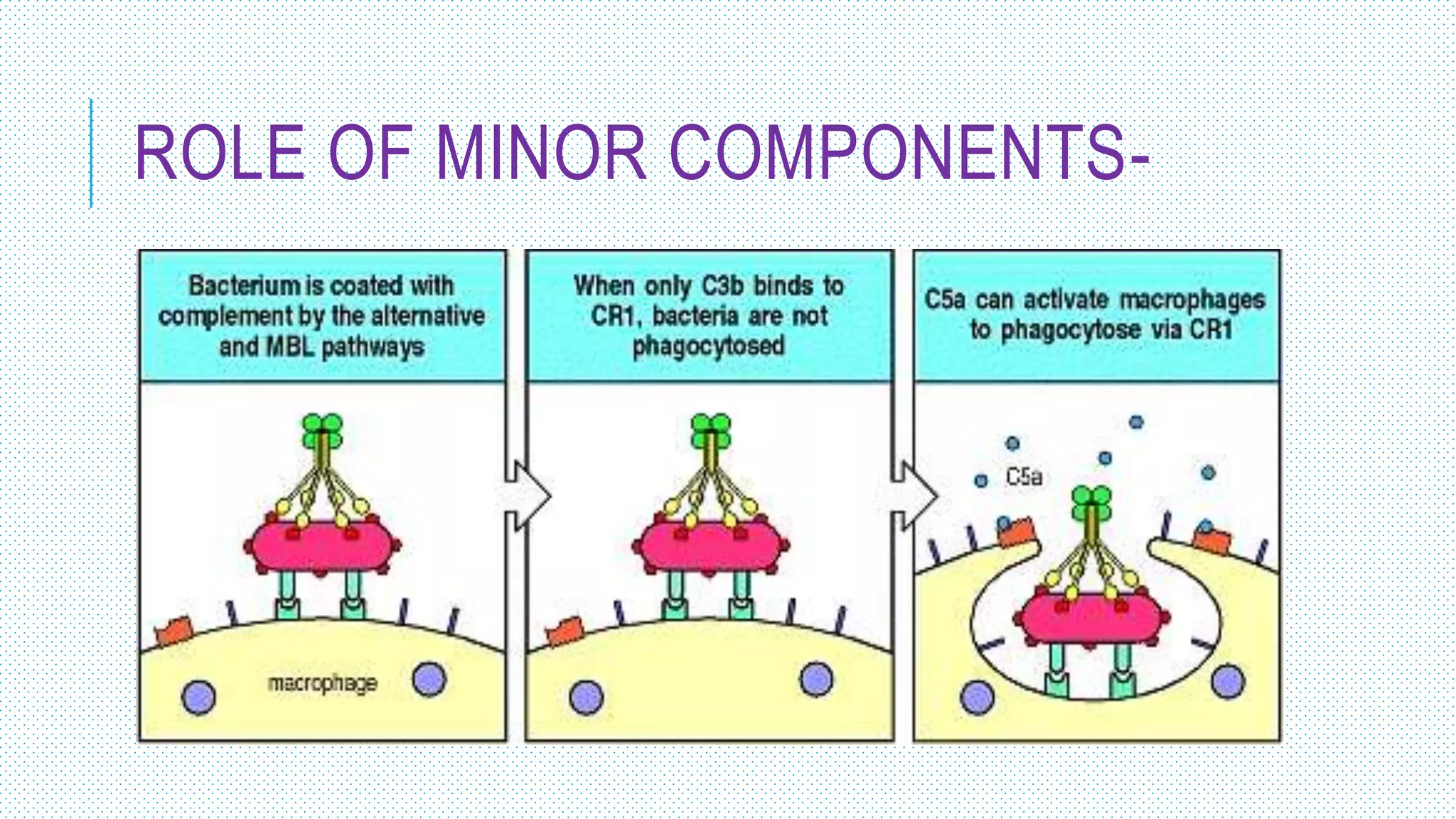
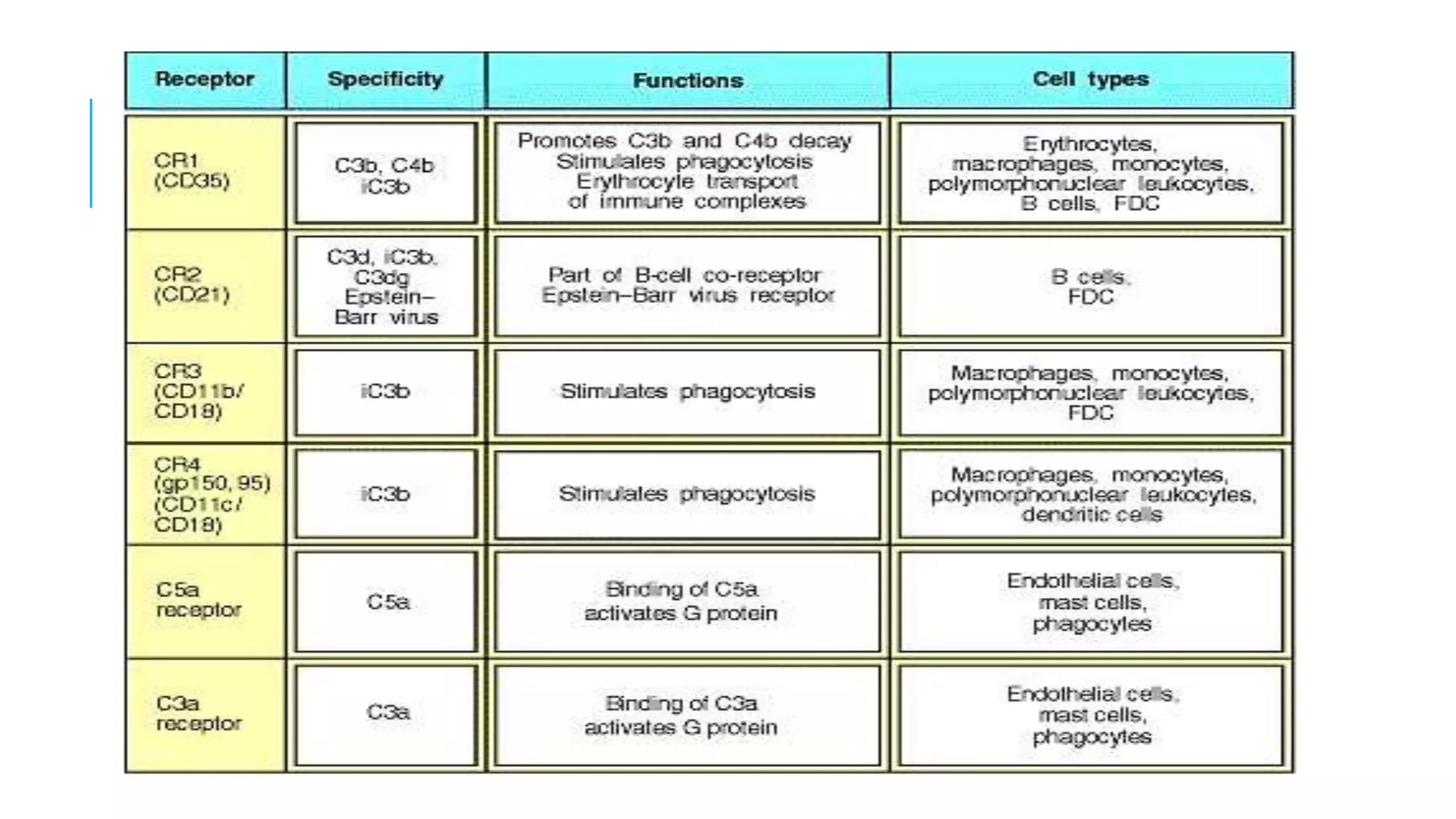
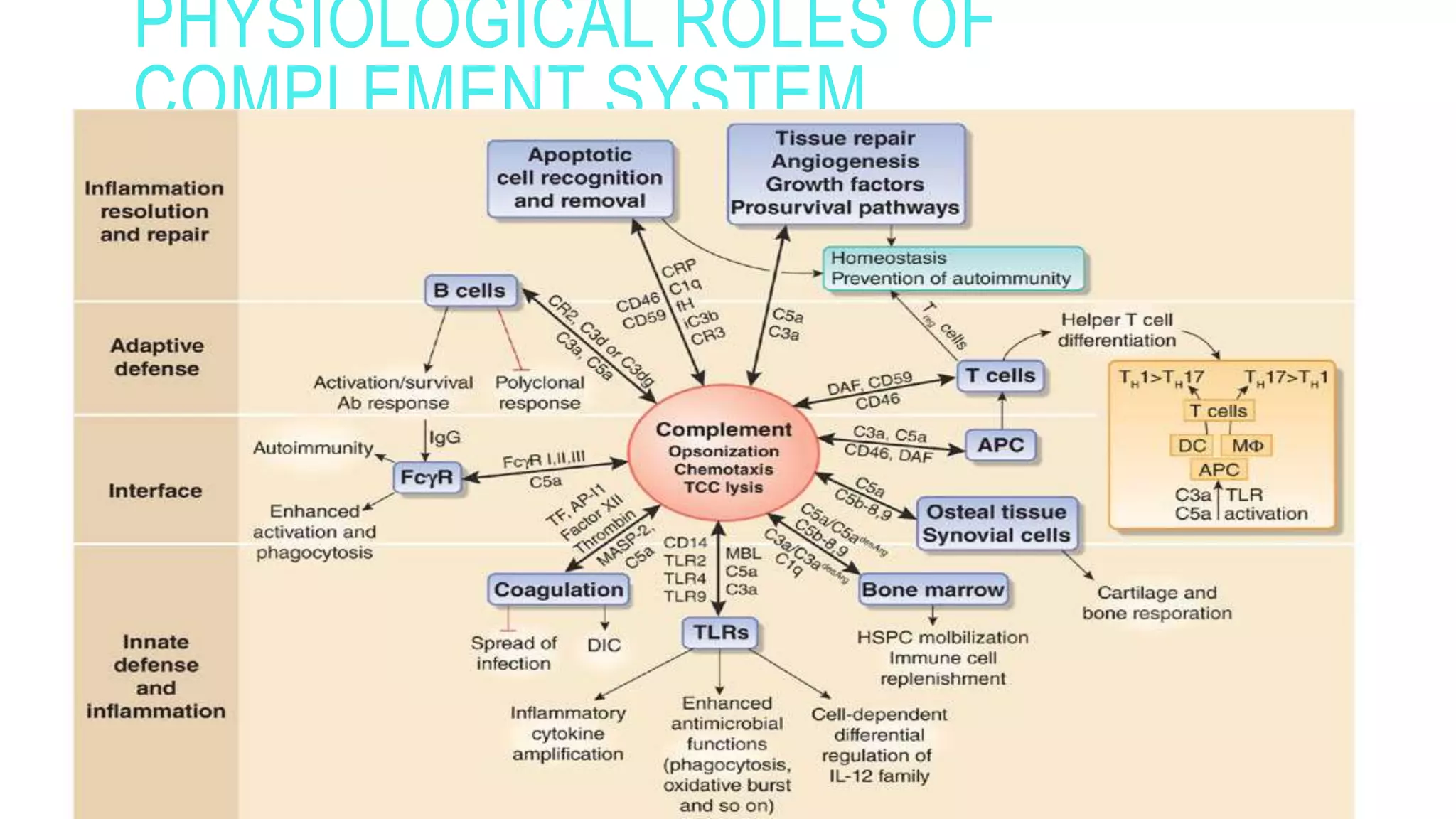
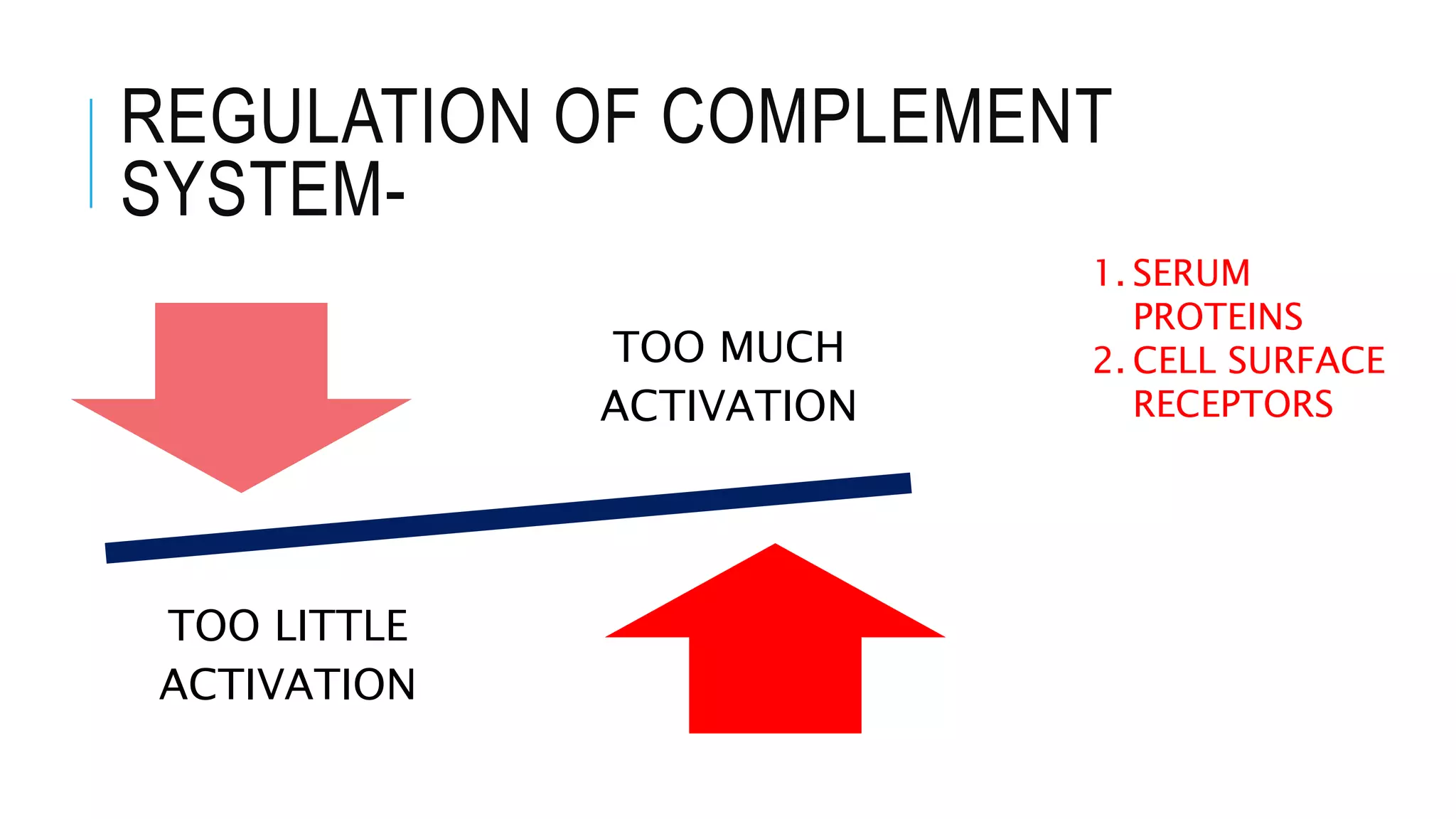
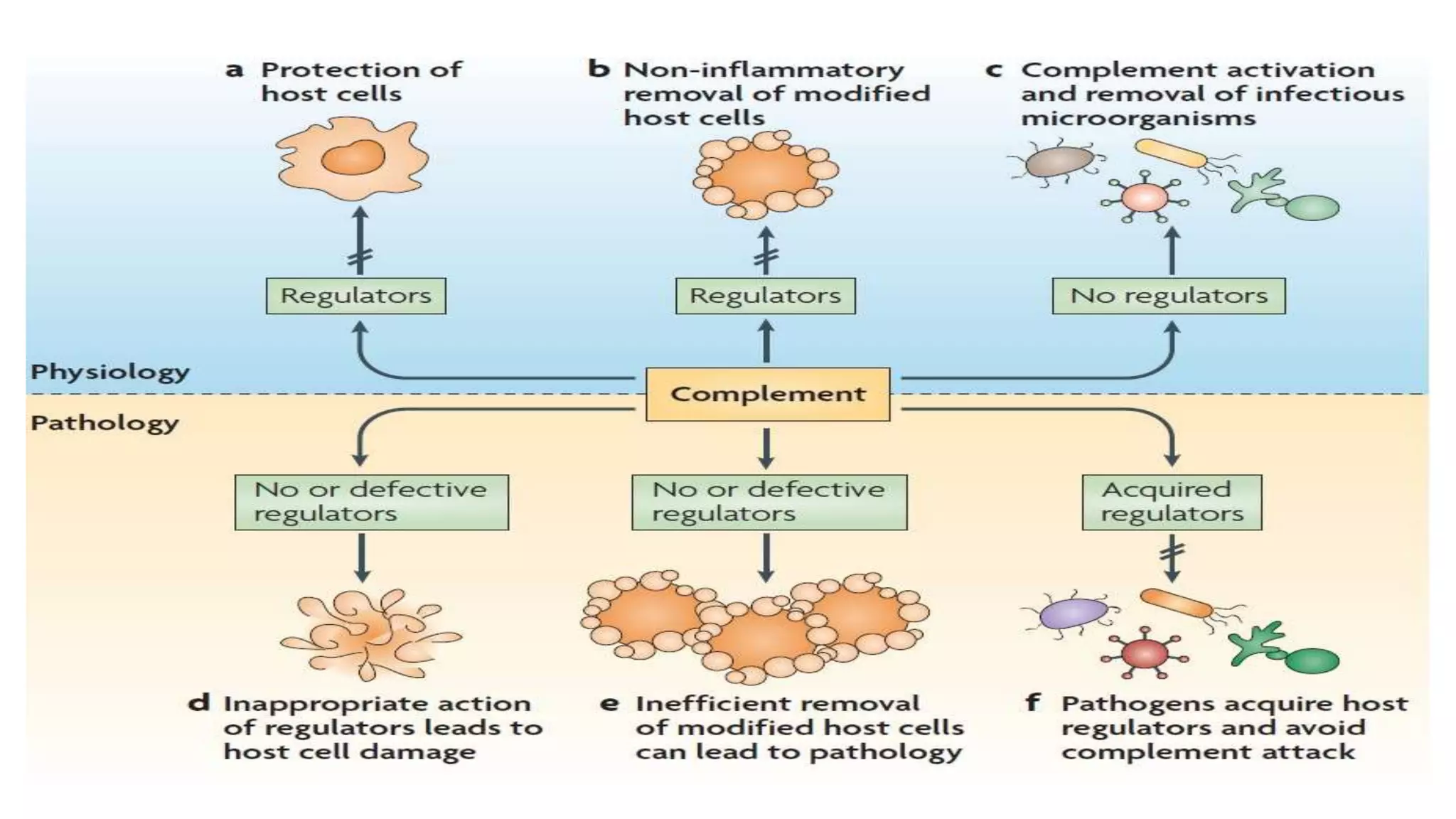
