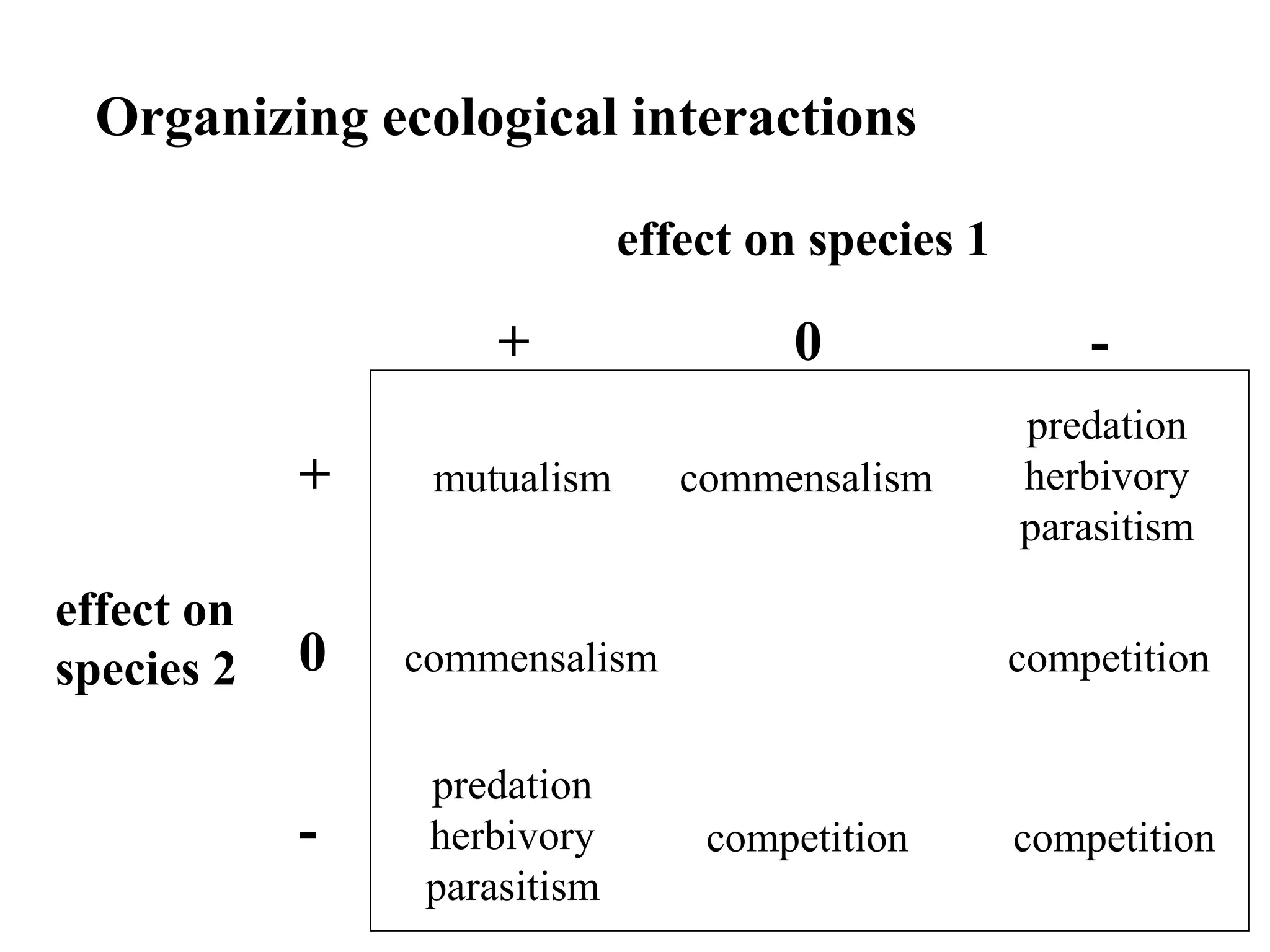
Populations of different species interact ecologically in communities. Ecological interactions like competition, predation, and mutualism can affect species' distributions, abundances, and evolution. These interactions include competition for limited resources, one species feeding on another, mutually beneficial relationships, and cases where one species benefits while the other is not affected.