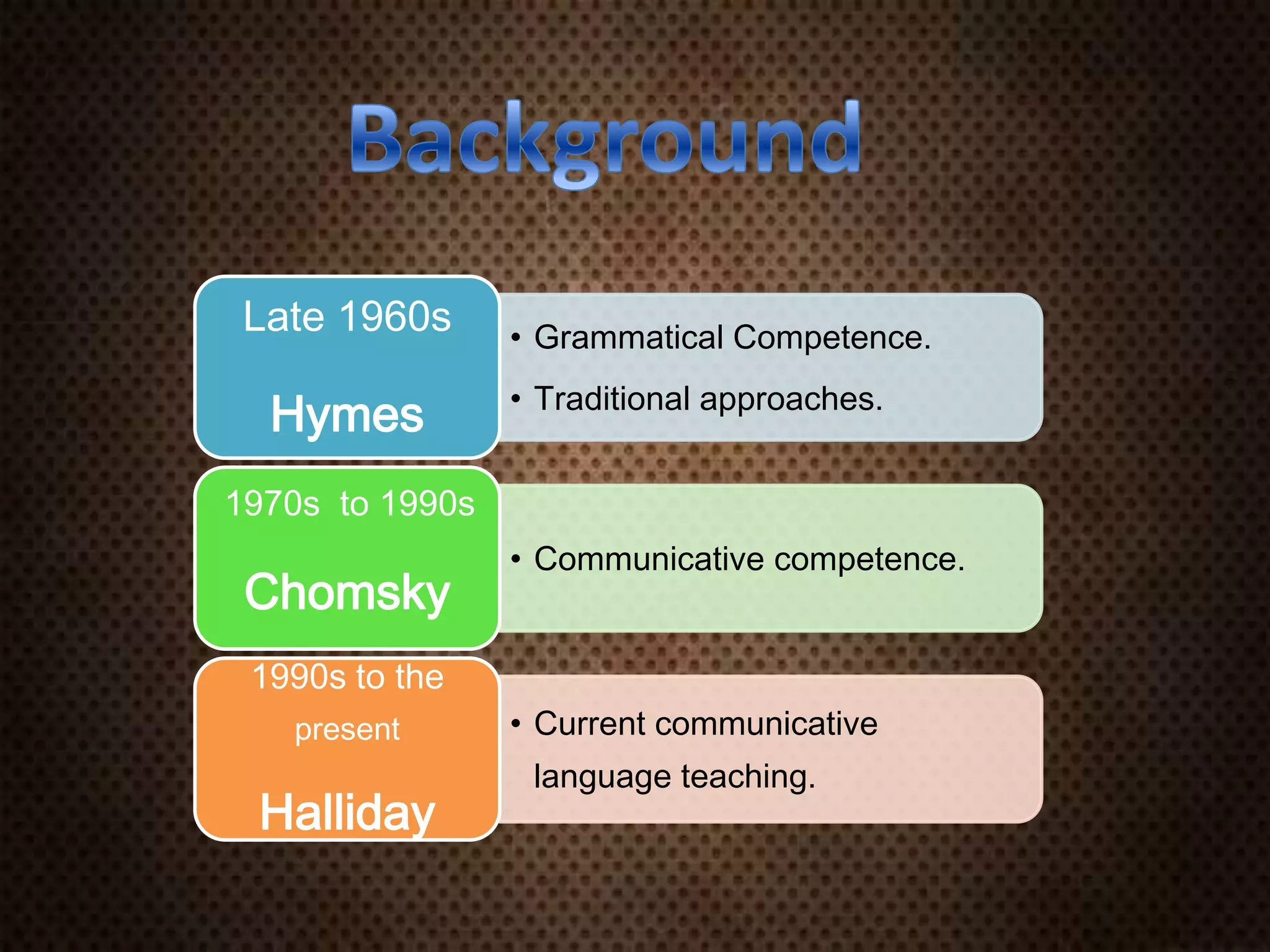
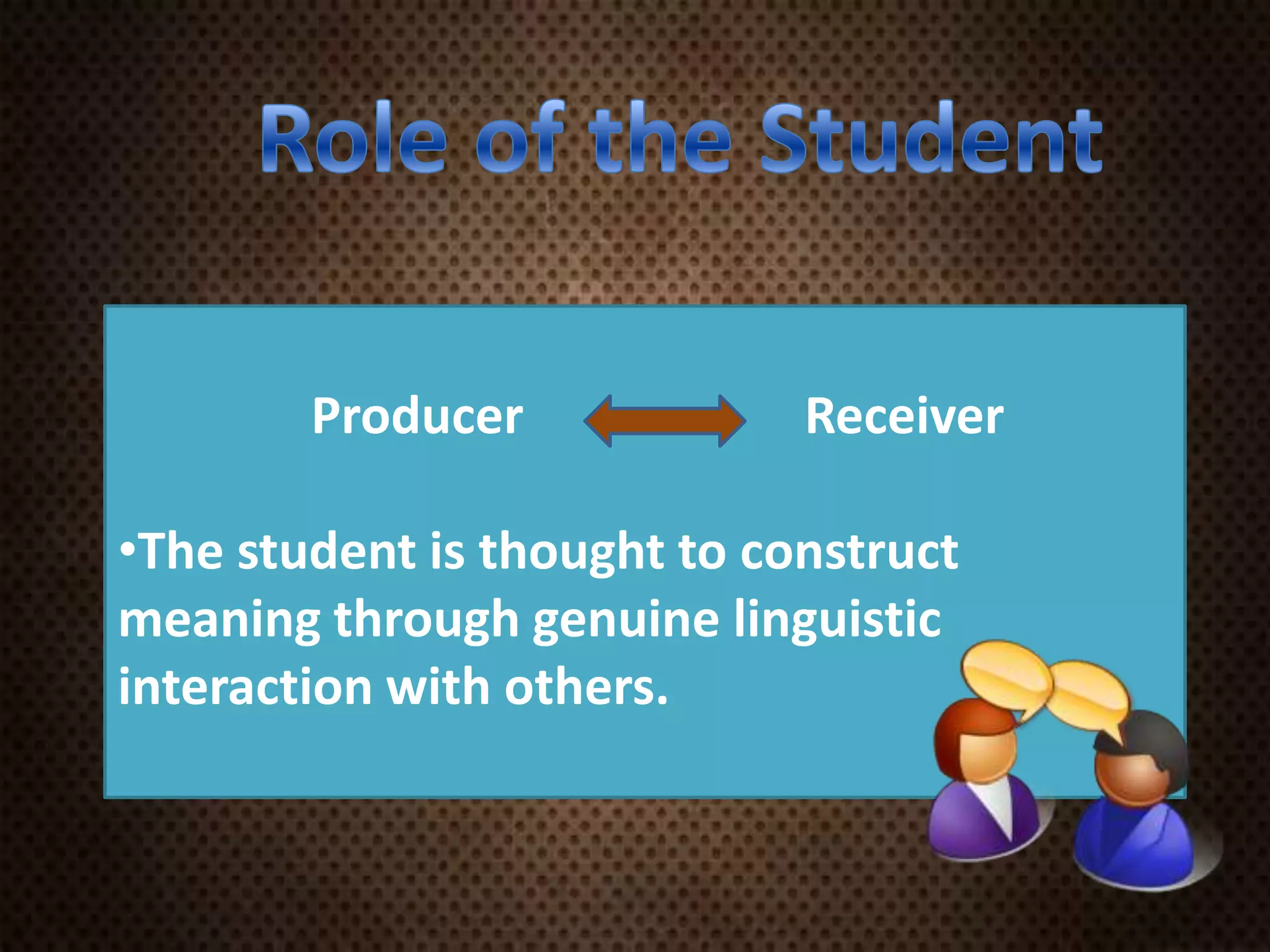
This document discusses Communicative Language Teaching (CLT) and Communicative Language Learning (CLL). It provides a brief history of the development of CLT from a focus on grammatical competence to communicative competence. The key principles of CLT/CLL are that it emphasizes communication and meaning over accuracy, prioritizes fluency, uses authentic materials, and encourages student interaction through activities like role plays, surveys and information gap exercises. The teacher acts as a facilitator rather than knowledge provider. Students construct meaning through interaction and practice language through trial and error.