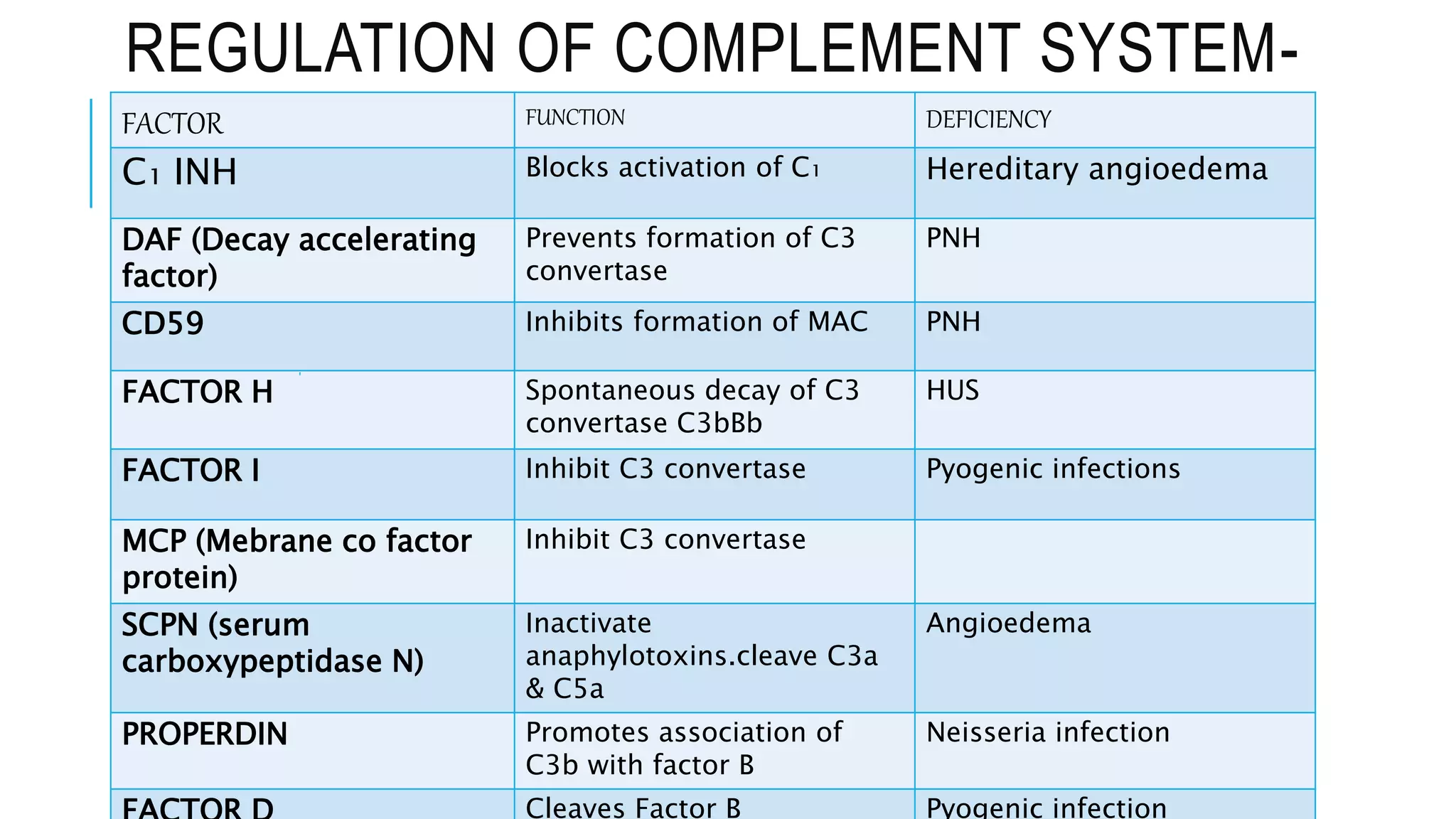
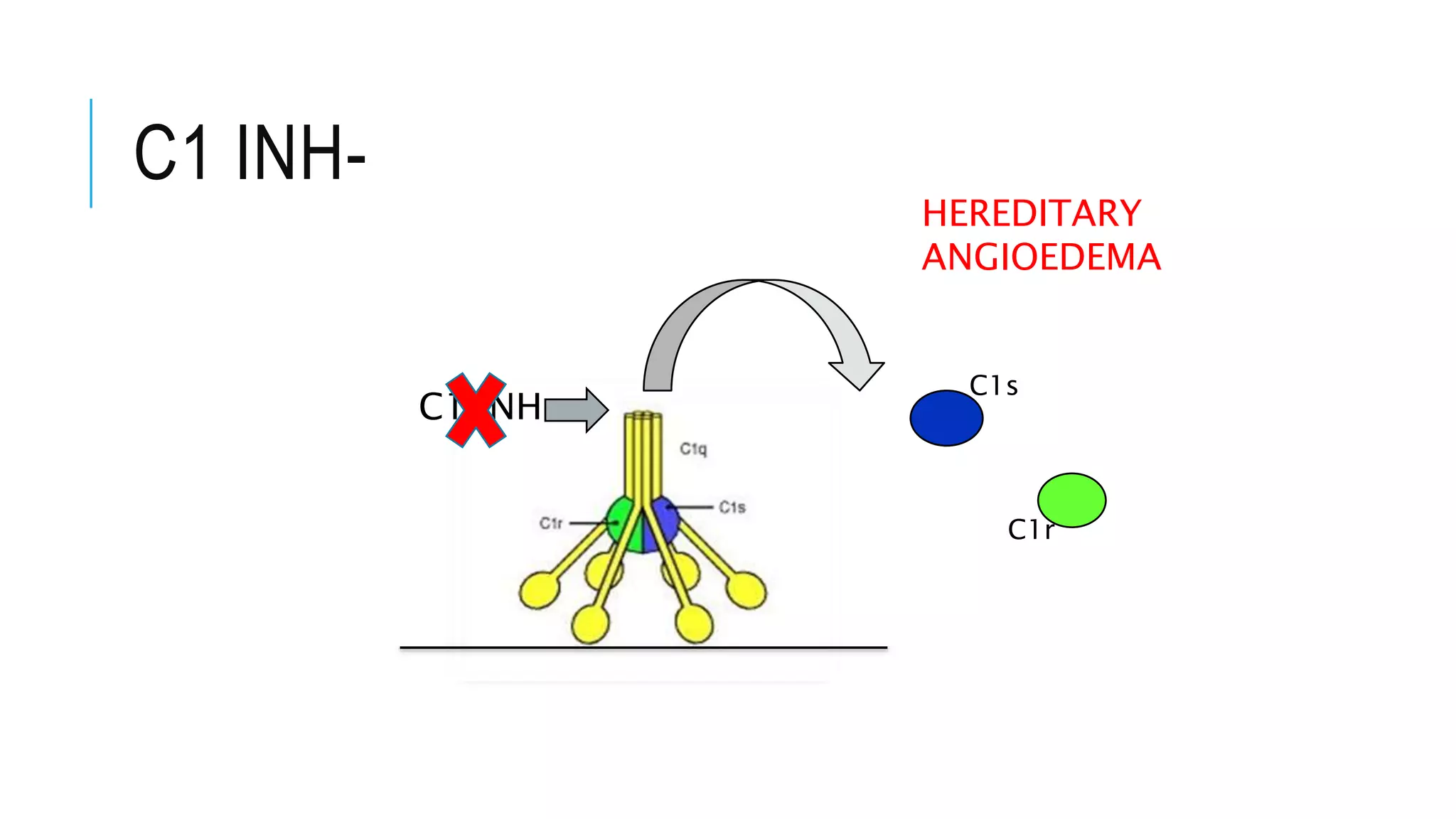
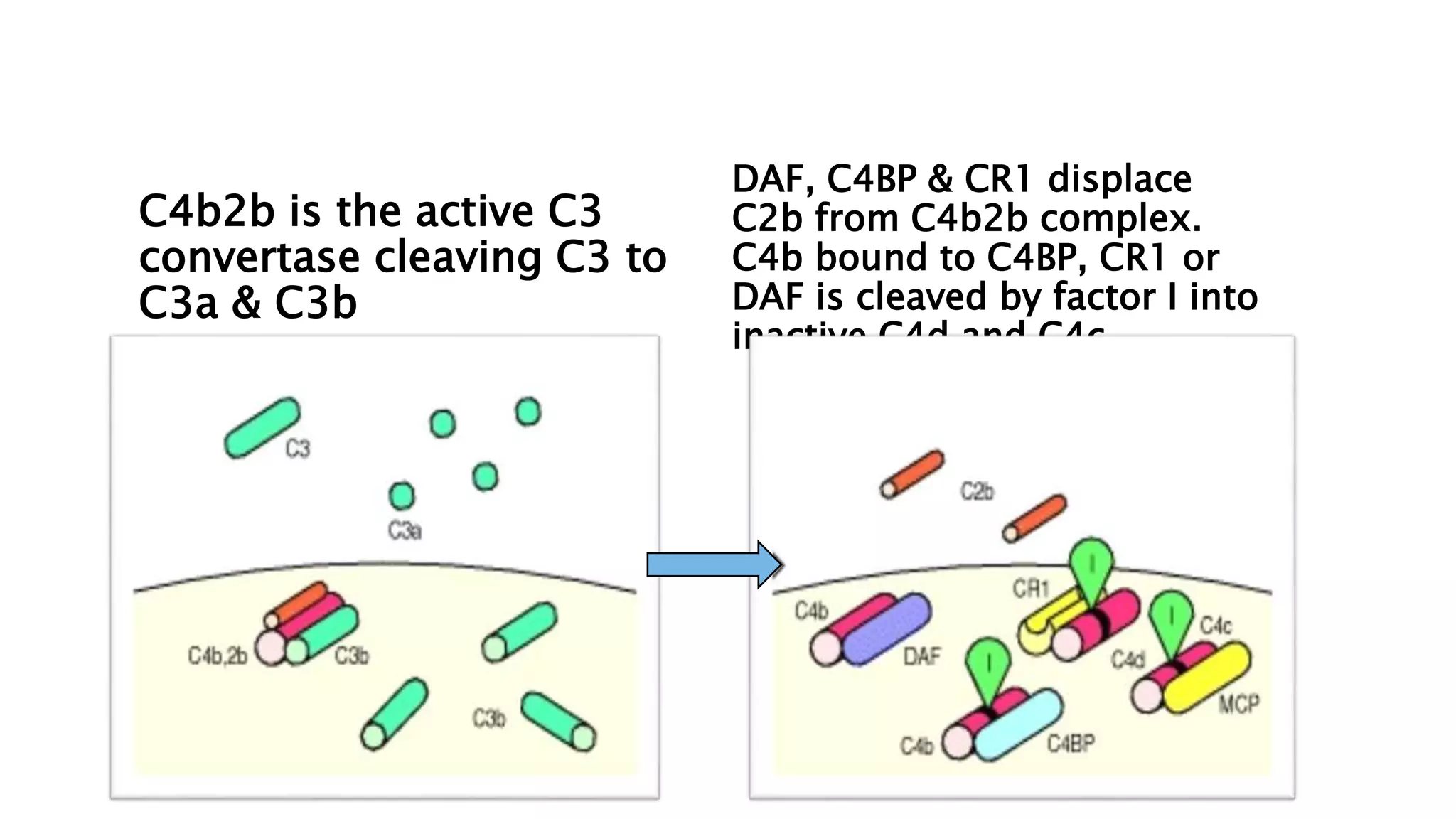
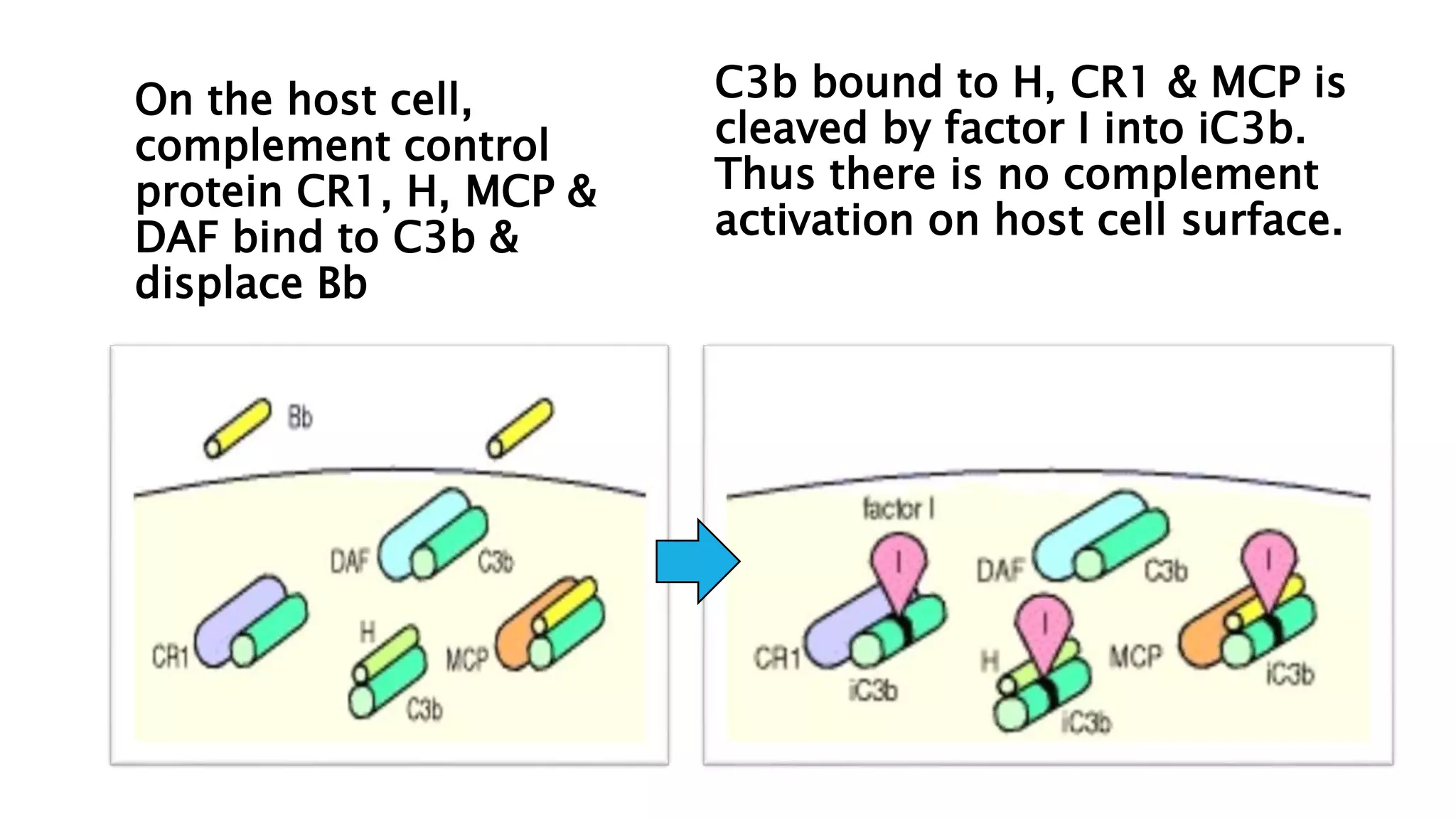
