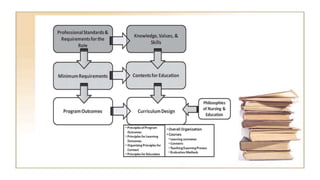
The document discusses competency-based and outcomes-based education. It defines key terms like competency-based approach and outlines common components of competency-based models which include partnerships between community colleges and four-year programs. The document also discusses defining outcomes at the beginning of curriculum development rather than predetermined contents. It recommends five core competencies for health professionals and discusses limitations of outcome-based education like not providing understanding of why learning is important.





![Outcomes -based education [OBE]
Is a currently favored internationally to
promote educational renewal and has been
implemented in countries such as Canada, the
United States and New Zealand.
William Spady is regarded as OBE's leading
advocate and a few points he makes would
suffice.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/competanoutcom-150518051443-lva1-app6891/85/educational-curriculum-part-2-9-320.jpg)