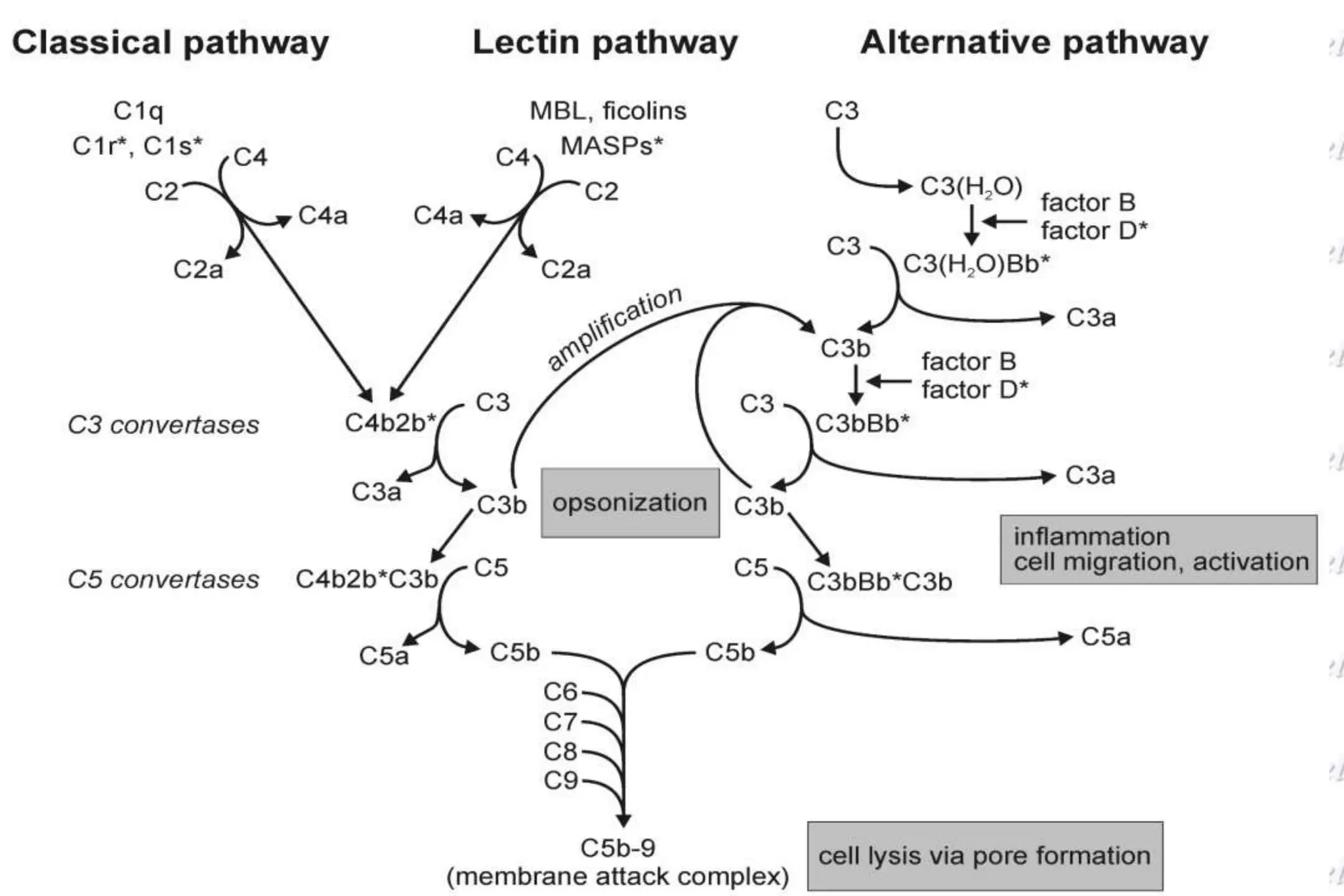
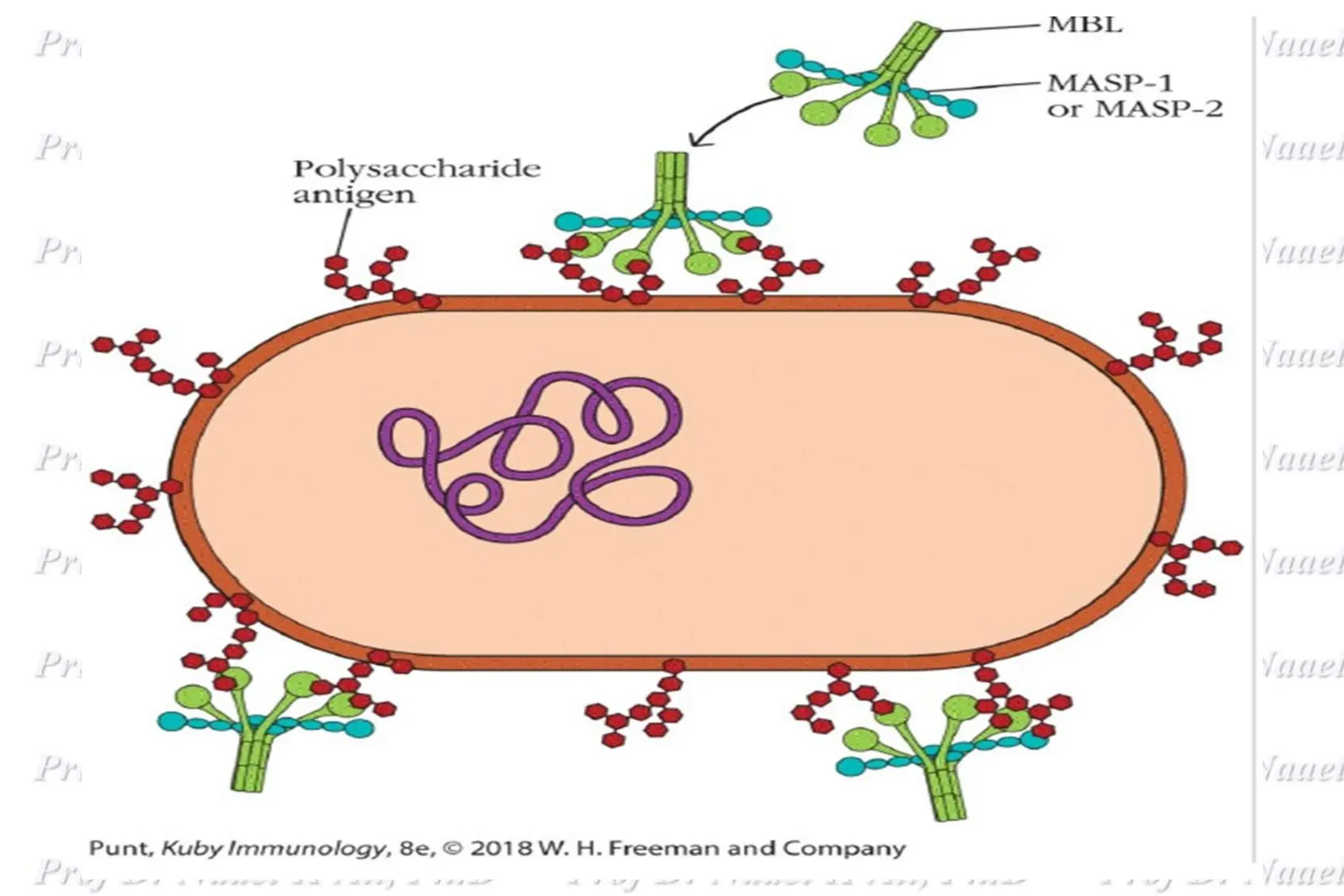
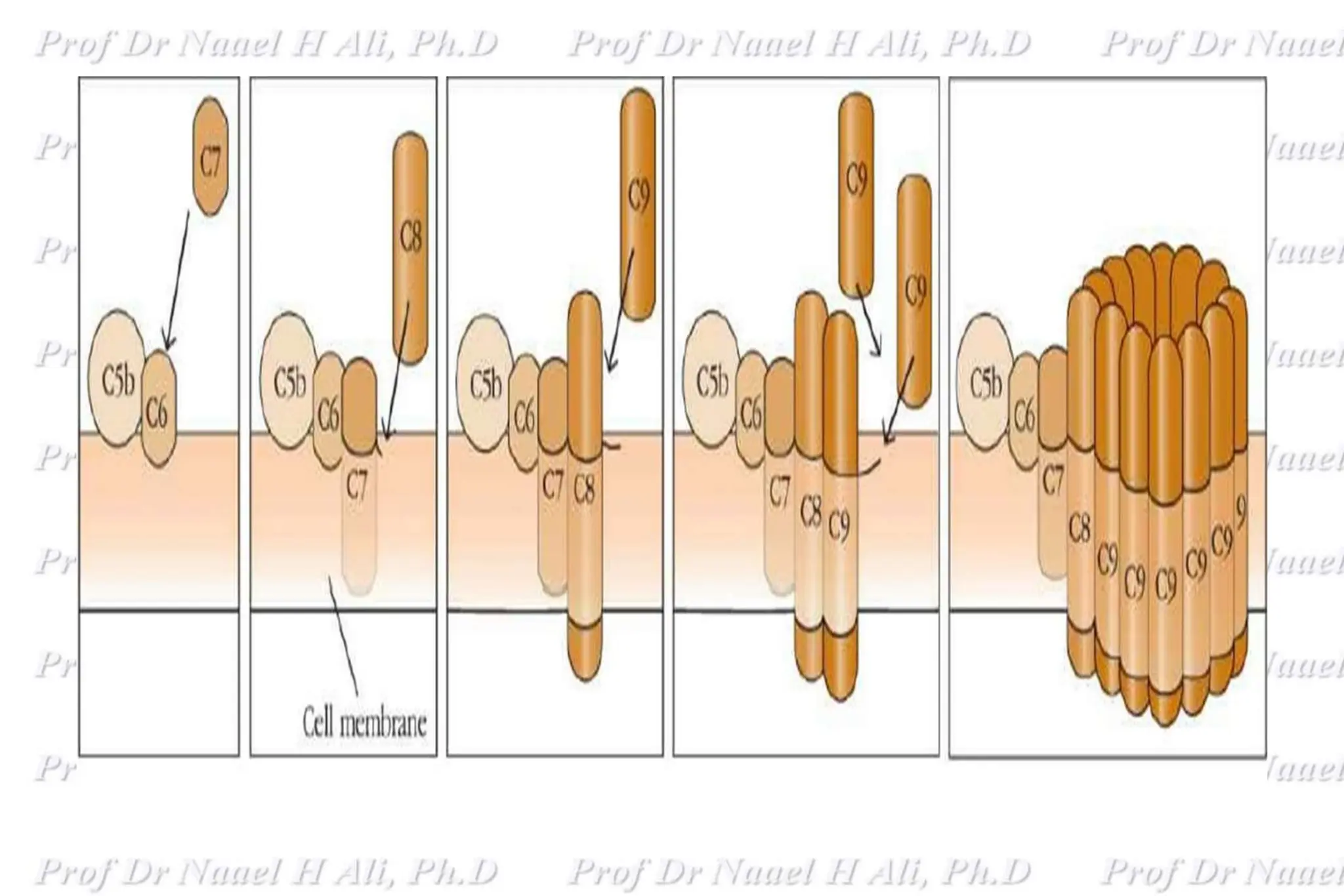
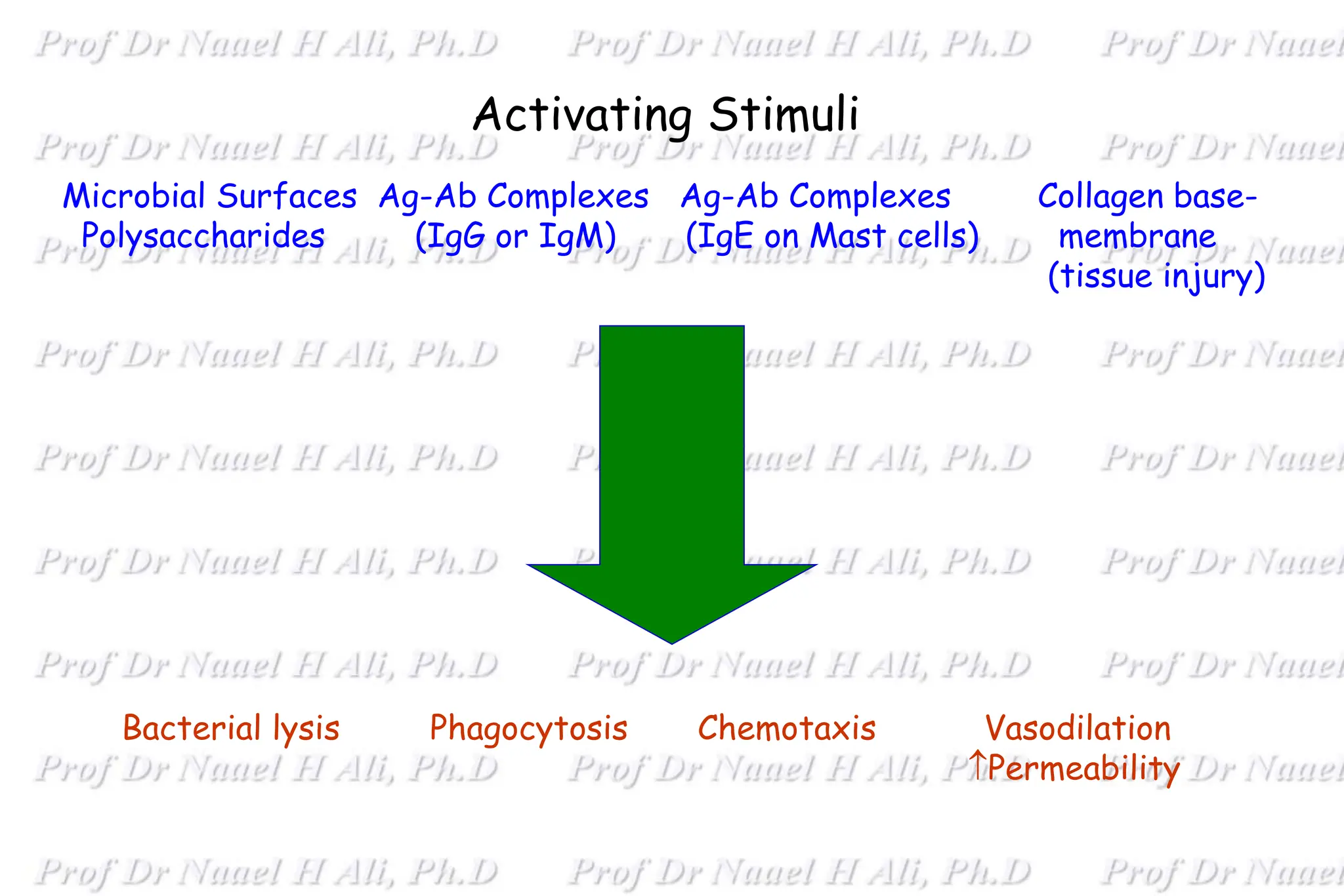