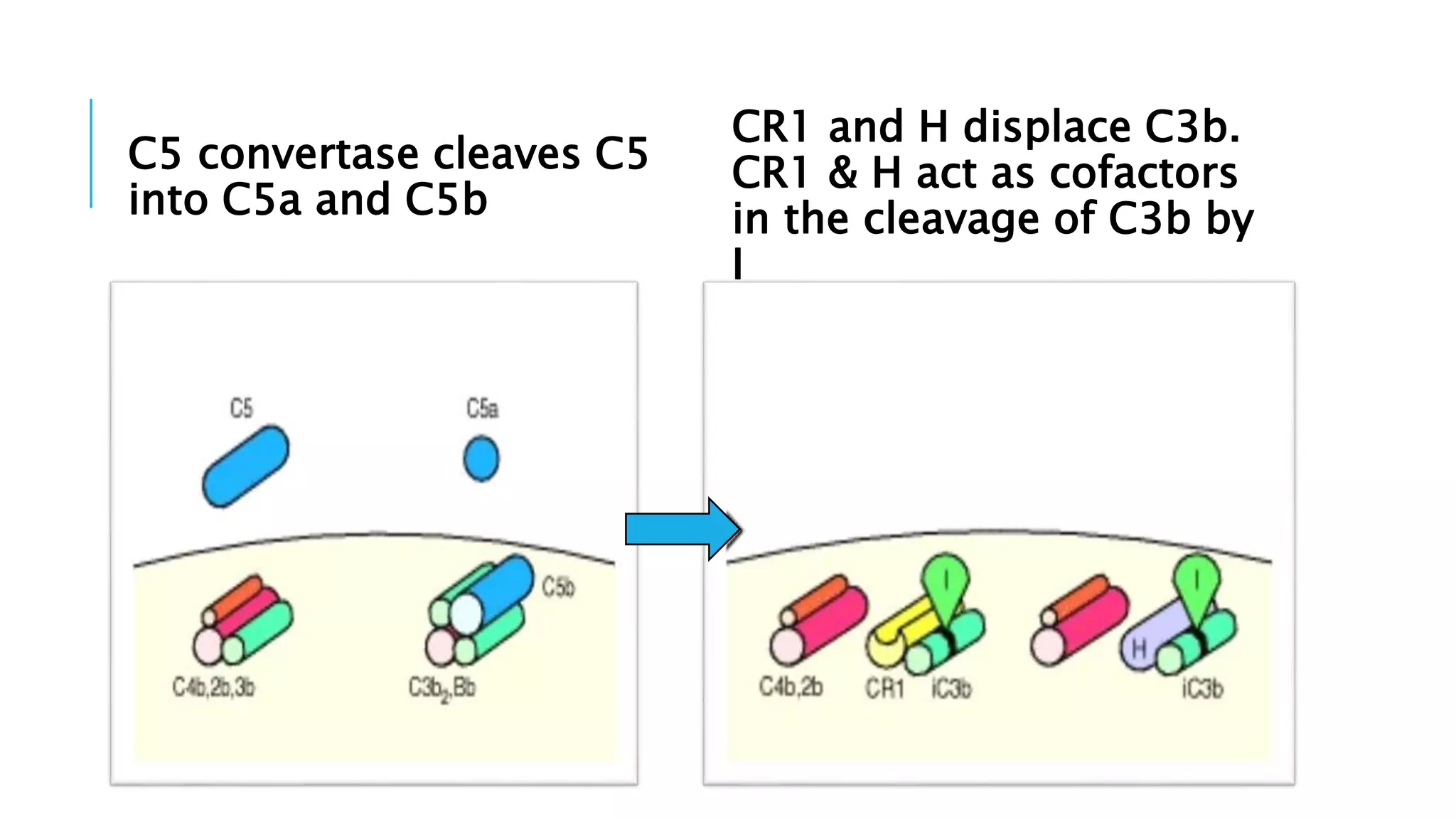
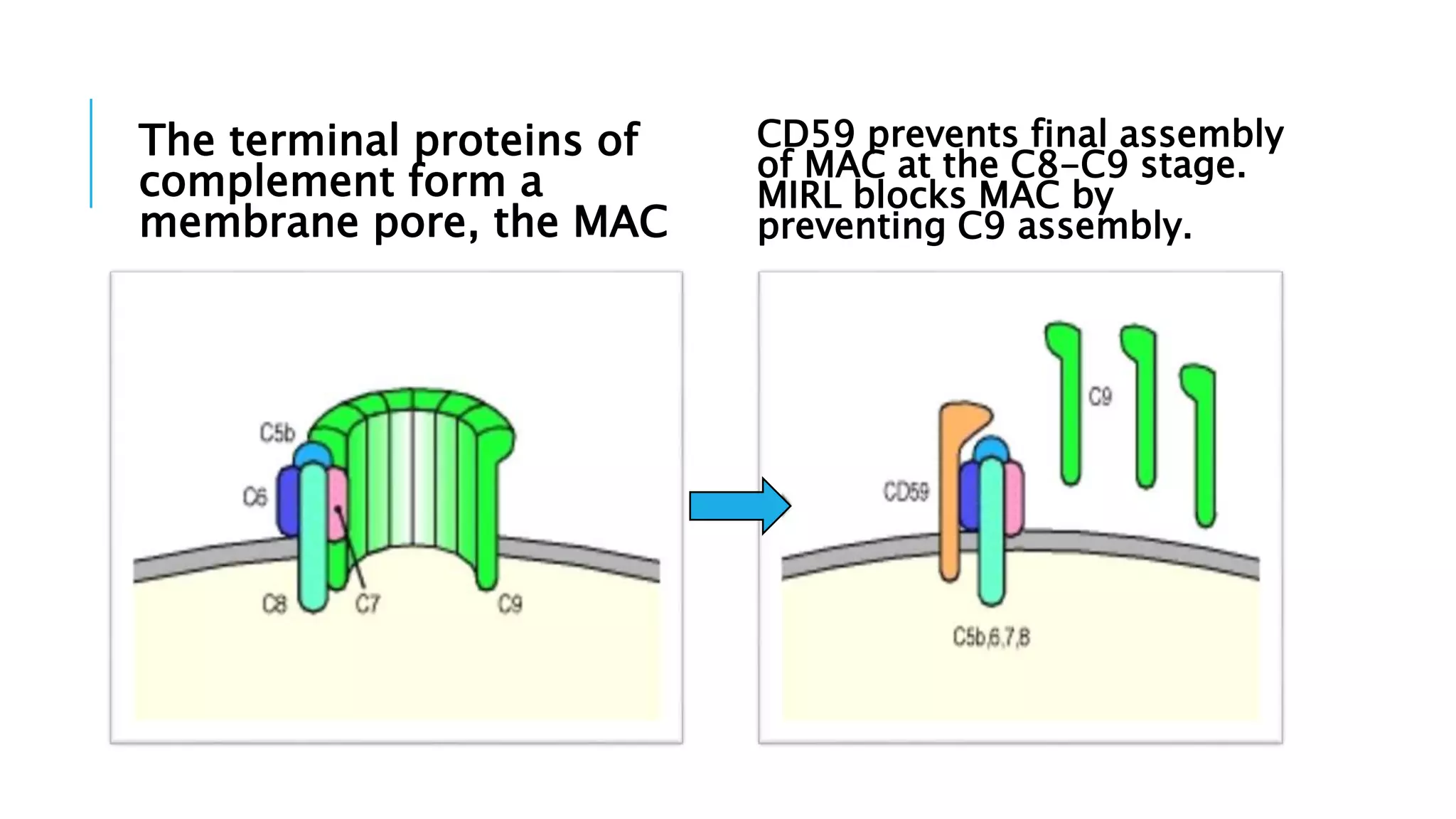
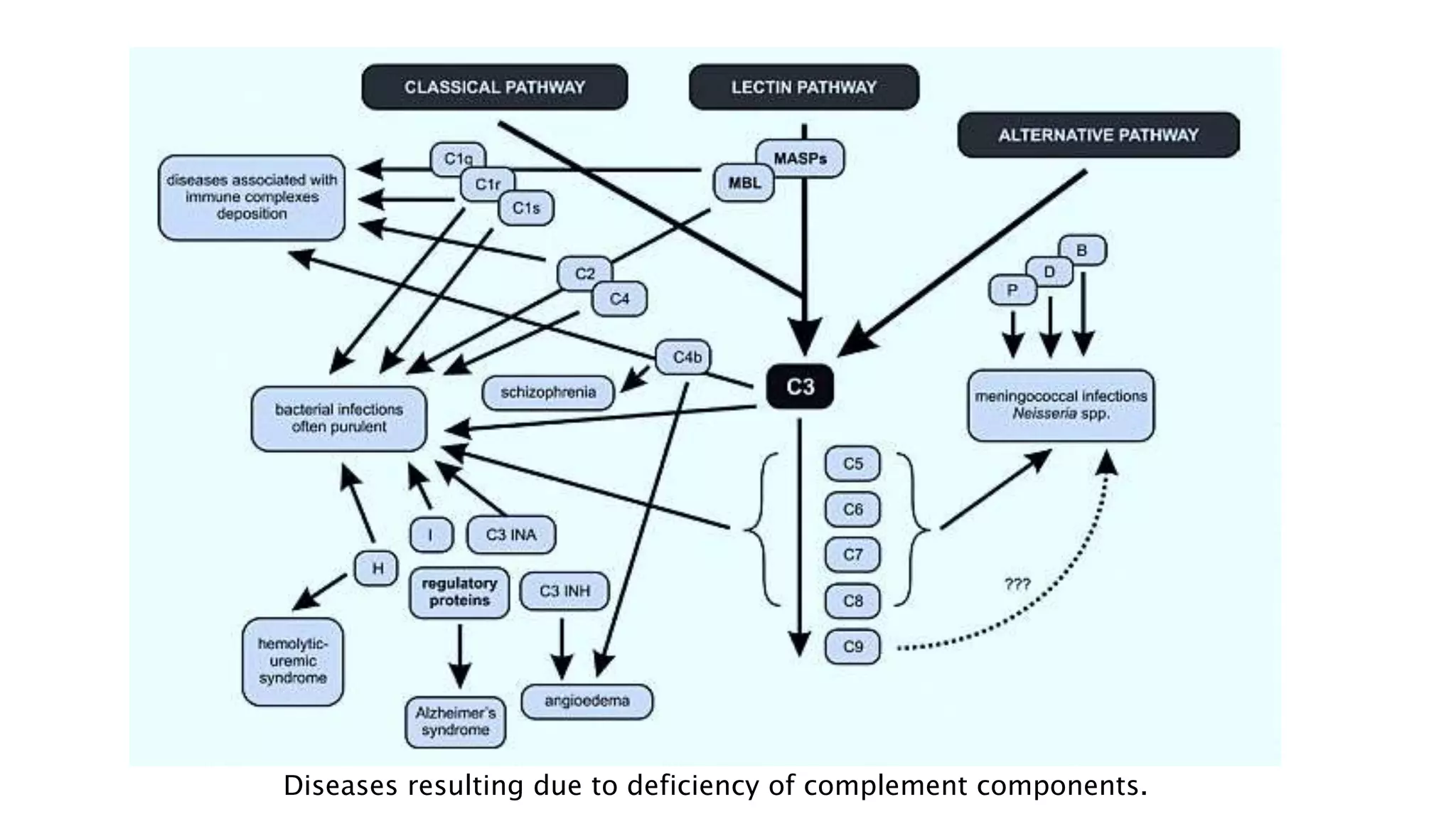
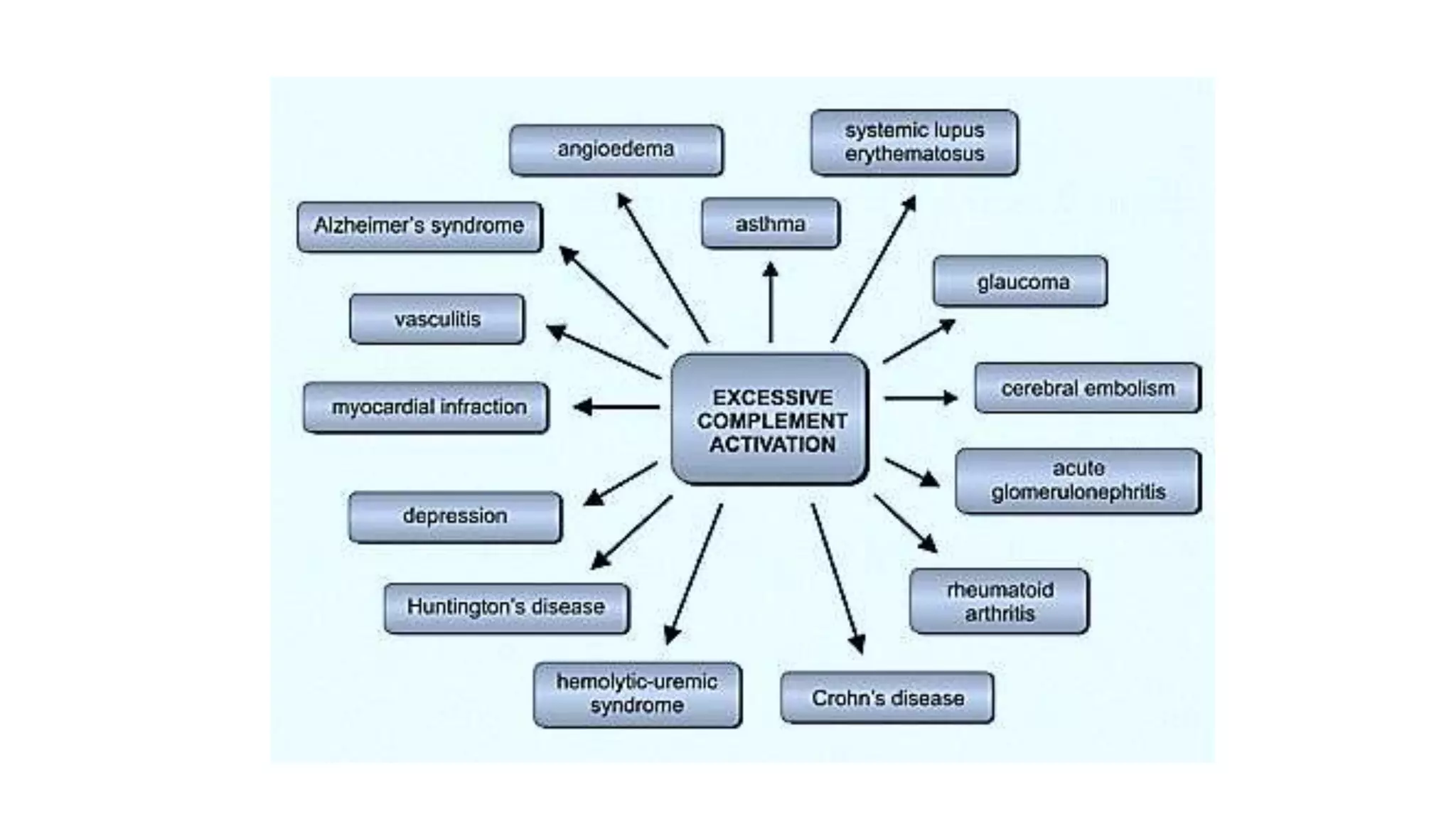
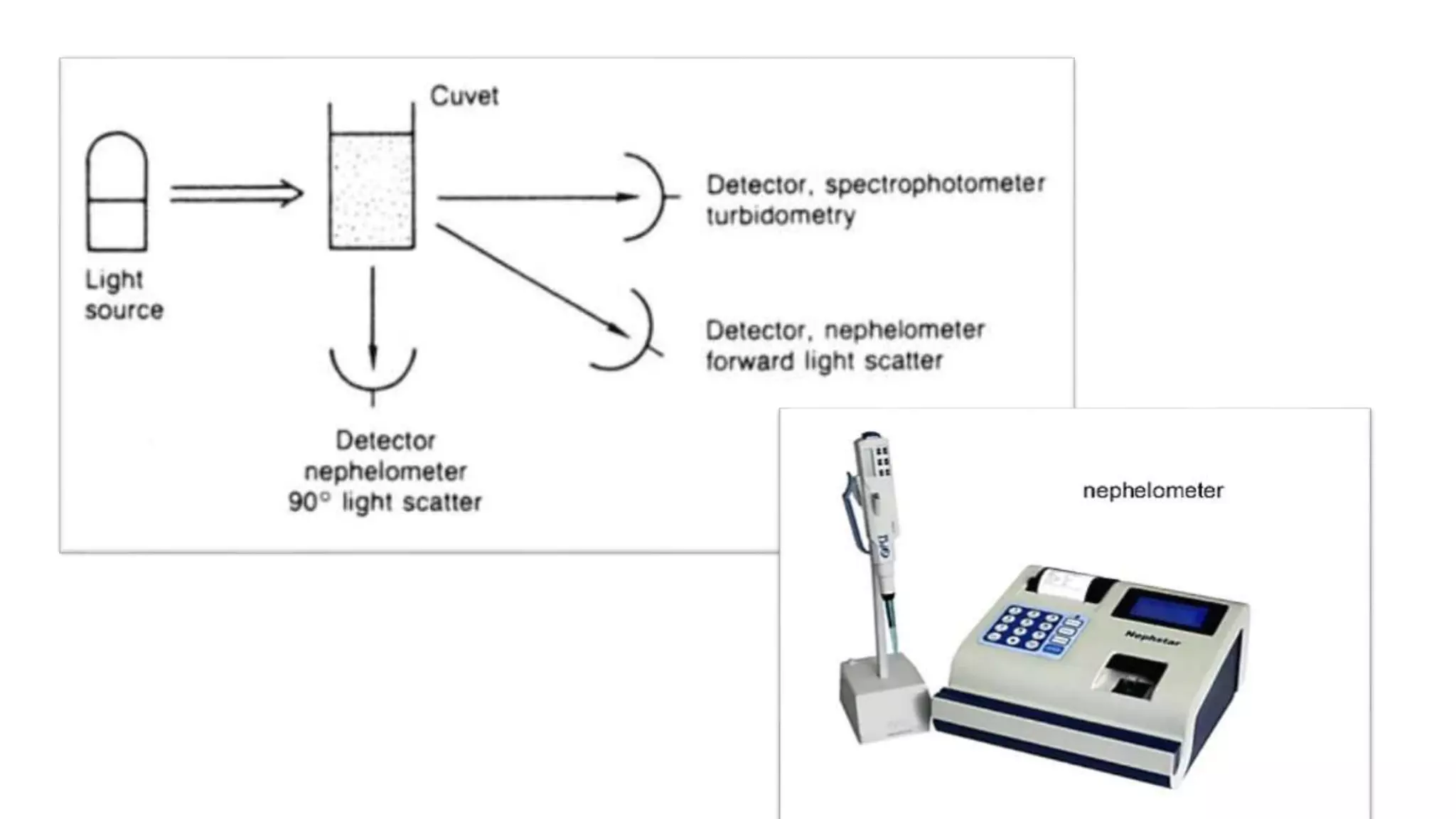
