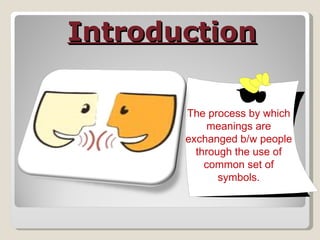
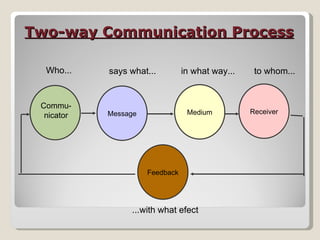
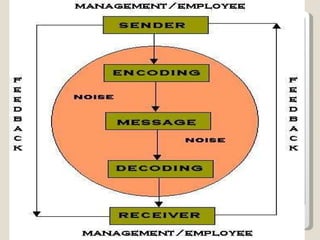
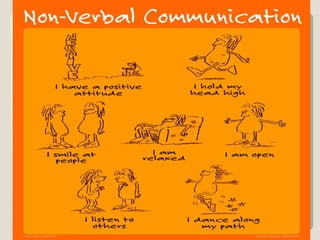
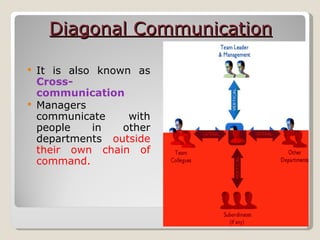
The document discusses various aspects of communication including definitions, processes, models, forms and patterns. It defines communication as the exchange of meanings between people using common symbols. The communication process involves a sender encoding a message, transmitting it through a medium, the receiver decoding the message, and providing feedback. Forms of communication include verbal like oral and written, and non-verbal like body language and paralanguage. Patterns within organizations comprise downward, upward and horizontal flows of information.