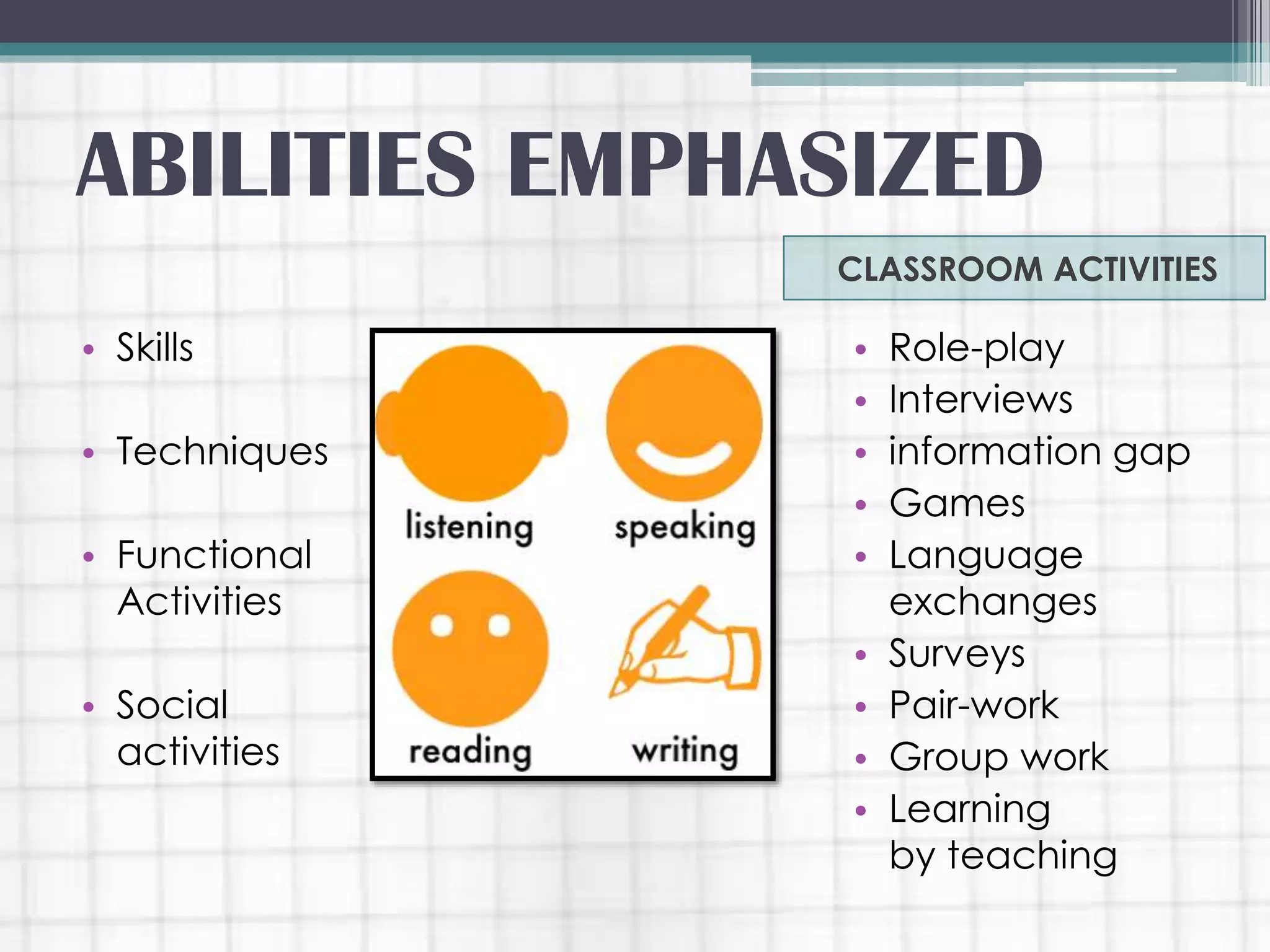
The communicative language teaching (CLT) approach emphasizes interaction and real-world communication as the means and goals of language learning. It developed in the 1970s-1980s due to demands for language learning and influences from linguists. CLT focuses on developing students' communicative competence through activities that involve real communication, such as information sharing, role-plays, and group work. The teacher acts as a facilitator, while students are actively engaged in trying to communicate. CLT is seen as motivating and learner-centered.