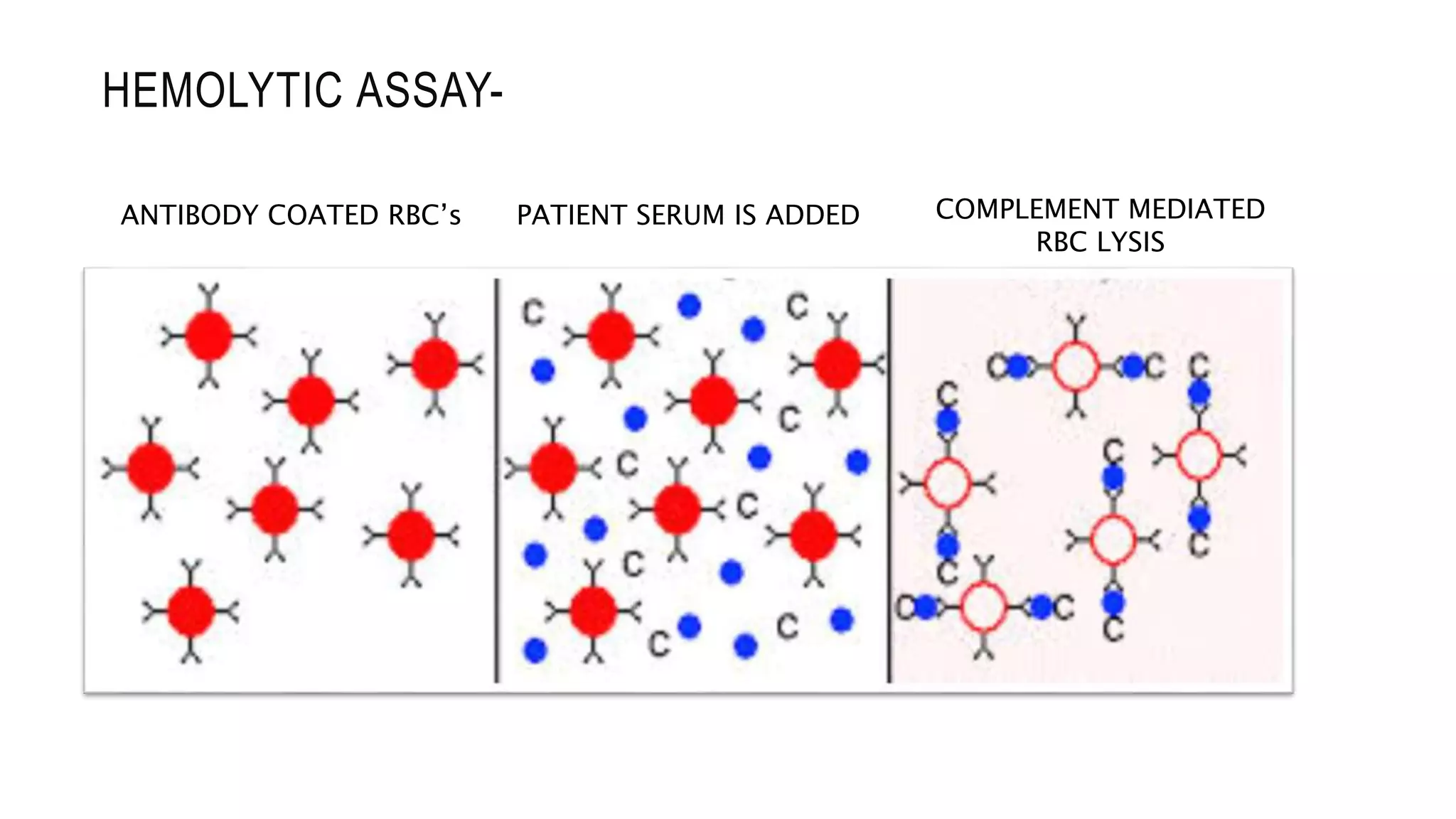
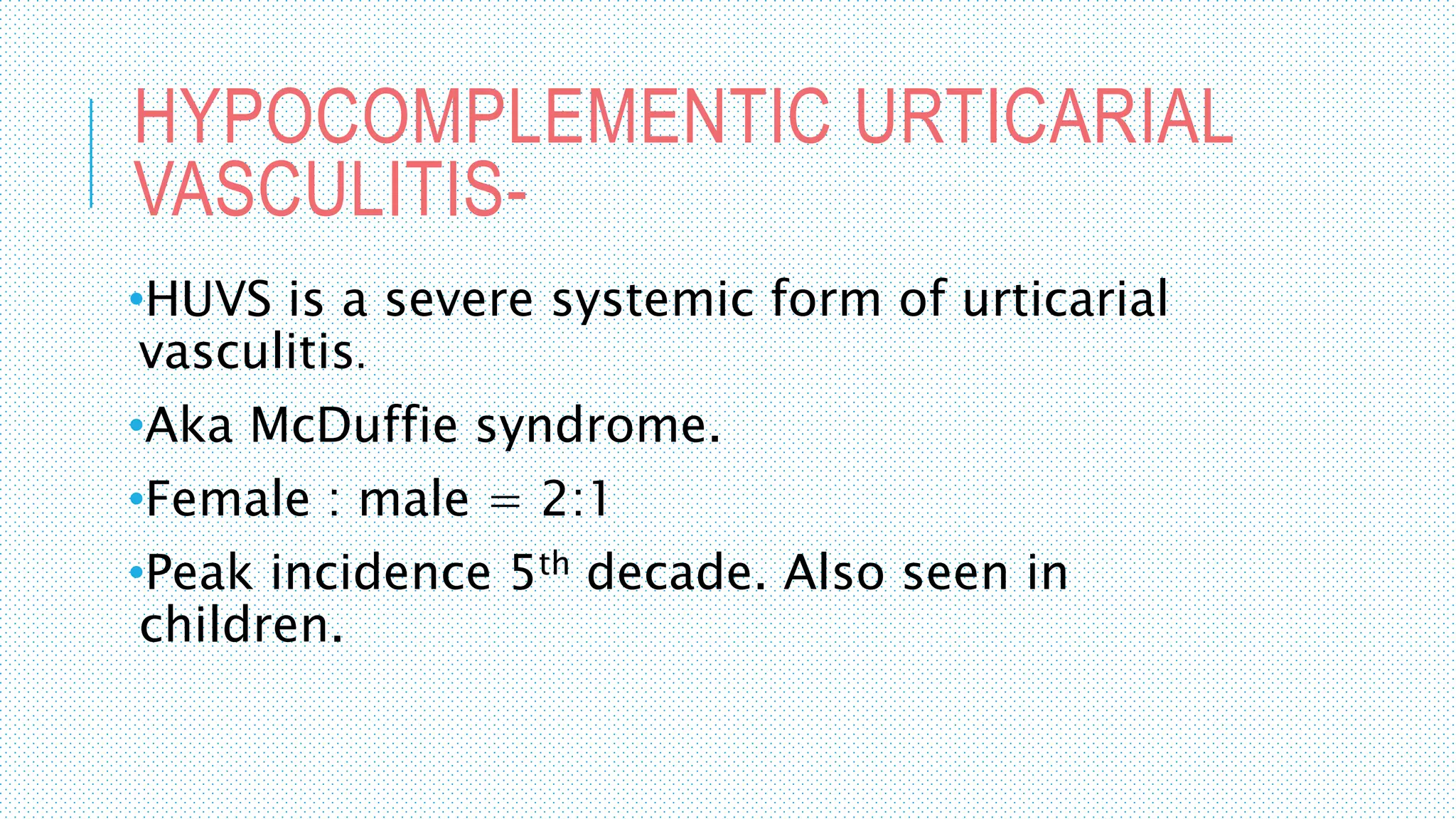
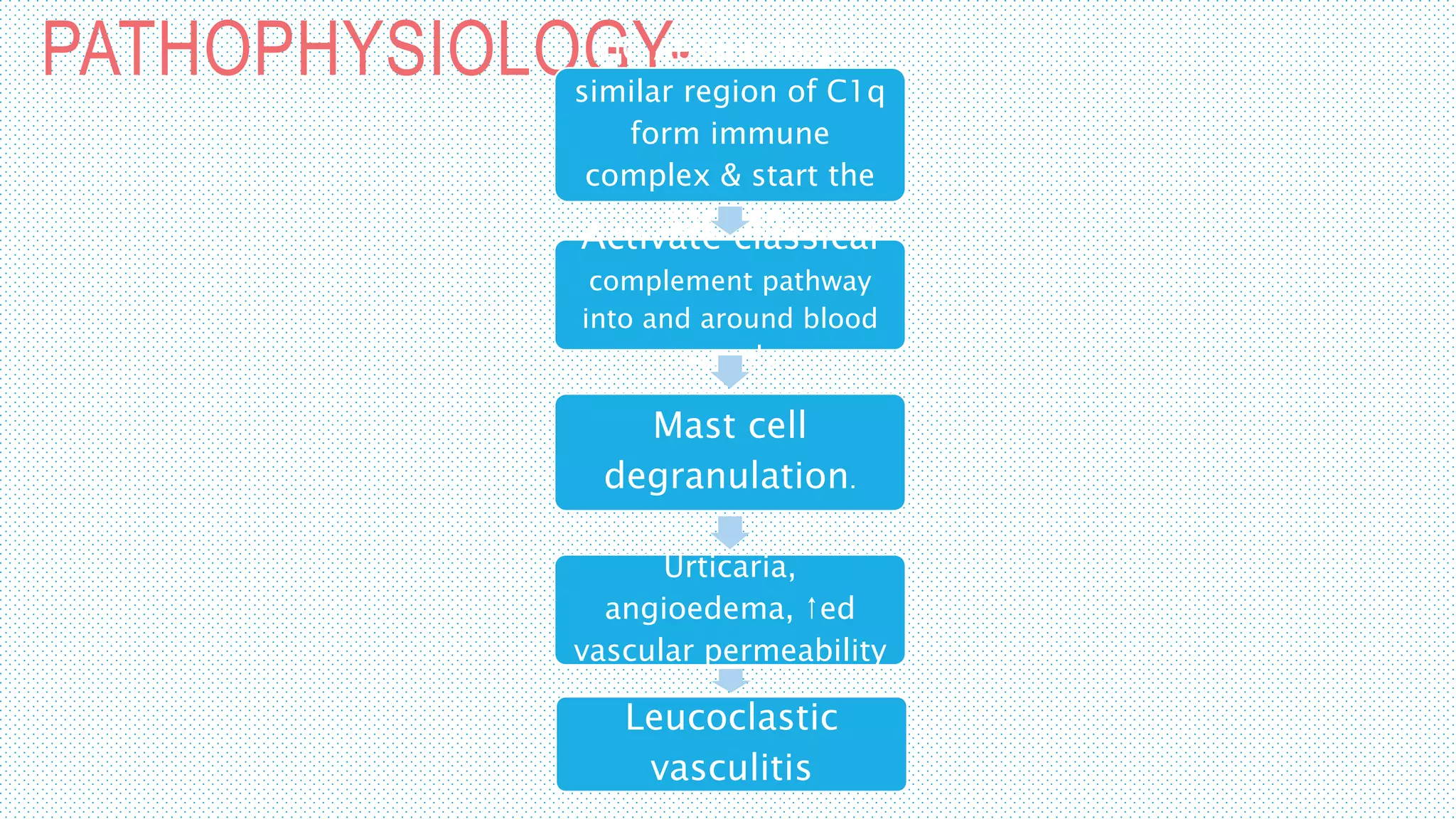
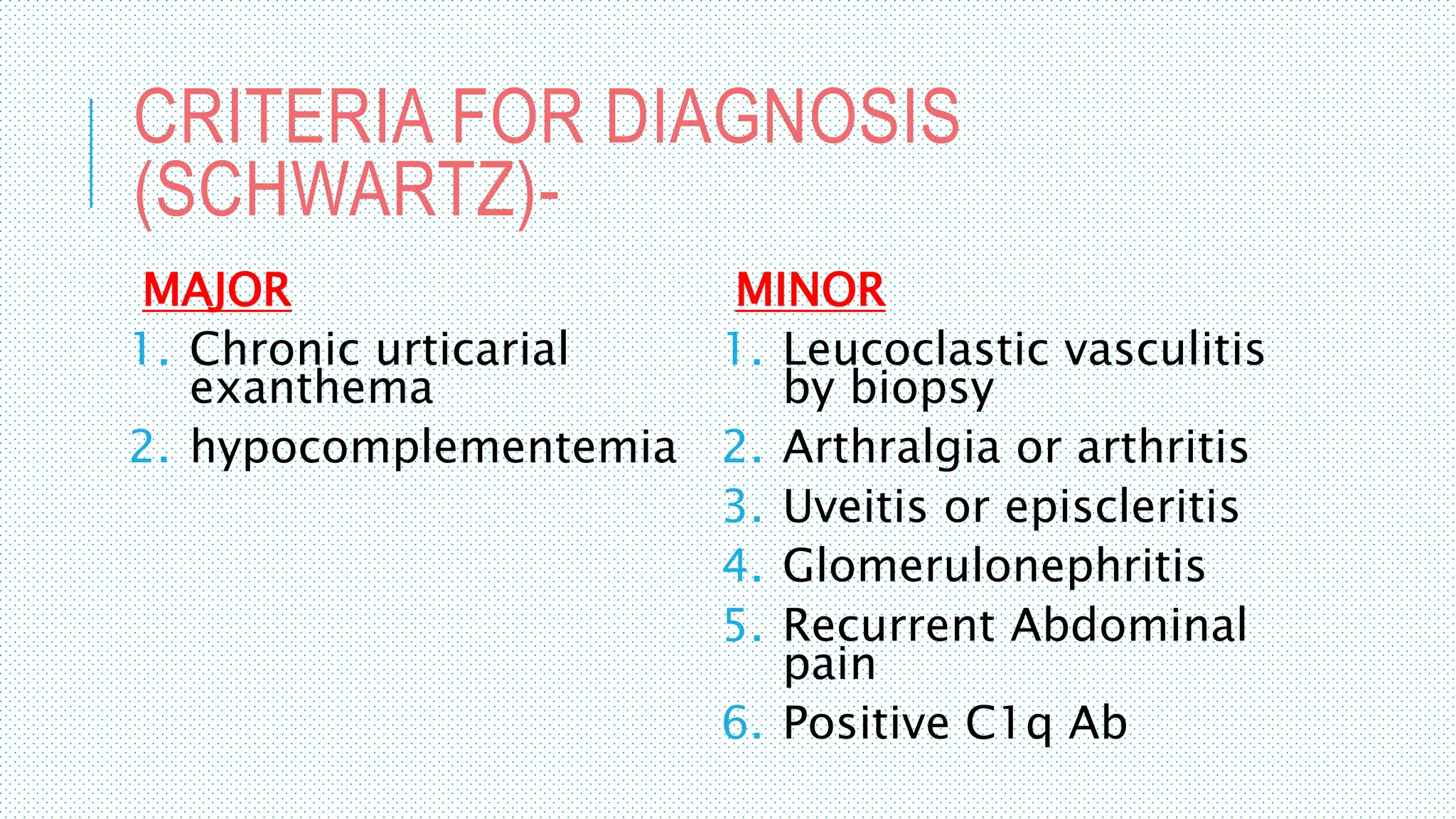
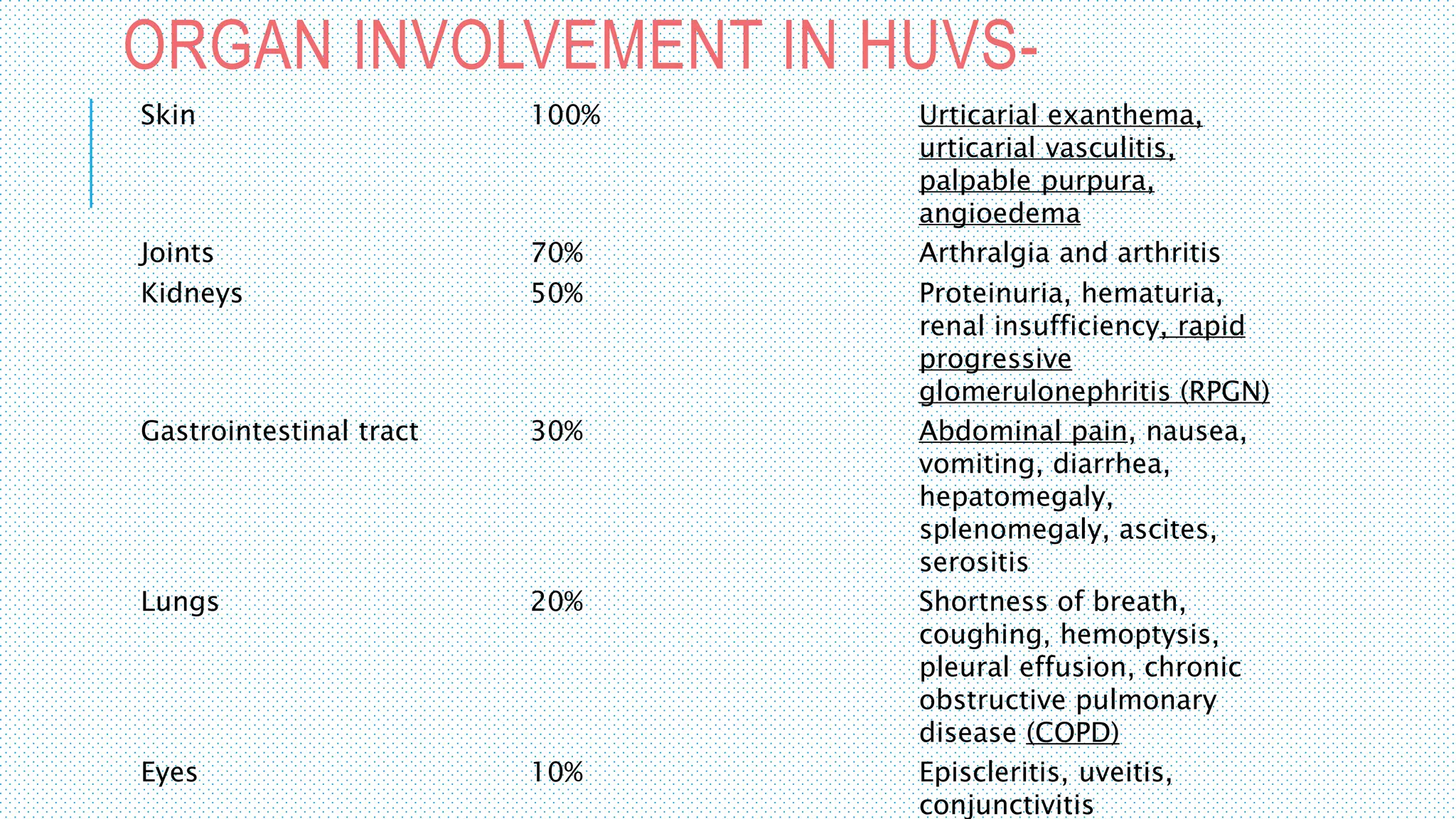
