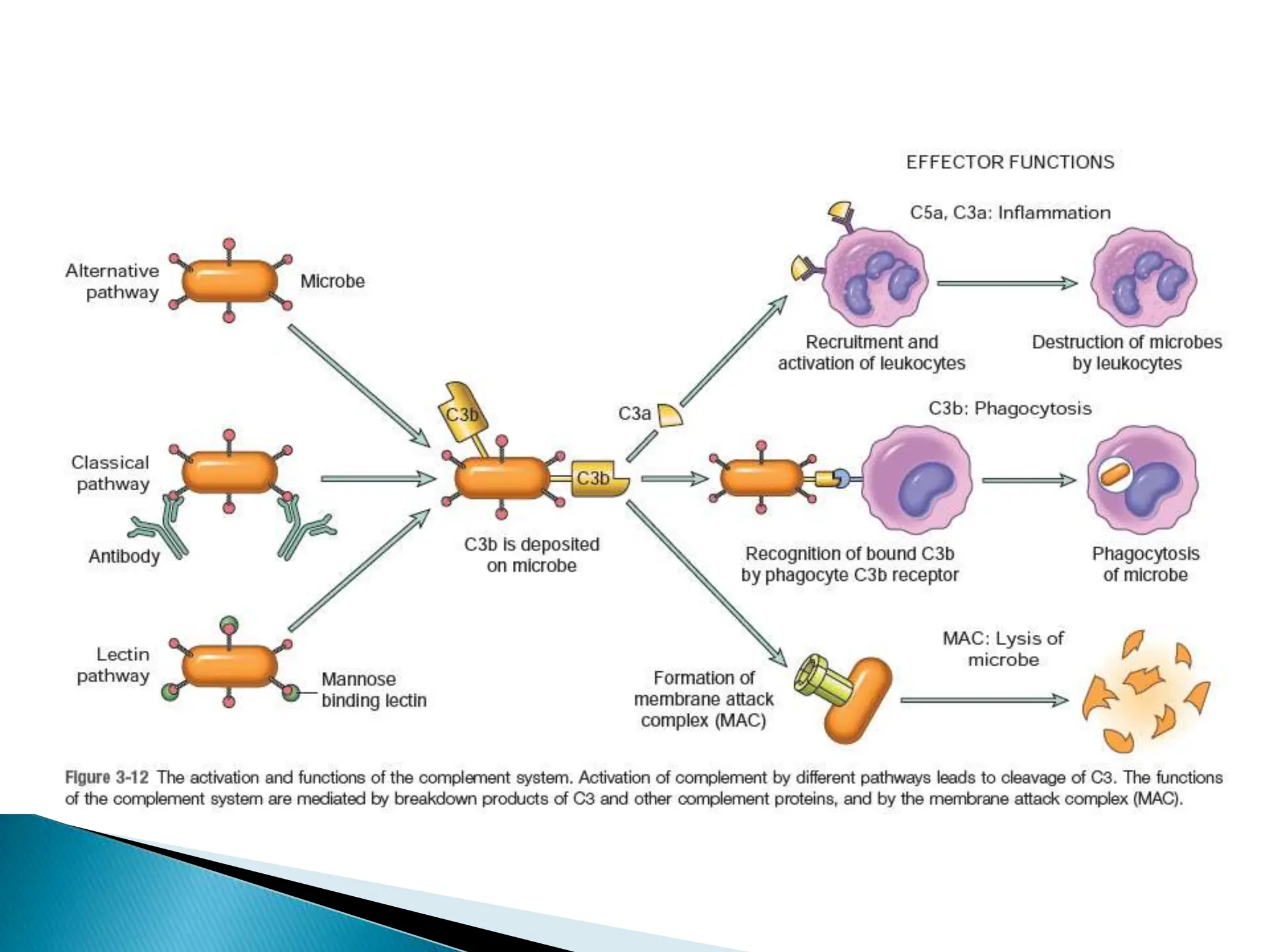
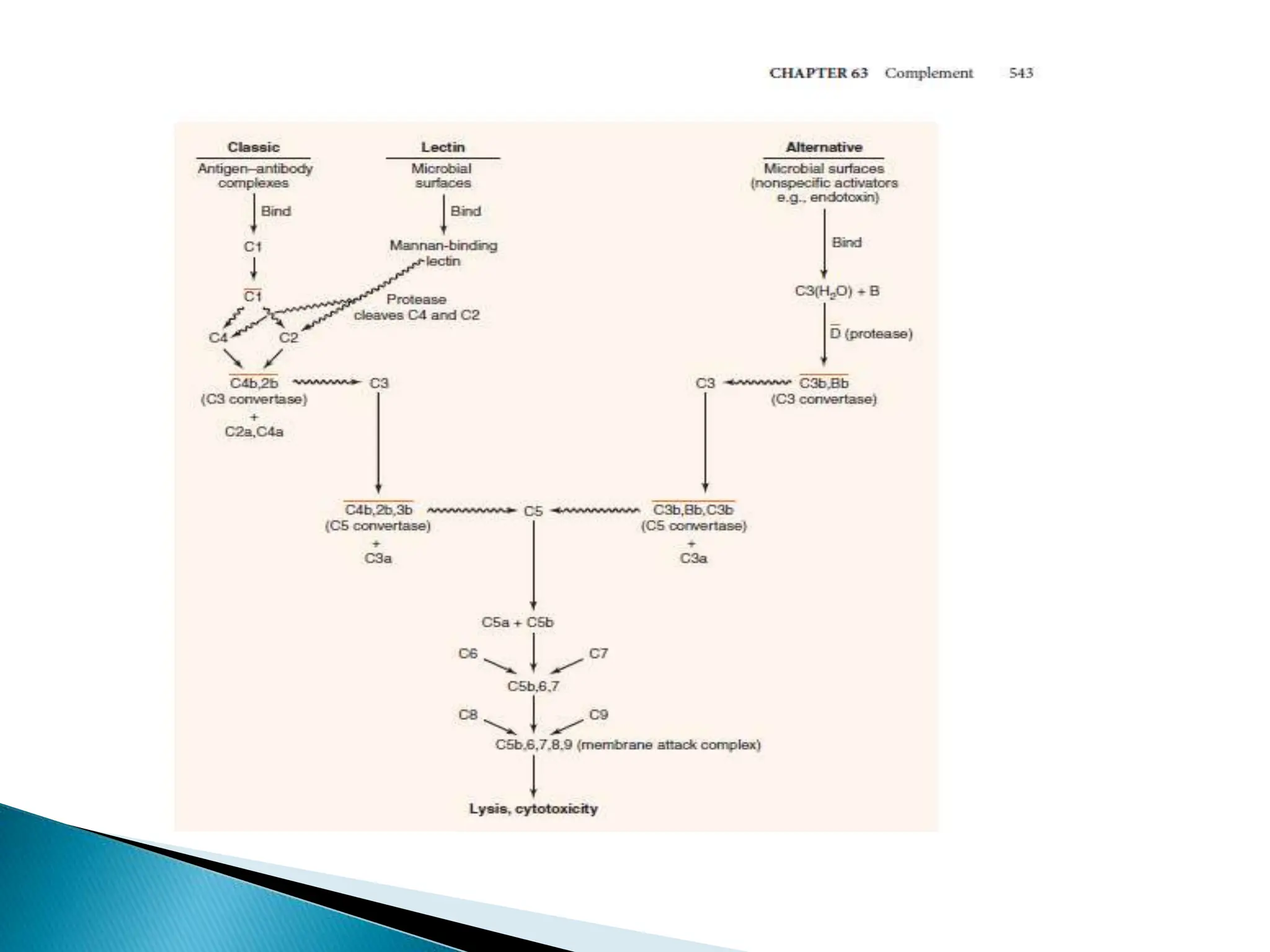
The complement system consists of 20 proteins that complement the effects of antibodies in the immune system. It plays an important role in innate immunity through lysing cells, generating mediators, and opsonization. The three complement pathways - classical, lectin, and alternative - are activated and converge on C3b, which opsonizes bacteria and generates the membrane attack complex. Complement is tightly regulated to prevent damage to host cells. Deficiencies or dysregulation of complement components can increase susceptibility to infection or cause diseases like hereditary angioedema or hemolytic uremic syndrome.