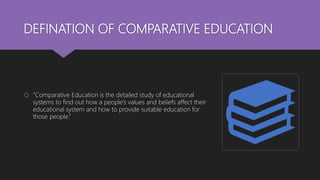
Comparative education involves examining education systems between countries to describe, understand, and evaluate them. It aims to explain differences in educational outcomes, processes, and systems; help develop education; highlight relationships between education and society; and form generalizations about education. Factors like culture, religion, and ideology influence education systems. Comparative education is used for description, understanding education systems, evaluation, planning, innovation, and addressing problems through ideas from other countries. It facilitates assessment and establishing standards between countries.