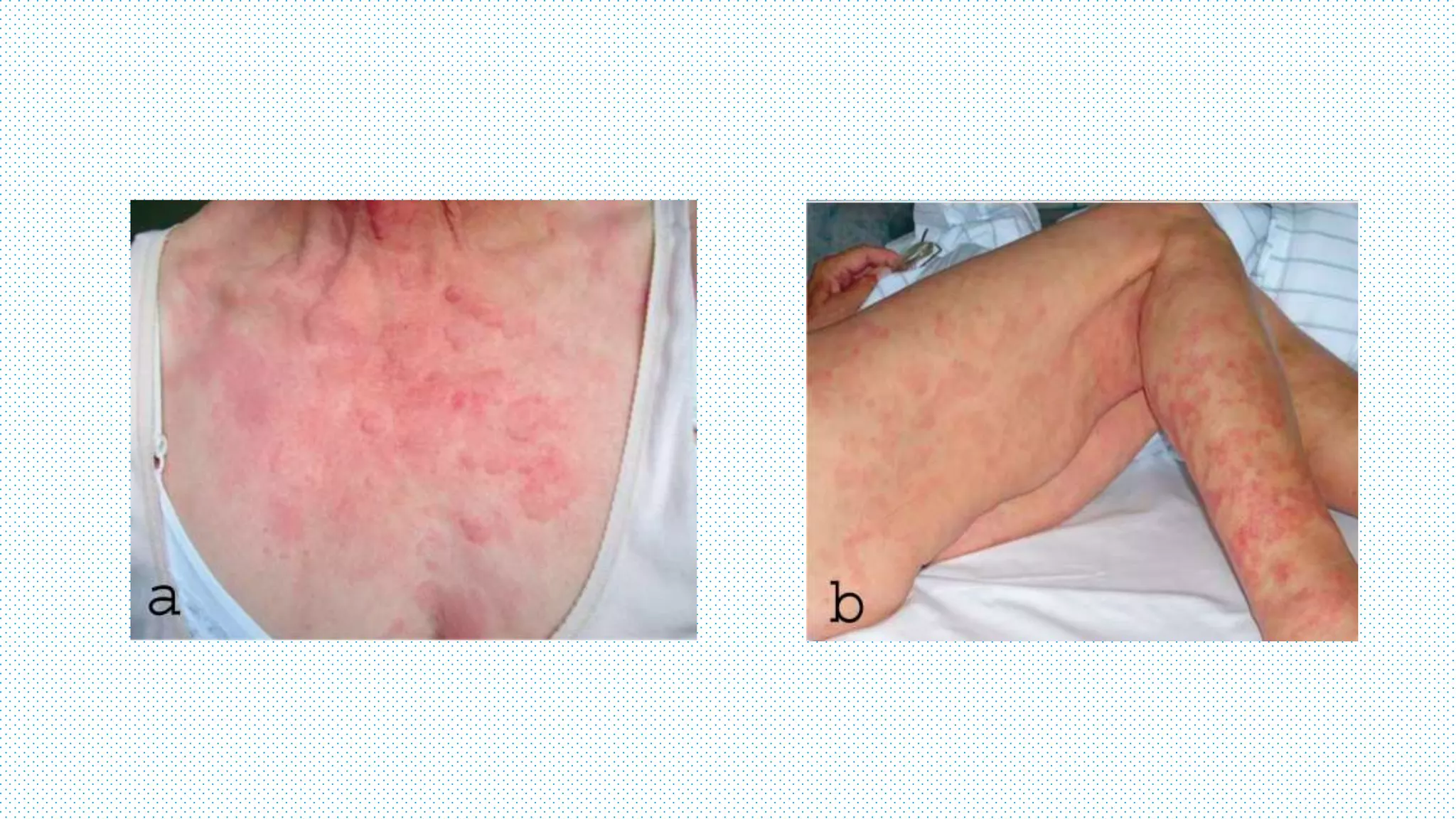
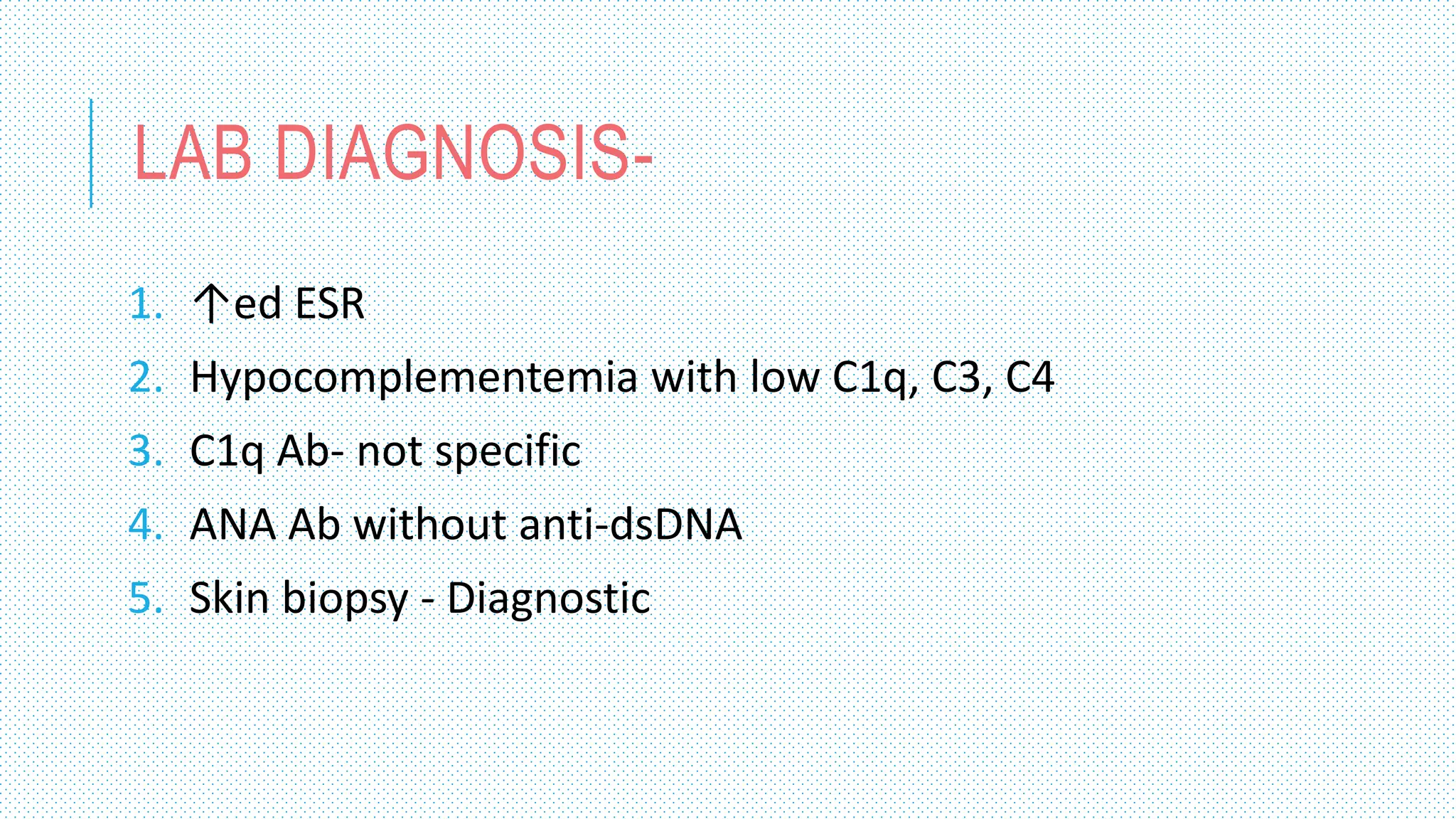
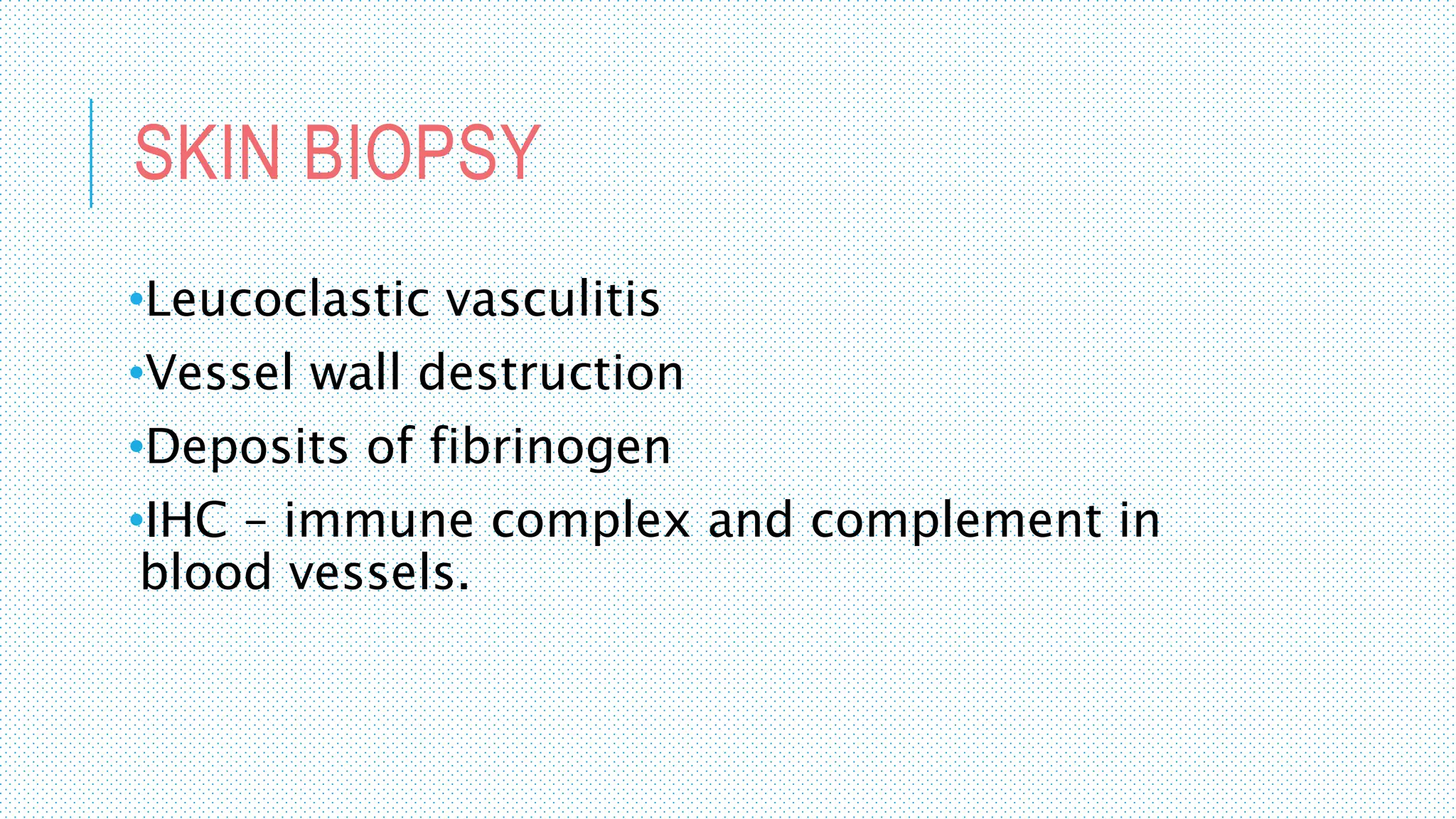
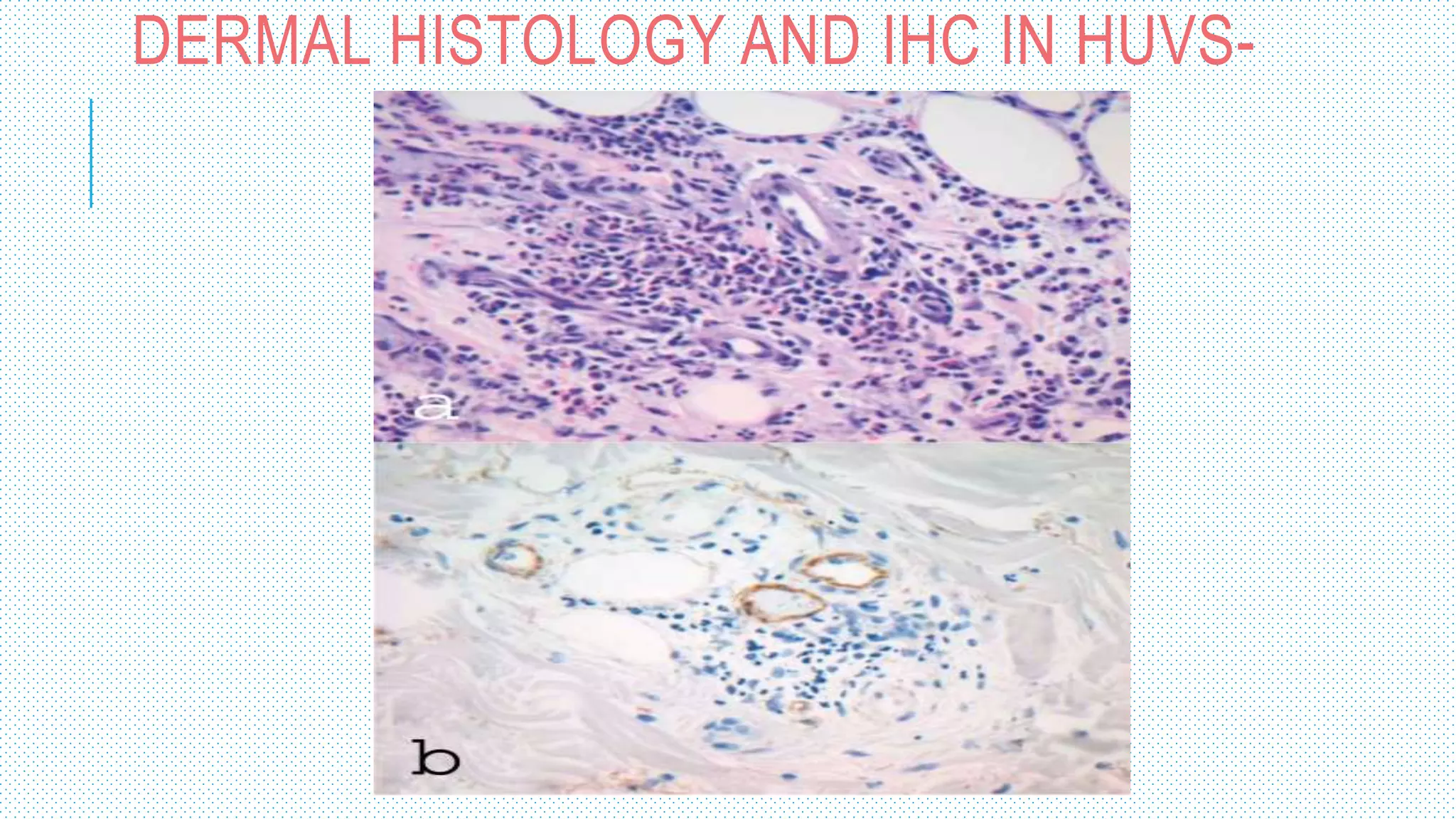