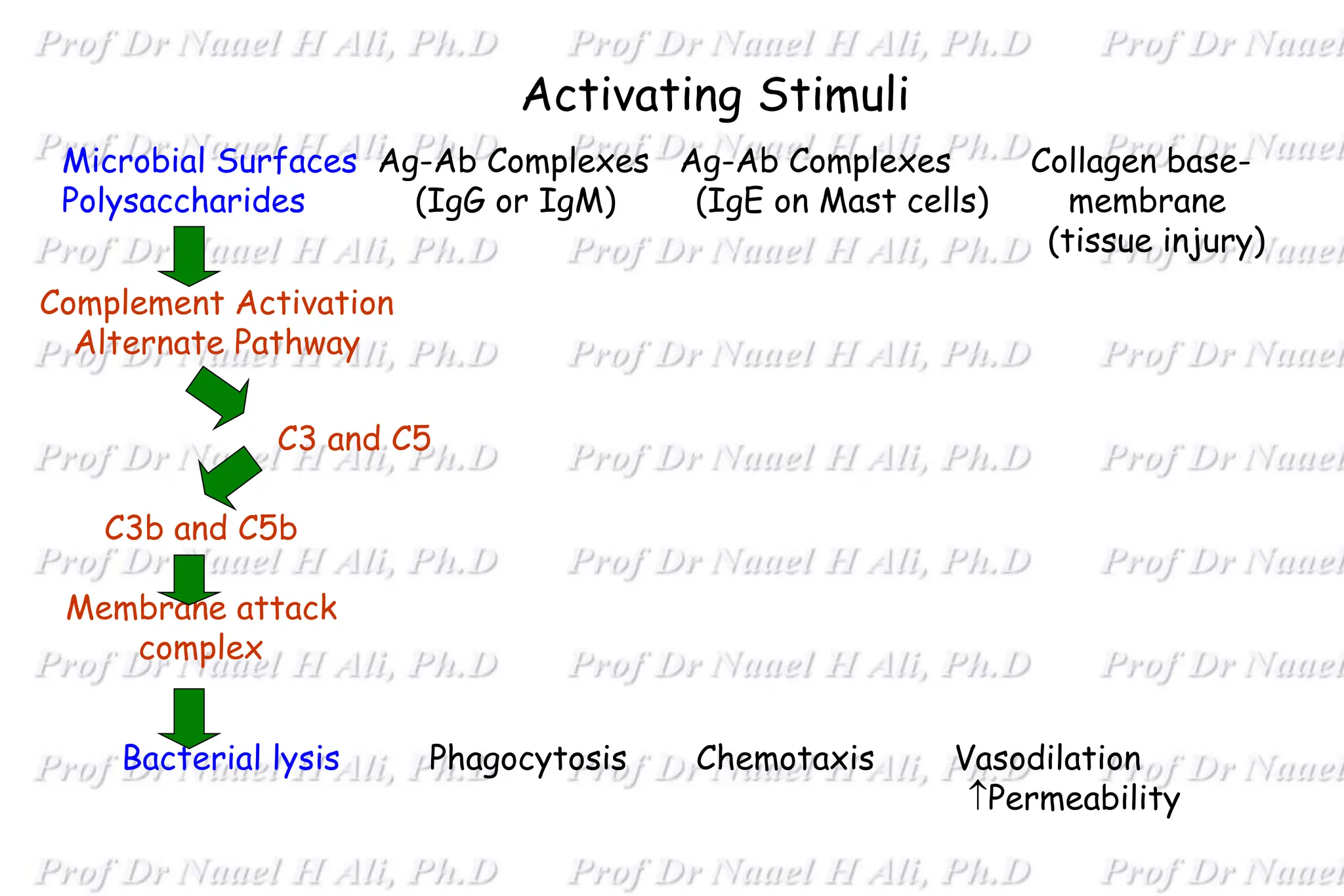
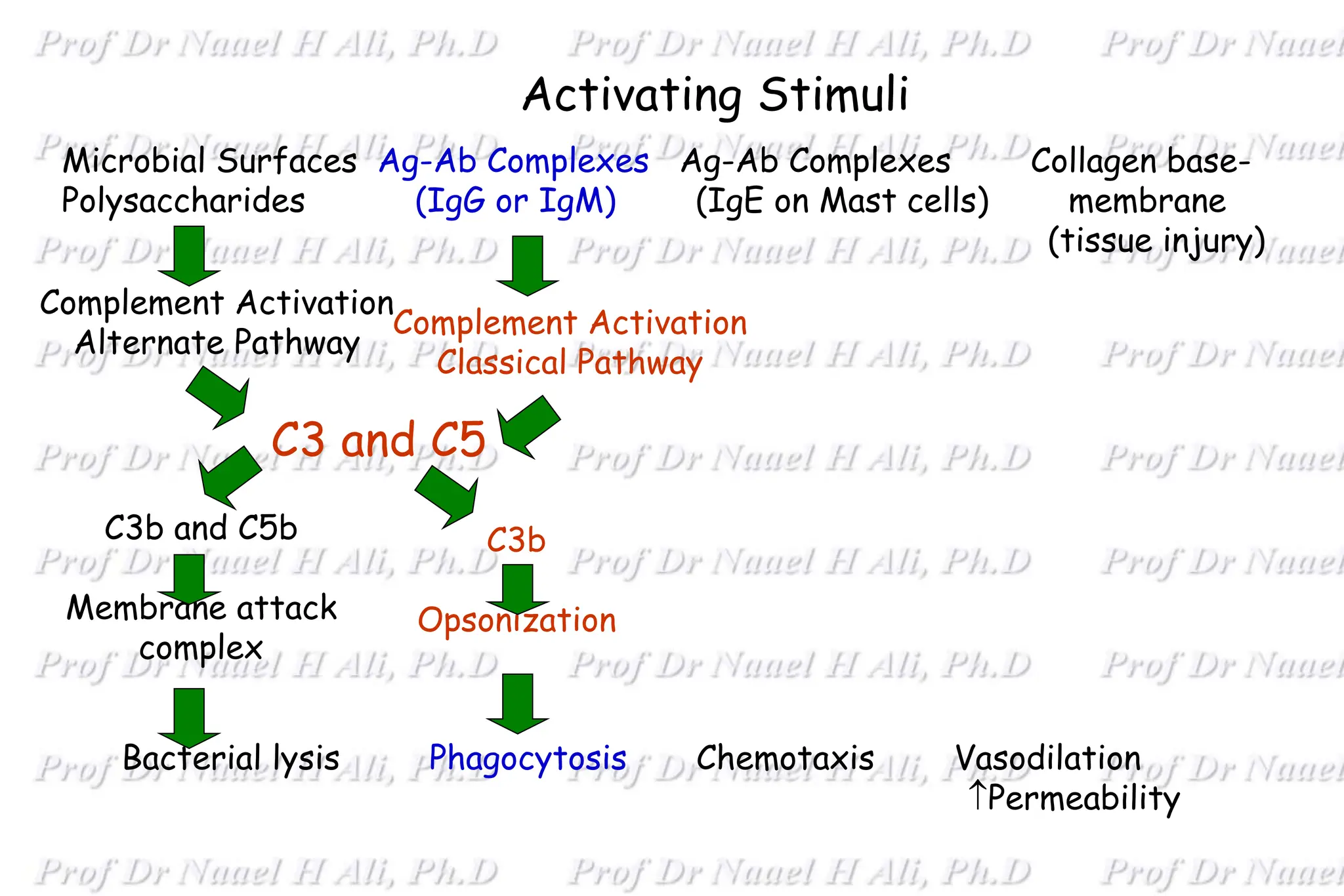
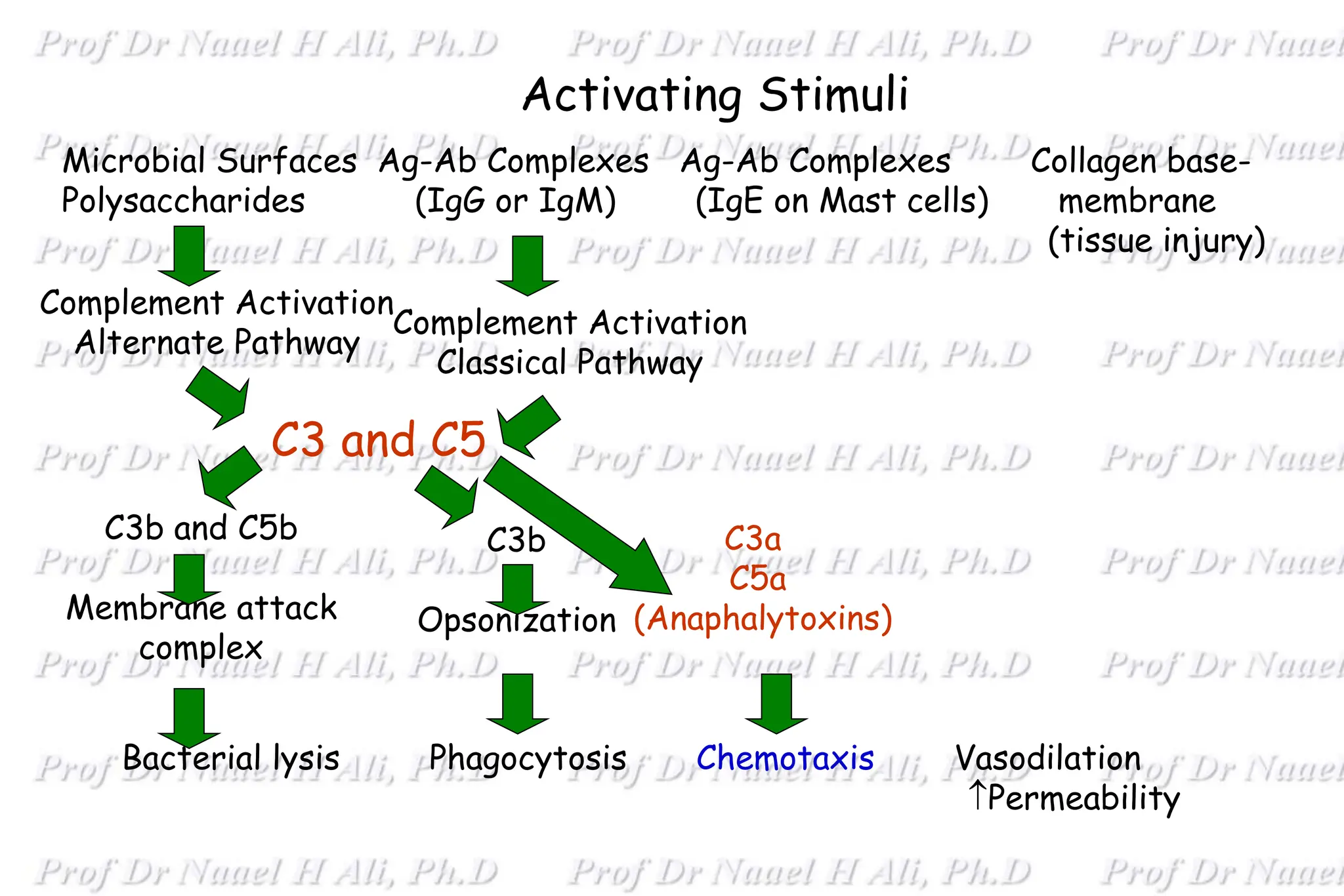
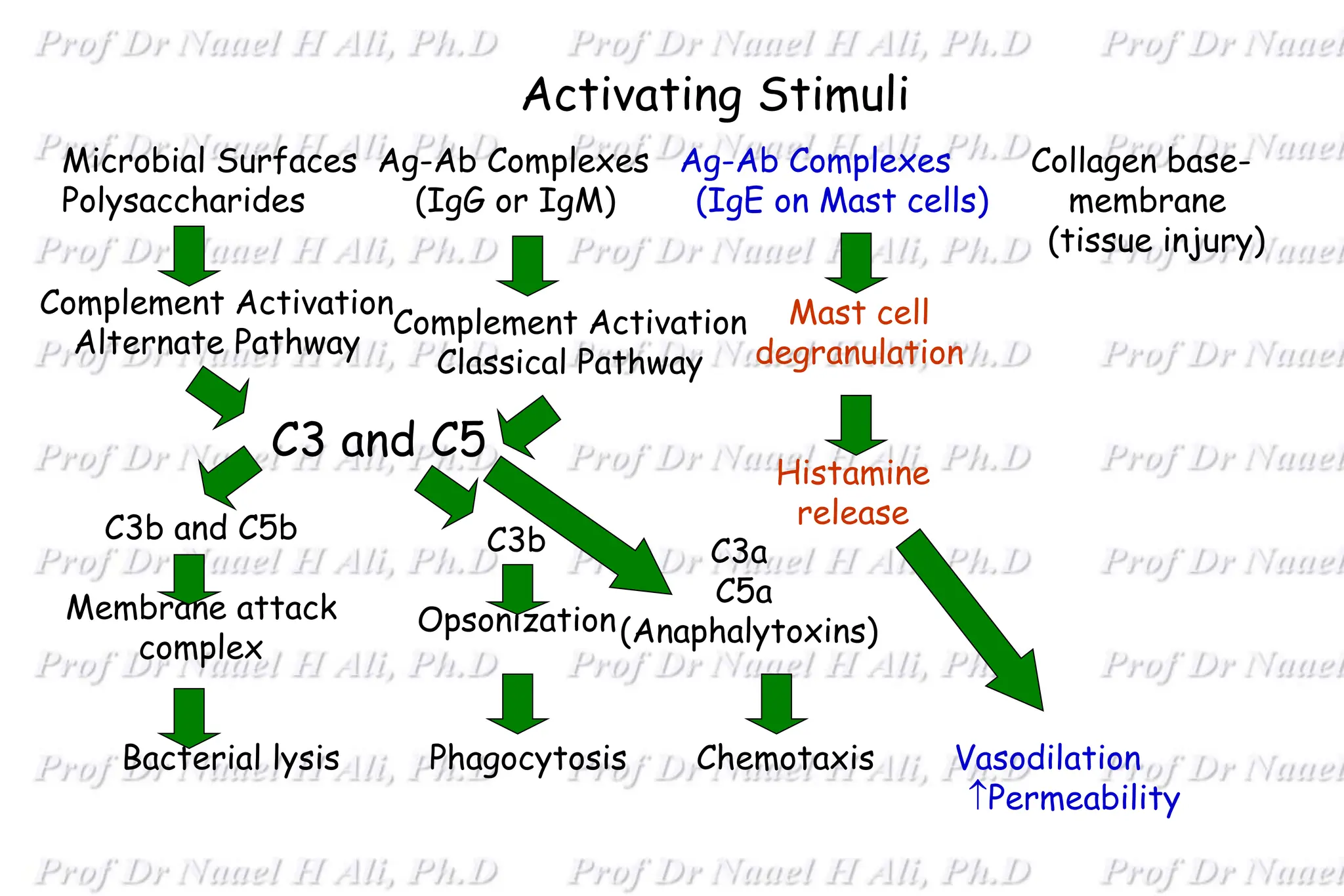
