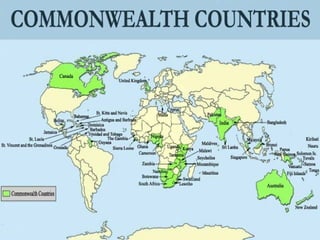
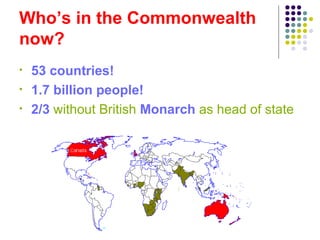
The document summarizes the history and structure of the Commonwealth of Nations. It began in the late 19th century as Britain's colonies gained independence and became dominions with self-government. Over time, declarations established the modern Commonwealth as a voluntary association of equal members united by common values of democracy, human rights, and rule of law. The Commonwealth now includes 53 member countries with over 1.7 billion people. While originally centered around Britain, most members are now republics. The Commonwealth is held together by shared history, language, and democratic traditions, and works to promote prosperity, democracy and international cooperation among its diverse members.