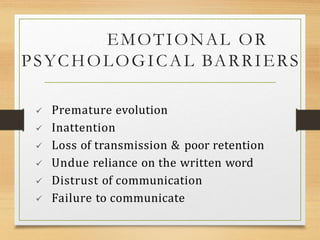
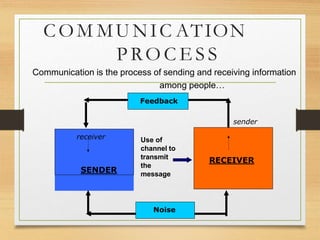
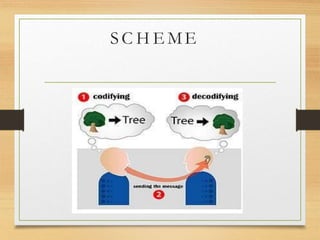
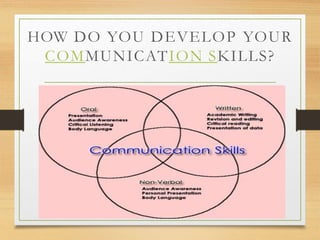
The document outlines the importance of communication skills in both personal and professional contexts, emphasizing the ability to effectively use language and express information. It discusses various barriers to communication, including semantic, emotional, and organizational factors, and describes the components of communication such as verbal, paraverbal, and nonverbal messages. Additionally, it provides tips for developing communication skills, highlighting the need for clarity, active listening, and effective expression.