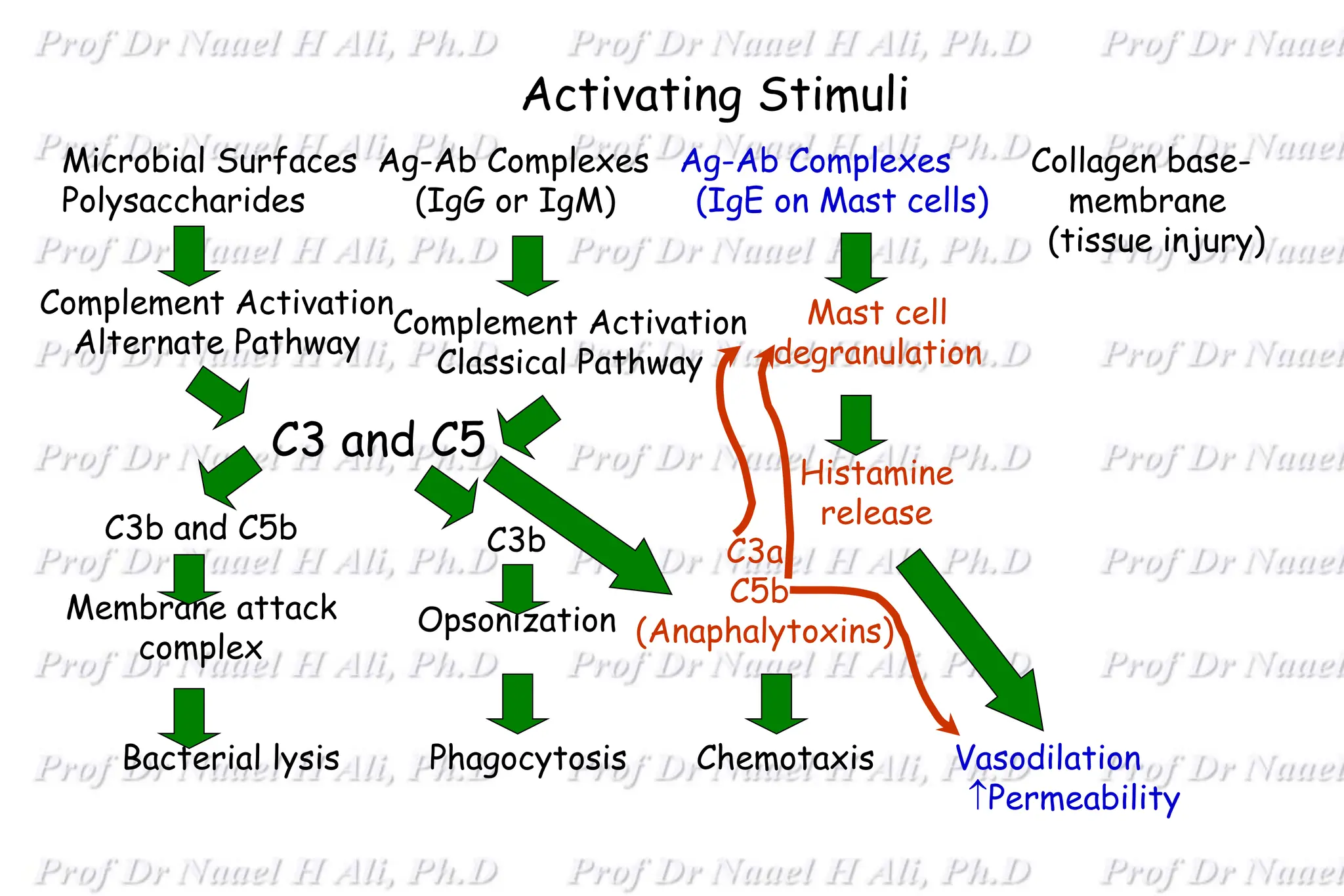
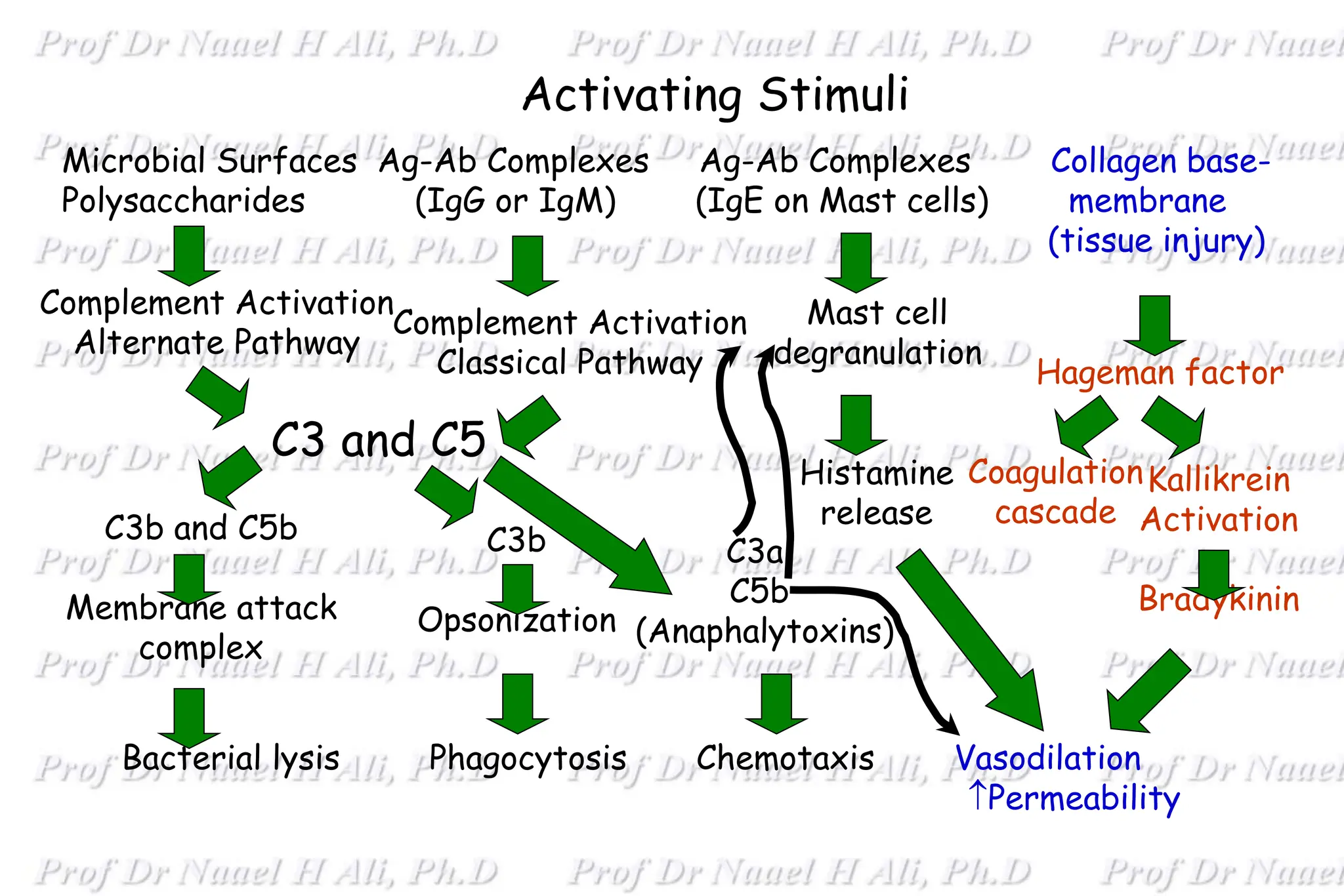
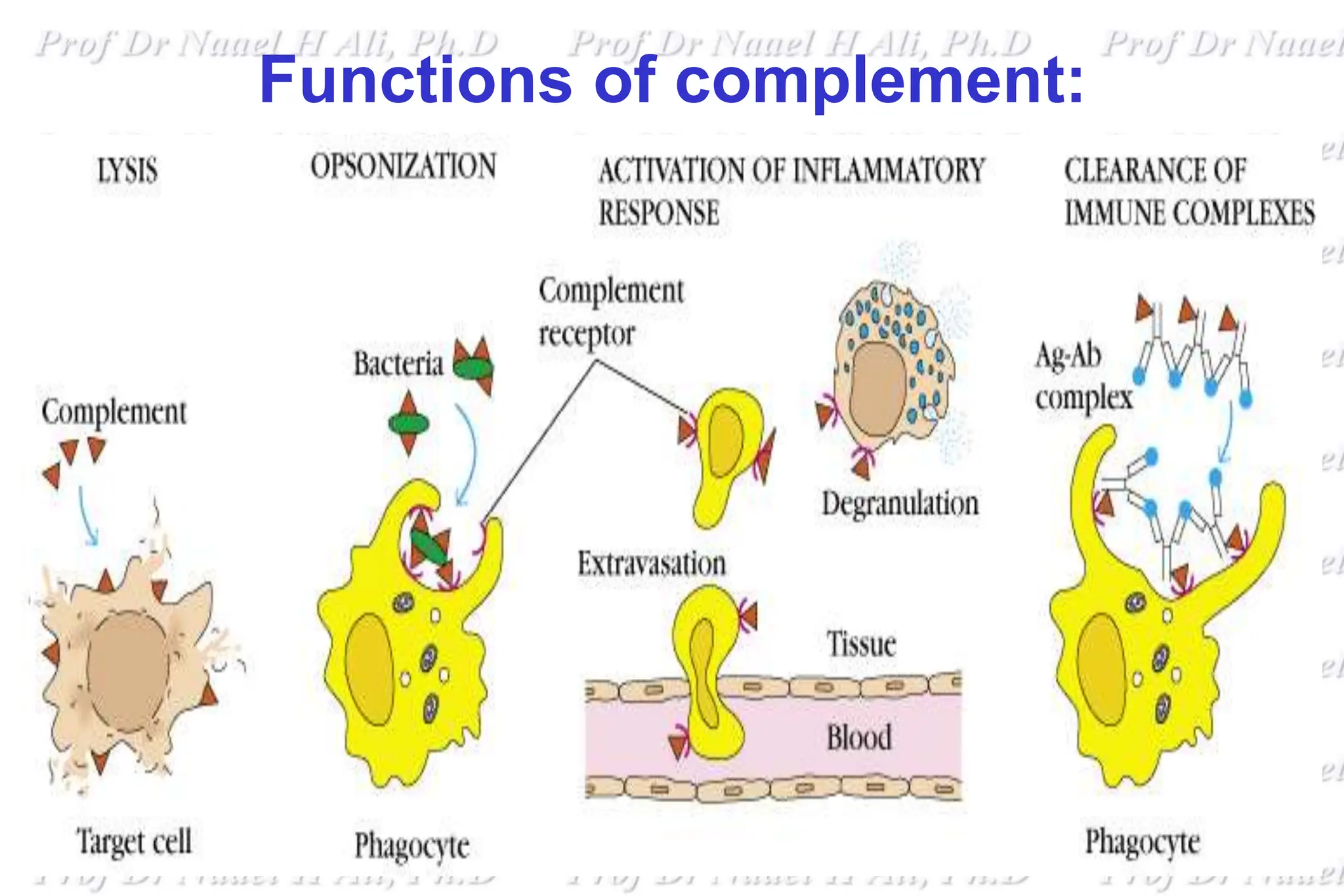
The complement system is comprised of over 50 proteins that work together with the innate and adaptive immune systems to eliminate pathogens, dead cells, and immune complexes. It was originally identified as a heat-labile component of serum that enhanced antibody-mediated killing of bacteria. There are three activation pathways: the classical, lectin, and alternative pathways. Complement proteins mediate inflammatory responses, cell lysis, and recruit other immune cells. Complement activation results in opsonization, anaphylatoxin production, mast cell degranulation, and formation of the membrane attack complex. The complement system is tightly regulated to prevent damage to host cells.






