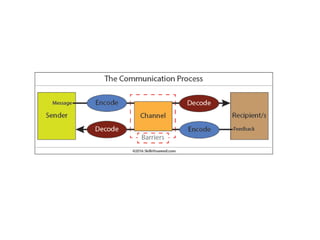
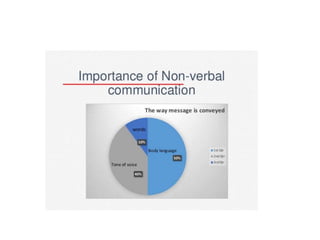
The document covers the fundamentals of business communication, detailing various types such as verbal, non-verbal, written, and visual communication, and describes the communication process involving encoding and decoding messages. It emphasizes the seven characteristics of effective communication identified by Scott M. Cutlip, which include completeness, conciseness, consideration, concreteness, courtesy, clearness, and correctness. Additionally, the document discusses the importance of communication in management, highlighting its role in motivation, decision-making, attitude adjustment, socialization, and control within organizations.