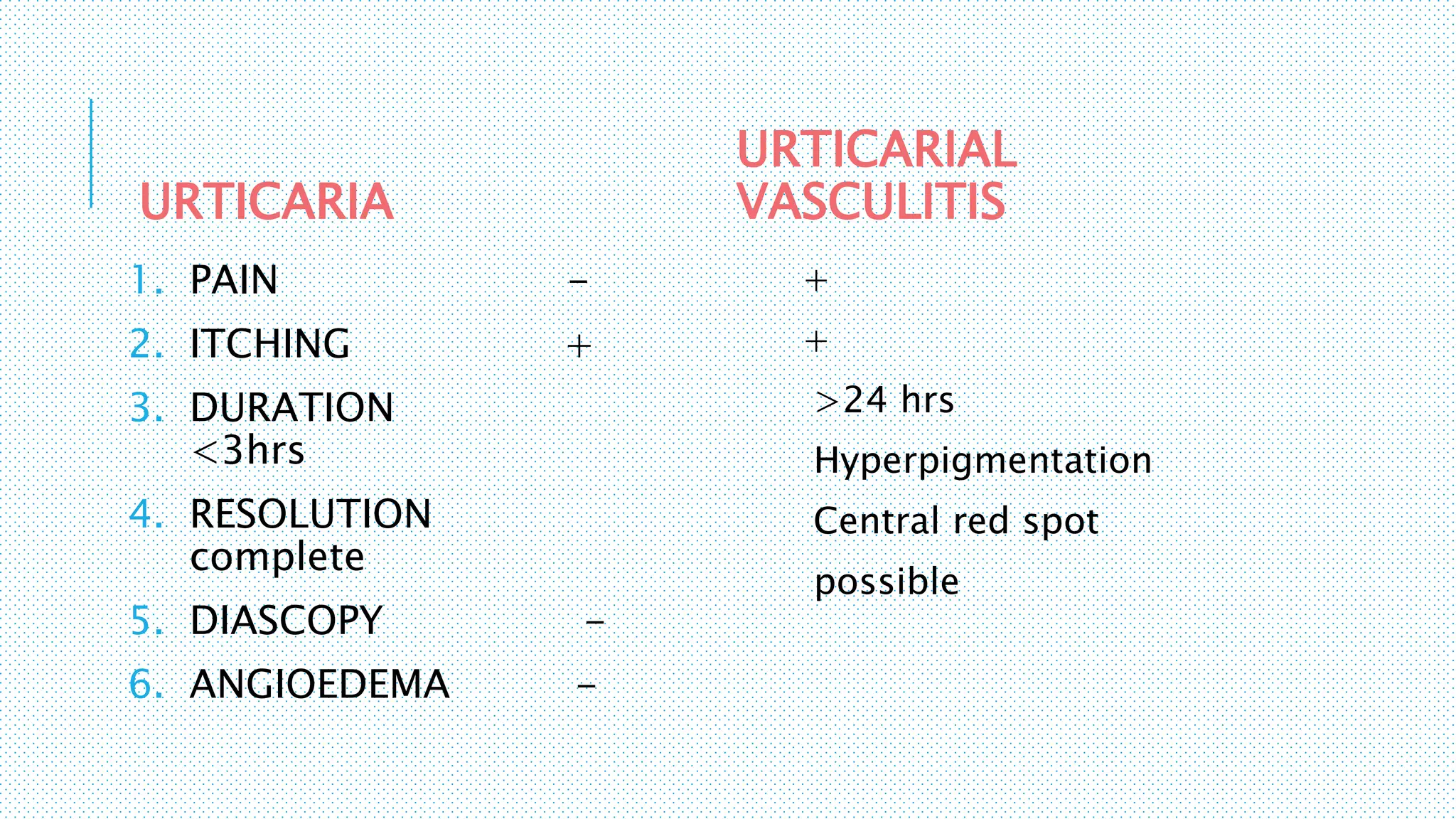
The document discusses the complement system, a crucial component of the immune response that consists of about 40 proteins in plasma, which activate to target pathogens and facilitate inflammation. It details the activation pathways of the complement system, including classical, lectin, and alternative pathways, as well as regulatory mechanisms that prevent excessive activation. Additionally, it covers the condition of hypocomplementic urticarial vasculitis (HUV), its pathophysiology, diagnostic criteria, and organ involvement.