![Regulation of complement system:
1- CI Inhibitor (C1-INH) Classical pathway .
2- C3a inactivator (C3a-INA; Carboxypeptidase B) It inactivates C3a.
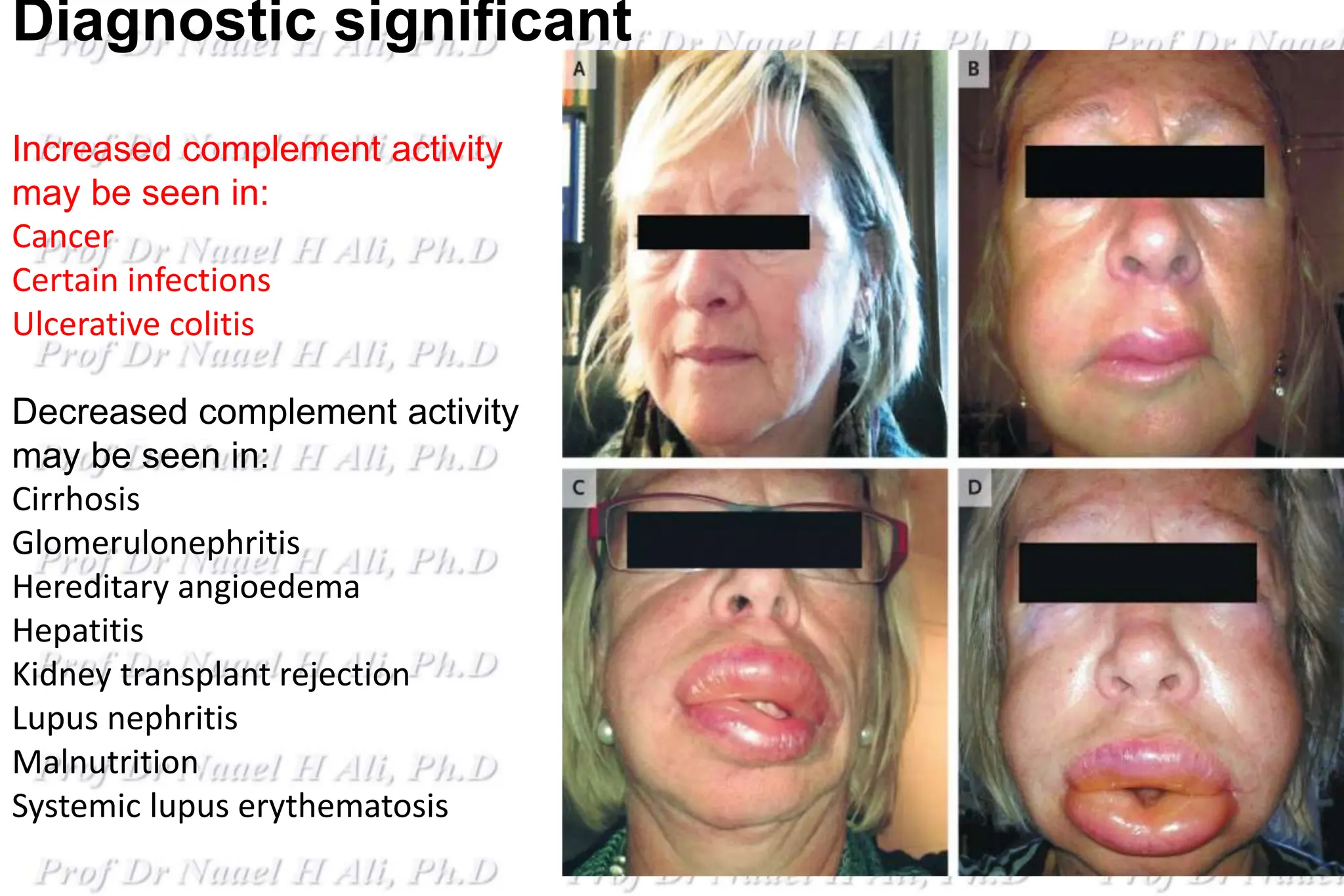
3- Factor H & I: Alternative pathway
4- Decay accelerating factor [DAF] Both.
5- C4 binding protein (C4-BP) and Factor I Alternative .
6- Protein S (vitronectin): MAC pathway.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/complement24new-240416214400-195169bf/75/Complement-system-proteins-and-enzymes-s-20-2048.jpg)
