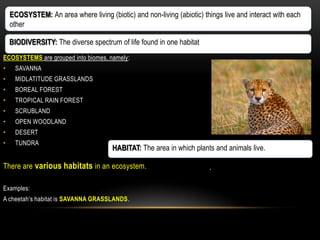
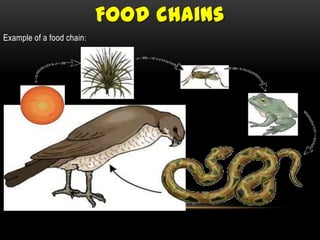
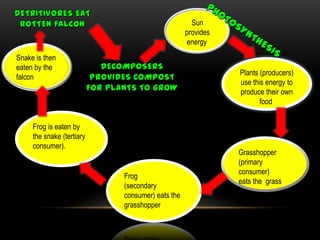
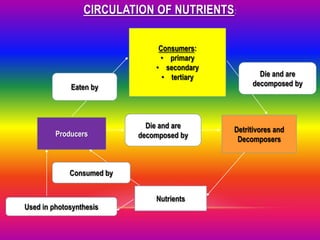
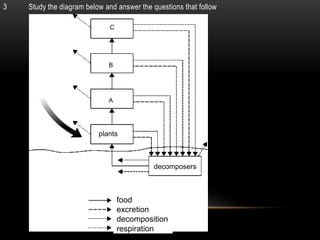
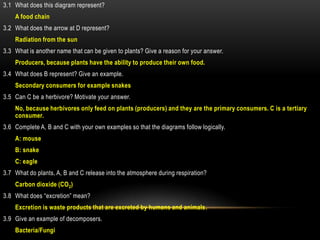
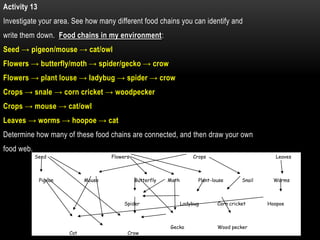
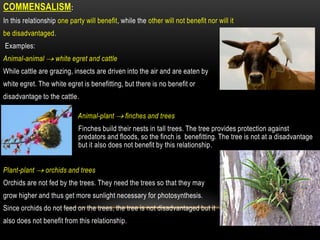
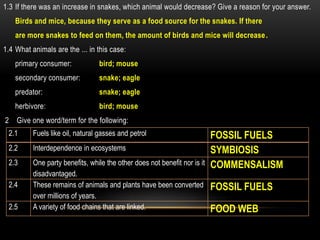
The document discusses food chains and food webs. It defines key terms like ecosystem, habitat, population, community, food chain, and food web. It provides examples of food chains like grass-springbok-cheetah. A food web shows how different food chains are interlinked, with herbivores serving as food for various predators, carnivores and omnivores. Decomposers play an important role in food webs by recycling nutrients from dead plants and animals back into the soil.